The basis of the structure is a reliable foundation. It absorbs existing loads, distributes them evenly over the ground surface, and also insulates rooms and protects them from moisture penetration. As a result, the durability and stability of the building is ensured, and the likelihood of cracking of the frame is eliminated. At the design stage, it is important to competently select the type of foundation and determine the characteristics. The determining parameter is the depth of the foundation, which depends on the type of foundation and a number of other factors. Let us dwell on these issues in detail.
Building foundation depth
What it is?
The depth of the foundation is the distance from the base to the surface of the earth.
In fact, this is the height of its underground part, which determines the location of the supporting platform and the area of the side, recessed foundation walls.
By changing the depth, you can solve the following problems:
- Increasing the stability of the structure by increasing the area of the underground part with lateral support on the ground.
- Increasing load-bearing capacity by increasing the size of the base.
- The optimal location of the contact area between the foundation and the ground, which makes it possible to install the base on the most durable and stable layer.
The rules for determining this parameter are established by regulatory documents: SNiP 2.02.01-83 and SP 22.13330.2011.
Example of calculating the weight of a house
To determine what size the tape will be, you need to calculate the mass of the future structure.
We calculate the approximate mass of the future structure; the area of the walls, the surface of the floor and ceiling, as well as the roof will be required.
Let's consider an example: a house is being built with walls 6 m and 5 m long, with one main transverse wall inside, the length of which is 5 m. The height of the walls is 3 m. The length of the external walls is 22 m plus a transverse wall of 5 m, it turns out 27 m. Multiply the length of the walls is 27 m by their height of 3 m - we determine the total area of the walls is 81 sq. m.
The floor and ceiling area will be 30 square meters. m.
Next, we calculate the roof area. We measure the height of the pediment using geometric formulas, calculate its area, then calculate the area of the roof.
We multiply each resulting area by the specific gravity of 1 square meter. m. of relevant material. We add up the numbers and get the approximate weight of the future house. To this you need to add the weight of the attic and basement floors.
What does it depend on?
The design depth of the foundation, in general, depends on the geological, hydrological, climatic and structural features of the area, site and the building itself.
The following factors have the most significant impact:
- Purpose of the structure and features of its operation.
- Design factors: size of the structure, type of foundation, number of floors, presence of a basement, location of utilities.
- The load on the foundation, determined by the total operational weight of the structure, as well as the mass of snow accumulation.
- Soil properties: type and structure, stability, heaving, moisture, etc.
- Soil freezing depth.
- Depth of groundwater.
- Climatic factors: degree of wind load, seismicity, flood situations, etc.
- Relief of the site.
There are general rules for determining the depth of the foundation, but each type of foundation also has certain nuances. Various methods are used for shallow and buried foundations.
SNIP regulations for foundation depth
All rules for the arrangement of foundations, namely the depth of foundation, are regulated in SNiP No. 20201-83 “Foundations of buildings and structures.”
Clause 2.25 of these regulations contains reference tables that help determine the depth when taking into account a number of parameters. Parameters required to work with the table:
- Type of soil for foundation construction.
- Average temperatures for the month and year in this region.
- Typical construction project.
- Depth of groundwater, obtained by expert means.
Soil freezing
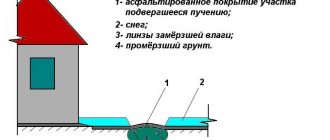
One of the most important influencing factors is the depth of soil freezing . The fact is that when freezing, the water in the soil expands, increasing its volume. As a result, the foundation begins to experience additional load from the soil.
If it is not so dangerous for the side, reinforced walls, because... is extinguished due to the high strength of the structure, then a force appears from below aimed at pushing out the support.
The magnitude of such a load depends on the heaving of the soil, i.e. the degree of its expansion upon freezing . Accordingly, in the spring, when thawing occurs, the reverse process occurs. As a result of annual fluctuations, the foundation material gradually deteriorates, reducing the durability of the building.
