A traditional strip foundation performs its tasks perfectly when built on fairly dense and stable soils.
In more difficult conditions, other support structures are required that can create a solid foundation on problematic or completely unstable soils.
The optimal option is piles that are able to rest on deep dense layers, passing through unstable surface layers and practically not forming a structural connection with them.
This solution to the problem allows you to get a stationary and reliable foundation, saving money and, often, time.
Let's consider one of the most successful options - the pile-grillage type.
What is a pile-grillage foundation
A pile-grillage foundation is a system of vertical supports (piles) rigidly connected by a common external load-bearing belt (photo below).
The piles rest on dense layers of soil, and the grillage carries the walls of the house, evenly distributes the load and transfers it to the pile system.
This type of foundation has a lot of structural options, can withstand loads of various types and can be used in the most difficult conditions. Different types and materials of piles can be used; the grillage can be a simple support line or a powerful reinforced concrete strip.
Various combinations of these elements make it possible to create a foundation with the necessary parameters, optimally suited to the existing loads, operating conditions and hydrogeology of the site.
IMPORTANT!
The presence of a grillage is typical for any type of pile foundation, so they can all be classified as part of this broad group.
Purpose and functions.
Construction of a pile grillage foundation.
Piles are optimal for areas with difficult terrain.
When designing your own private house, you definitely need to understand what a pile foundation with a monolithic grillage is, and whether it is suitable for this particular case.
As load-bearing supports, piles are the best option in difficult geological conditions, when heaving forces have a significant impact on underground structures, and a high level of freezing will require a monolithic strip to be buried more than 2 m.
The diagram shows how the pile grillage design works:
Pile grillage foundation pros and cons photo.
The manufacturing technology differs from the usual installation of a building on piles in that all the supports are connected into a single base by a solid belt that receives and distributes the loads on the columnar supports.
Types of grillage.
Types of grillage.
The grillage connects the piles to each other.
Using design calculations, based on the conditions of the site and the total weight of the building, it is chosen which type of pile-grillage foundation is appropriate to use.
The decision is influenced by the need to install a ventilated underground under the crown, the possibility of flooding with flood waters, and the slope (relief) of the site.
Based on these conditions, determine the height of the pile foundation grillage:
Pile grillage foundation pros and cons.
A low grillage has the advantages of a strip foundation.
Construction of a pile grillage foundation.
A low grillage is a combination of a shallow strip foundation with piles, which significantly increases the reliability, rigidity, and stability of the entire supporting structure.
This option combines the advantages of pile and strip foundations, despite the fact that the combination significantly compensates for the disadvantages that appear separately:
- the weight load of the building is transferred to the foundation concrete strip and, due to the presence of a reinforcing frame, is redistributed over the entire support area;
- a monolithic low strip rests its lower part between the piles on a cushion (soil), providing a contact area with the support along the entire perimeter;
- In winter, the effects of forces at the surface are compensated by buried pile columns.
High grillage.
Raised grillages are used on complex unstable soils.
As the groundwater level rises, the height of the concrete grillage relative to the soil surface increases.
The elevated type is used on quicksand, peat bogs, karst, forest, fertile soils, more than 1.4 m thick.
This arrangement eliminates the impact of lateral forces on the monolithic grillage, and the piles are not only supports, but also an anchor in moving rocks.
The construction of such a foundation reduces the volume of excavation work and will require less materials and cash costs than a concrete strip or slab. During installation, a monolithic reinforced concrete grillage will require strict adherence to the design dimensions and work technology.
Material for grillage.
Wooden beams are the cheapest material.
The basis for the grillage for the pile foundation is selected from raw materials that are capable of withstanding, according to their characteristics, the constant and variable loads included in the design calculations of the house.
A durable grillage on piles is made from the following materials:
- steel profiles (channel, I-beam);
- wooden beam (rounded log);
- concrete (reinforced concrete) casting.
A low pile-buried foundation can only be with a concrete grillage.
Material for grillage.
Concrete structures are used for heavy houses.
Metal grillages are made high because, despite their great strength, they need protection from moisture.
The reinforced concrete type, rising above the ground, is used in the construction of fairly heavy houses, since concreting at a height will require good formwork.
Another criterion is the service life of the building wall materials. The selected grillage foundation must match or exceed the performance of the structures located above it.
How a pile foundation with a grillage made of different materials is supported on piles is shown in the diagram:
Pile grillage foundation pros and cons.
Before calculating the bearing capacity of pile foundations taking into account the total load, it is necessary to take into account that the safety factor for them should be 1.4 (in other types of foundations it is usually calculated at 1.2).
Existing types
Types of pile foundations are distinguished by the type of piles.
There are:
- Rack piles . They are immersed in the ground until hard contact with dense soil layers appears. They form the strongest supporting structure and are capable of supporting buildings of any weight and number of storeys.
- Hanging piles . The load-bearing capacity of these supports depends on the frictional force on the side walls and on the strength of the soil cushion under the tip, formed during immersion. This design is convenient when dense layers of soil are too deep, but can suddenly change its parameters due to changes in groundwater levels or other processes.
The material for making piles is:
- Wood . The most ancient and traditional material, which has many disadvantages. With the advent of other, more stable and durable types, wooden piles have practically disappeared from the arsenal of builders, although they are still used in some places (in private construction, for the construction of auxiliary buildings).
- Metal . Driven piles are not specially produced; in this role, pieces of rails, channels or I-beams of suitable size are used. Screw piles are manufactured completely ready for use. The specificity of the metal does not allow for durable supports due to corrosion caused by electrochemical processes and the presence of stray currents.
- Reinforced concrete . The most common type of piles. The most durable are driven ones, manufactured using special technology using stressed reinforcement. Bored piles are cast from concrete directly on the site, which is convenient, reduces transportation costs and the overall level of use of construction equipment, but significantly increases the production time due to the need to cure the concrete to gain structural strength.
