Soil freezing depth (df) is a standard value that shows the level of freezing of the soil horizon in winter and is determined on the basis of long-term observations in each region of Russia. The lower limit of this zone is called soil freezing point.
The GPG value is one of the most important parameters when determining the depth of the foundation, which means finding this coefficient is mandatory for any construction. Knowing the depth of freezing allows you to protect the foundation, since in winter the stress in the soil is redistributed, groundwater passes from a liquid state into ice, its volume increases to 10-15% and heaving processes begin.
If the base of the foundation is not deep enough, then colossal vertical pressure will be exerted on the walls, which will certainly lead to deformations and disruption of the integrity of the foundation. If the base of the foundation is located below the level of the HGG, then the forces of frost heaving will act on the side walls tangentially , that is, the foundation will be pushed out in winter, and sink back in in summer.
Calculation of soil freezing depth
Until recently, calculating the depth of soil freezing was carried out manually using SNiP and other regulatory documents - this is not very convenient, since you have to scroll through more pages to find the region/city you need. We suggest using our online calculator, which allows you to determine the standard and estimated depth of soil freezing in ONE CLICK - you need to select a locality and click the “ Calculate ” button. The database of our program is based on information from SNiP 23-01-99 (SP 131.13330.2012 “Building climatology”).
Our tool contains information on all regions and cities of Russia, including: Moscow region, Leningrad region, Nizhny Novgorod, Sverdlovsk, Rostov, Samara, Chelyabinsk, Kaliningrad regions, Perm, Khabarovsk, Primorsky Territories, Bashkortostan, Tatarstan, Crimea.
The influence of frost heaving of soil
The term “frost heaving” refers to the level of soil deformation during thawing or freezing. It depends on how much liquid is contained in the soil layers. The higher this indicator, the more the soil freezes, since according to physical laws, when freezing, water molecules increase in volume.
The power of frost heaving
Another factor influencing frost heaving is the climatic conditions of the region. The more months with sub-zero temperatures, the more the ground freezes.
Silty and clayey soils are most susceptible to frost heaving; they can increase in size by 10% of their original volume. Sands are less susceptible to heaving; rocky and rocky sands do not have this property at all.
The depth of ground freezing specified in SNiP was calculated taking into account the worst climatic conditions in which snow does not fall. The actual level to which the ground freezes is less, since snowdrifts and ice act as heat insulators.
The ground under the foundations of buildings freezes less, since in winter it is additionally warmed by heating.
The impact of soil heaving on a slab foundation
To protect the soil from freezing, you can additionally insulate the area at a distance of 1.5–2.5 meters around the perimeter of the base of the house. This way you can arrange a shallow strip foundation, which is also more economical.
Soil freezing depth by region of Russia (map + table)
| City | Soil freezing depth, cm |
| Arkhangelsk | 175 |
| Vladivostok | 180 |
| Vologda | 170 |
| Ekaterinburg | 190 |
| Irkutsk | 190 |
| Kazan | 175 |
| Kaliningrad | 80 |
| Krasnoyarsk | 200 |
| Kursk | 130 |
| Moscow | 130 |
| Nizhny Novgorod | 155 |
| Novosibirsk | 220 |
| Omsk | 220 |
| Eagle | 130 |
| Permian | 190 |
| Pskov | 120 |
| Rostov-on-Don | 90 |
| Ryazan | 130 |
| Samara | 165 |
| Saint Petersburg | 120 |
| Saratov | 145 |
| Simferopol | 70 |
| Surgut | 270 |
| Tyumen | 210 |
| Khabarovsk | 190 |
| Chelyabinsk | 215 |
| Yakutsk | 240 |
| Yaroslavl | 170 |
Our services
This is pile driving and leader drilling.
We have our own fleet of drilling and piling equipment and are ready to deliver piles to the site with their further immersion at the construction site. Prices for driving piles are presented on the page: prices for driving piles. To order work on driving reinforced concrete piles, leave a request: Sand cushion for the foundation
The sand cushion provides a stable support in the form of coarse sand, gravel or concrete for any type of foundation, which also ensures its overall stability and eliminates…
More details
Photos from leader drilling
More details
Types of grillages
A grillage is the upper part of the foundation connecting piles or pillars, distributing the load evenly. Grillages are divided: by design, by material, by degree...
More details
Soil heaving
From this material you will learn what frost heaving of the soil is and what danger it poses to the foundation.
Soil testing
Soil testing is the construction phase that precedes foundation design. Soil testing is carried out for density and shear.
Soil freezing depth in the Moscow region
| City | Soil freezing depth, cm |
| Moscow | 130 |
| Balashikha | 125 |
| Podolsk | 130 |
| Kolomna | 115 |
| Serpukhov | 120 |
| Orekhovo-Zuevo | 125 |
| Sergiev Posad | 130 |
| Zelenograd | 130 |
| Solnechnogorsk | 125 |
Effect of snow cover thickness
According to SNiP, the value of freezing depth also depends on the thickness of the snow layer that lies on a given soil in winter. The graph of this dependence is well illustrated in the graph below.