These processes occurring in the freezing zone require that the foundation base on heaving soils be located below the freezing level. In low-heaving soils (sandstones, rocky outcrops, etc.) the impact is less significant and a shallow foundation can be used.
The depth of soil freezing is determined based on the results of long-term observations and varies for different regions of the country. It depends on the average daily temperature and soil type.
So in the Moscow region, with an average daily temperature of minus 10⁰C, the freezing depth is:
- clays and loams – 78 cm;
- sandy loam and dusty sand – 95 cm;
- medium and coarse sand, gravelly soil - 1 m;
- coarse-clastic soils – 1.16 m.
Average data on the level of soil freezing in different regions of the Russian Federation are given in SNiP 23-01-99 and SP 131.13330.2011. Based on them, a map of the entire territory is drawn up.
During the operation of buildings, changes in the freezing process may occur due to heat flows.
The freezing depth is adjusted using the formula: H = mx But, where:
- But – standard (tabular) freezing depth,
- m – coefficient of influence of the thermal regime of the structure, incl. heating devices.
The coefficient ranges from 0.4-1.1.
If tabular data is not available, then the freezing depth can be calculated using the formula: H = Hi√Mt, where:
- Hi is the standard freezing depth of a certain type of soil,
- Mt – average monthly subzero temperature in winter.
General estimate
To summarize, to make the whole theory presented a little clearer, we will give an example of calculating the foundation for a one-story house.
The building measures 6x10 m, with an internal six-meter wall. At the same time, the height of the first floor is 3 m, and the height of the attic is 2 m.
- The foundation is strip, made of reinforced concrete, 1.5 m deep, 0.5 m wide. The roof is gabled from slate.
- Wall surface area = (6+10+6+10+6)*3 + (1/2*6*2)*2 = 126 sq.m.
- Floor surface area = 6*10 = 60 sq.m.
- Roof surface area = 4*10*2 = 80 sq.m.
- Foundation load = 126*270 + 60*300 + 60*200 + 80*50 = 68020 kg.
- Foundation area = Area along external borders – Area along internal borders + Area of internal wall = = 6*10 – (6-2*0.5)*(10-2*0.5) + 0.5*(6- 2*0.5) = 17.5 sq.m.
- Foundation volume = 17.5*1.5 = 37.5 sq.m.
- Foundation weight = 37.5*2500 = 93750 kg.
- Load per 1 sq.cm. soil = (93750+68020)/(17.5*10000) = 0.9244 kg/sq.cm. This load is permissible for the weakest soils - for sands saturated with water.
- Volume of concrete = Volume of foundation = 37.5 sq.m.
- Ribbed reinforcement = (2*(6+10)+6)*3*2 = 228 m
- Number of reinforcement connections = (2*(6+10)+6)/0.5 + 1 = 77
- Smooth reinforcement for 1 connection = (0.5-2*0.05) + (1.5-2*0.05)*3 = 4.6 m
- Smooth reinforcement total = 4.6*77 = 354.2 m
- Knitting wire = 0.3*3*4*77 = 277.2 m
As you can see, calculating foundations is not such a complex science that one should refuse to build on their own, and this example of calculating a foundation is given here as the main evidence.
Determination of depth
When building a house, the question arises: how to determine the depth of the foundation? For a buried foundation, there is the following rule: it should be 20-30 cm greater than the freezing depth and 50-60 cm less than the depth of groundwater. The choice of parameter value is little influenced by structural and operational loads.
For economic reasons, it is believed that it is advisable to build a strip foundation with a laying depth of up to 2.5 m. For larger values, it is better to use a columnar or pile type.
A shallow foundation has a depth of about 35-50% of the freezing depth. This option is typical for a monolithic slab in any soil, as well as a strip or columnar foundation when building on low-heaving soils.
The foundation depth is calculated taking into account the loads from the structure and the bearing capacity of the soil . The depth of freezing also makes its own adjustments, but through practical recommendations.