Graph of soil freezing versus snow cover thickness
This circumstance goes logically contrary to the generally accepted procedure for clearing the area around the house from snowdrifts. People, trying to restore order, without realizing it, create a zone of uneven soil freezing on their site. This can damage the foundation, the ground under which can freeze very much and begin to deform the foundation.
With additional insulation of a shallow strip foundation, it is not afraid of frost deformations
In order to create additional insulation of the foundation, as a tip, it will help to plant a low shrub around the perimeter of the house, which will be able to collect snow and protect your foundation from the cold.
3.7 / 5 ( 4 voices)
Soil freezing depth in the Leningrad region
| City | Soil freezing depth, cm |
| Saint Petersburg | 120 |
| Gatchina | 120 |
| Vyborg | 125 |
| Pinery | 120 |
| Kingisepp | 120 |
| Meadows | 115 |
| Volkhov | 120 |
| Tikhvin | 120 |
| Sviritsa | 125 |
Foundation depth.
When determining the thickness of the foundation, you can slightly deviate from existing standards and reduce the depth of the foundation, but then it is necessary to provide a device for insulating the upper layers of the earthen cover from freezing.
On heaving, deeply frozen soils, the construction of a strip foundation with a depth of more than 1 m is not economically justified; it is necessary to consider options in the form of pillars (columnar supports in the ground). In such soils, foundation elements are made with an increased base area in order to avoid the manifestation of buoyant tangential forces that arise during winter heaving. This platform will not allow the foundation to rise from the ground. Reinforcement of such a foundation is mandatory
In neighboring buildings, pay attention to the posts of gates and fences, if they are not parallel or perhaps their upper parts are in different horizontal planes relative to each other, this is the effect of frost heaving forces, the soil here is heaving. Ask the owners and you can find out the reason for the appearance of such metamorphoses. Here is a clear example of heaving:
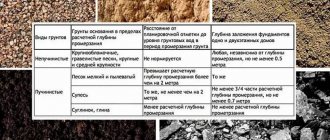
Soil density and its features
Soil density in the Moscow region can have very different values. Provided that the soil is characterized by a sufficiently high density and homogeneity, the laying depth can be chosen at a level of about 0.5 m. This group includes rocky type soils, with an abundance of cartilaginous mixtures, including sand, crushed stone and clay, soils with a sandy base and minimal freezing rates.
If we are talking about heaving soils, then the depth of the foundation should be about 0.7 m.
In a situation where the site is dominated by weak soil with high mobility, you will have to work hard - the laying depth can reach 2.5 m, which is the maximum value according to English recommendations.
Do you have any questions?
Leave a request and our manager will contact you shortly.
By clicking the “Leave a request” button, you consent to the processing of personal data under the conditions and for the purposes specified in the Privacy Policy.
When planning the construction or purchase of a plot, you must pay attention to the soil. This is necessary to understand what kind of foundation should be built, as well as to determine whether agricultural activity is possible
Peat, plant soil, and chernozems are suitable for crop production, but are not suitable for foundations. Bulk and alluvial soil are extremely unfavorable for laying a structure. The best option for construction is compacted sand and clay.
Methods for protecting soil from freezing
All other options, at low temperatures, require insulation, which is done by retaining snow, loosening the soil, embanking it, insulating backfill, or an electrical heating device.
And this is not a complete list of methods for protecting soils from freezing used in construction. These activities should be carried out in the fall, before the first frost occurs. If we are not talking about the surface of the earth, but about the bottoms of pits or trenches, then measures to protect them should be taken immediately after the soil is removed. We will briefly describe some of the methods used today.
Loosening and insulation
Changing the structure of the soil by loosening it, which can be done to a depth of up to one and a half meters, is one of the most effective ways to protect the soil. At the same time, ridges are formed on the soil surface that trap snow. By the way, it covers the ground no worse than a blanket and prevents it from freezing.
Even in the coldest winter, the freezing depth of loosened soil is half that of dense soil. Therefore, the loosening method is used before the development of sandy loams and loams, carried out in the second half of winter. First, the soil on the surface of the future pit is loosened and spread with an excavator.
Excavator attachments designed for loosening soil
- Then, they dig a deep trench into the dump, which during subsequent excavation is covered with soil from the new trench. The last penetration, which is located outside the pit, is completely backfilled. The loosened soil retains snow, and when construction begins in winter, it is easily removed, since there is only a frozen crust on the surface.
- If you need to protect small surfaces from freezing, then natural thermal insulation materials are used for this purpose: straw, sawdust, leaves, slag. Recently, builders are increasingly giving preference to fast-hardening polystyrene foam. The abundance of pores in the foam contributes to the best thermal insulation of the surface. A layer of 40-50 cm can delay the onset of freezing for a couple of months - and then spring.
Sawdust is an excellent soil protection against freezing.
- In the southern regions, and some areas of the middle zone, where the temperature on the ground surface in winter does not fall below -15 degrees, a chemical protection method is often used. For this purpose, technical salts (potassium chloride or sodium) are used. They are laid on the surface or deepened by 10-15 cm.
- In the presence of dense clay soils, solutions of these salts are even injected into the soil. However, it is worth noting that salts can have an aggressive effect on buried structures and increase the electrical conductivity of soils. Therefore, the use of this method for protecting soils from freezing and thawing is limited.