Formula for calculation
How to calculate the depth of the foundation for a house? The calculation is carried out in accordance with SP 22.13330.2011 using the formula.
Formula for calculating freezing depth
Н = Hi√Mt
- H – freezing depth,
- Hi is the standard freezing depth of a certain type of soil,
- Mt – average monthly subzero temperature in winter.
The Hi value is:
- 23 cm in clays,
- 28 cm in dust type sandstone,
- 30 cm in coarse sandstone,
- 34 cm in rocky soils.
Example
Let's consider the construction of structures on clay soils in the Moscow region. Moscow is characterized by average temperatures: December – minus 10, January – minus 16, February – minus 18⁰C. Then we calculate the freezing depth: Н= 0.23√(10+16+18)= 1.1 m.
The adjustment is made taking into account the coefficient of influence of the thermal regime of the structure m . Its value is established by SNiP 2.02.01-83 and SP 25.13330, taking into account the average daily temperatures maintained in the room.
In these documents, you can use the table to clarify m for buildings with different modes of residence, different floor structures, taking into account the presence of insulation and a basement.
For a house with an insulated base in the Moscow region, with an average daily room temperature of 10-12⁰C, m = 0.9 can be taken.
Finally, the calculated freezing will be: N x m = 1.1 x 0.9 = 0.99 m.
Depth of foundations in accordance with the requirements of Table 2 of SNiP 2.02.01-83*
Next, you need to take into account the location of groundwater . If they are located at a depth of more than 3 m, then the depth of the foundation must be no less than the freezing depth.
Taking into account the recommendations, the depth is assumed to be H+0.3 m, i.e. 1.3m. This depth should ensure the reliability and durability of the strip or column foundation.
Minimum and maximum values
For a buried foundation, the minimum depth is equal to the depth of soil freezing, and the maximum depth of the foundation should not reach groundwater by at least 0.5 m.
The minimum laying of a shallow foundation is established by SNiP 22.13330.2011, taking into account freezing in the following dependence:
- non-heaving soils with freezing up to 2 m or slightly heaving soils with freezing up to 1 m - the foundation depth is at least 0.5 m;
- when the specified soils freeze within 2-3 and 1-1-1.5 m, respectively - 0.75 m:
- when freezing more than 3 m and within 1.5-2.5 m, respectively - 1 m;
- when slightly heaving soils freeze to a depth of more than 2.5 m - 1.5 m.
The temperature inside the house allows you to adjust the depth of a shallow foundation.
So for an unheated house in the Moscow region, the minimum foundation depth is 0.5 m. If the average daily temperature in the room is maintained at least 10 degrees throughout the year, then the minimum depth is 0.4 m, and at a temperature of 20 degrees - 0.28 m .
The minimum values given are for one-story buildings . When constructing a 2-story structure, they should be doubled. Taller buildings are not erected on shallow foundations.
When building on high-strength soils (rocky outcrops, coarse soils), the foundation is intended only to redistribute loads evenly over the entire area.
The minimum foundation depth is 0.3 m. The depth for a monolithic slab foundation is selected in the same way.
Determining the groundwater level
To do this, in the area where the house will stand, they dig a ditch about 3 m deep. Or, if there is a well on the site, thanks to it you can find out the groundwater level. The most accurate information can be determined in the off-season (spring, autumn), when the groundwater level is highest.
You can also find out the composition of the soil. The top layer is fertile and is removed during construction. It is easy to recognize by its color - it is darker. Under the top layer is the main one. It will be load-bearing; the foundation and the house will exert load on it.
If after all the calculations it turns out that the soil cannot support the weight of the house, then you need to increase the area of the foundation or use other materials in the construction of the house. After each change, you will have to recalculate the dimensions of the foundation again.
When does it change stepwise?
When building a house on a site with a slope, a stepwise change in the depth of the foundation is necessary . In such cases, tape and column type structures are used.
Concrete tape is the most reliable. This type of foundation can be constructed on slopes with a slope of up to 28-35 degrees.
The essence of the stepped foundation is that the lower wall is a retaining wall and has an increased depth .
Its diagram is as follows: first, a trench is prepared for the upper wall with a depth equal to the calculated depth.
A trench of the same depth is dug under the lower retaining wall, but the formwork is raised to such a height that its upper boundary is strictly in the same horizontal plane with the upper cut of the formwork of the upper wall.
After pouring, a support slope is poured from the outside of the lower wall, and therefore the actual depth of the lower wall will be equal to the depth of the upper wall plus the height that compensates for the slope.
The side wall of the strip foundation in question has a stepped design . Its entire length is conventionally divided into sections of approximately 2 m. In each section, a horizontal trench bottom is formed. The starting point is to deepen the upper wall.
The structure of the side wall of a foundation on a slope can be illustrated with an example. For example, a house 6 m wide is being built on a slope with a slope of 15 degrees. Conventionally, we select 3 steps of the side wall, each 2 m long.
The steps must compensate for the slope, and the sole of each of them must be strictly horizontal. The starting point is located on the top, and the ending point is on the bottom wall, where the foundation depth is 0.8 m.
However, due to the slope, the end point is located below the top by 6xsin15=1.55 m . The height of each step will be 1.55:3 = 0.53 cm.
The upper step at the starting point will have a depth of 0.8 m, and at the final point – 0.8-2sin15=0.28 m. The lower step: at the final point – 0.8 m, and at the starting point – 0.8+sin15= 1.32 m. The middle step has a similar value.
Calculation of sole width
Each foundation has two horizontal planes. The upper one, in contact with the walls, is called the edge, and the lower one, in contact with the soil, is called the sole. Determining the size of the sole is the main thing in its calculation. In the video you can see the process of laying the lower part of the foundation.
To accurately calculate the width of the sole, in addition to the weight of the structure, you also need to know the type of soil on which the construction is being carried out. Each type of soil has its own bearing capacity. It is determined according to the table:
We found out the mass/weight of the building. Now, knowing the type of soil, you can determine the width of the base of the monolith.
We will increase the total mass of the building by the weight of the furniture located in it and the supporting platform, which will also exert pressure on the soil and the possible weight of precipitation - snow.
The total weight of the house, taking into account additional loads, was 200 tons. We choose the width of the sole equal to the width of the block material - 50 cm. The length of the house is 3000 cm. We multiply 3000 by 50, the total is 150,000 sq. cm. - the area of the house that will exert pressure on the ground.
Our house is built on wet clay. On average, it accepts a weight of 2 kg/cm2.
We multiply 150,000 by 2, we get 300,000 kg/cm2 - the maximum weight that this soil can support. Our house weighs 200 thousand kg.
300,000 – 200,000 = 100 thousand kg – safety margin.
The soil will easily support the construction, even additional loads are possible. The width of the base of the tape will be 50 cm.
Set of rules
The rules for determining at what depth to make the foundation are established by SP 50-101.2004. They include the following basic requirements:
- It should be selected taking into account the main influencing factors (purpose of the structure, design features, geological and hydrological factors, seasonal freezing).
- The depth of soil freezing is taken taking into account the results of observation over a period of at least 10 years, as an average annual value.
- In the absence of tabular data for a specific calculation, a calculation is carried out taking into account the standard freezing of a certain type of soil.
- Determined separately for external and internal walls.
- It is adjusted taking into account the coefficient of influence of the operational features of the room.
- The base of a buried foundation should be located below the freezing depth of the soil, but above the groundwater level. The minimum depth of a shallow foundation is set taking into account the properties of the soil and takes into account the freezing depth.
- When designing the foundation, water-reducing (drainage) measures must be taken into account.
- When constructing a foundation on a slope, stepwise deepening is used to ensure the formation of a horizontal floor base.
- You should not dig according to the principle: the deeper, the stronger and more reliable. So you can just uselessly bury a lot of money in the ground. The foundation must be optimal for the given type of building.
The design rules are also specified by other regulatory documents indicated above. The characteristics of different types of foundation must be taken into account.
Video description
Watch a video that explains the principle of constructing shallow foundations:
To prevent deformation of such a foundation, special measures are taken to eliminate heaving of the soil under the house.
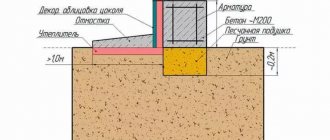
- Insulation of foundation walls to prevent cold penetration under the house, for which concrete is poured into permanent formwork made of extruded polystyrene foam.
- Insulation of the soil under the blind area, protecting it from freezing along the entire perimeter.
- Installation of drainage systems for drainage of groundwater and sediments from the foundation.
Preliminary research
Before you start planning your house, you must decide where on the site you want to place the house. If there are already geological studies, take into account their results: in order to have fewer problems with the foundation and have a minimum cost, it is advisable to choose the “dryest” area: where the groundwater is as low as possible.
First of all, you must decide on a place for the house on the site
Next, geological soil studies are carried out in the selected location. To do this, holes are drilled to a depth of 10 to 40 meters: it depends on the structure of the layers and the planned mass of the building. At least five wells are made: at those points where the corners are planned and in the middle.
The average cost of such a study is about $1000. If the construction is planned on a large scale, the amount will not greatly affect the budget (the average cost of a house is 80-100 thousand dollars), but can save you from many problems. So in this case, order research from professionals. If you want to build a small building - a small house, a cottage, a bathhouse, a gazebo or an area with a barbecue, then it is quite possible to do the research yourself.
The soil
The choice of foundation depends on the correct determination of soil type
The very first factor that should be carefully studied is the soil on the site that is chosen for building a house. A lot depends on its type:
- foundation type;
- the depth of its occurrence;
- choosing the type of waterproofing;
- possibility of arranging a basement.
In order to correctly assess the soil, it is necessary to dig holes or drill wells in several places. The distance between them should be at least a meter. Soils in the same area can be different, and, therefore, their properties differ.
It is very important not to focus on the properties of the soil of the neighboring site and ignore the examination of your own. The well is drilled to a depth of 2 meters
This depth is sufficient to get an idea of what type of soil predominates
The well is drilled to a depth of 2 meters. This depth is sufficient to get an idea of what type of soil is dominant.
Next, the type of foundation and its depth are determined.
We present the characteristics of the most common types of soil and solutions for calculating the foundation of a house.
Rocky and semi-rocky soils have a very high bearing capacity. Based on this, it is possible to carry out work on constructing any type of foundation, except for piles.
How and with what to determine the depth
After calculations have been made using the formula for the depth of seasonal soil freezing, you can, in accordance with SNiP, use the table to calculate the foundation level.
| Foundation laying depth taking into account the degree of groundwater occurrence (Dw, in m) | Rocky, gravelly, coarse sand | Fine or dusty sand | Sandy loam with fluidity IL<0 | Sandy loam with fluidity IL>0 | Clayey, filled with clay, loams with IL≥0.25 | Clayey, filled with clay, loams with IL<0.25 |
| Dw≤Df+2 | Does not depend on the Df indicator | Not less than the calculated indicator Df | Not less than the calculated indicator Df | Not less than the calculated indicator Df | Not less than the calculated indicator Df | Not less than the calculated indicator Df |
| Dw>Df+2 | Does not depend on the Df indicator | Does not depend on the Df indicator | Not less than the calculated indicator Df | Not less than the calculated indicator Df | Not less than the calculated indicator 0.5*Df |
If you are unsure about the correctness of the calculations, it is better to order geological exploration work from specialists, which will give an objective assessment for the future construction of buildings or structures.