There are three main types of pile foundations:
- On driven piles . The immersion of trunks is carried out by special machines. The process does not take much time, the supports are strong and reliable. The disadvantage is the impossibility of carrying out work near the buildings in use due to soil movements that occur during immersion.
- On bored piles . This type of piles is convenient because it does not require transportation, unloading, or the use of lifting equipment. A sleeve (a type of formwork made from roofing felt or plastic pipe of suitable diameter) is lowered into a pre-prepared well, a reinforcement frame is installed and concrete is poured. All operations can be performed independently, but a fairly long period of holding the piles will be required for the concrete to harden.
- On screw piles . They are made of steel pipes with a wall thickness of at least 4 mm. The lower part has a welded or cast pointed tip and spiral cutting blades. Driving screw piles resembles the process of screwing a screw - the blades provide immersion, the sharp tip pushes apart or splits the obstacles encountered. Screw piles can be installed manually, if necessary, they are removed and reused in other places. The service life depends only on the intensity of corrosion.
NOTE!
All pile foundations cannot be created on rock or coarse rocks.
Advantages and disadvantages
Types of pile foundations are divided primarily according to the method of construction into driven, driven and screw. Each model of a structural element is characterized by its own characteristics.
The general advantages of all types of piles include the following:
- Applicability for all types of soils and reliefs of any complexity.
Where laying a strip or slab base would be ineffective or impractical, supports are used. Pile foundations can be built on unstable, waterlogged soils, areas at risk of landslides or flooding, wetlands, as well as on slopes and depressions. - Economic expediency. Laying single load-bearing elements connected into a single structure with strapping costs 30–40% less than constructing a slab or strip buried foundation.
- Possibility to select a power element for any conditions. The popularity of pile technology has led to an increase in offers from pile manufacturers. Today you can select supports with a load-bearing capacity from 0.8 to 15 tons or more, and composite elements are used for deep laying.
- Small amount of excavation work. If, in the case of a buried strip or slab base, it is necessary to dig a pit to the design depth, then to install cast-in-place piles it is enough to drill holes in the ground, and the driven and screw pillars are immersed in the soil by force.
Disadvantages of pile technology:
- Complexity of engineering calculations. Pile foundation technology can satisfy almost all hydrogeological and design conditions, but this will require a number of engineering calculations. Before designing, the designer needs to study the regulatory requirements for the construction of foundations in order to take into account possible nuances for each type of support.
- Labor intensity of work on arrangement of basements. It is possible to organize the construction of underground premises in the space between the power elements, but this will lead to a significant increase in the cost of the project, which will practically cover the benefits of using pile technology.
For a private home
Private residential buildings and cottages are relatively light in weight compared to high-rise buildings and industrial facilities. This feature allows you to abandon the laying of an expensive reinforced concrete strip or slab foundation in favor of factory-made or home-made piles.
Advantages of pile technology for private construction:
- the possibility of laying the foundation with your own hands (screw piles, cast-in-place piles);
- if necessary, methods are available to strengthen the foundation (when building extensions, increasing the number of storeys, replacing floors in a house, etc.);
- maintainability.
Why you should not build a private house on a pile foundation:
- significant heat loss due to the elevation of the house above ground level;
- labor-intensive procedure of engineering calculations;
- There is high seismic activity in the area.
Different types of piles
The choice of piles is based on the results of hydrogeological soil surveys, as well as engineering calculations for design loads. Comparative table of pros and cons for various types of power structures:
| Support type | Benefits of technology | Disadvantages of technology |
| Driven reinforced concrete |
|
|
| Driven steel |
| |
| Driven wooden |
|
|
| Bored |
|
|
| Screw metal |
|
|
| Screw reinforced concrete |
|
|
Types of grillages depending on location
Depending on the depth of immersion, there are three types of grillage design:
- Recessed . It is a complete analogue of a recessed strip base. It is immersed to a depth below the freezing level in order to eliminate heaving loads directed vertically upward. At the same time, the developed side surface of the wall experiences maximum values of lateral loads, which must be taken into account when designing. It is not used on difficult or waterlogged soils due to the lack of technological conditions for the production of concrete casting.
- Shallow . It is the most common design option for a pile-strip foundation, where the strip is immersed to a small (40-70 cm) depth. This option is much more economical than the buried one, since it does not require such a serious amount of excavation work.
- Unrecessed . In this case, the grillage is installed above the ground surface, forming a gap of a certain height. This option is used on soils that do not allow extensive excavation work - waterlogged, excessively loose, prone to heaving or seasonal movements.
IMPORTANT!
Some experts fundamentally distinguish between pile-tape and pile-grillage support structures due to the presence or absence of immersion of the tape into the ground. Others combine them into one group, since the general design of both is practically the same.
Main characteristics
First, let's remember what a grillage (P) is and why it is needed. In simple words, this is a horizontal piping of a pile foundation, the main task of which is to transfer and uniformly distribute the weight of the building.
Based on their depth, grillages are divided into three types:
- buried - the horizontal belt of the pile foundation is located in the soil thickness.
- ground - the structure is laid on the surface of the earth.
- raised - the belt is mounted 300-400 mm higher from the ground level.
Use Cases
There are several options for using grillage material:
- Wood . Either a solid beam 150:200 or 200:200 mm is used, or a pack of edged boards 50:200, assembled in 3 or 4 layers. The resulting beam has high load-bearing capabilities and is easy to process and install. The cost of wood is relatively low, so a grillage of this type is the best option for houses that do not have a lot of weight (wood, aerated concrete, foam concrete).
- Metal . This type of grillage allows you to get a strong base, rigidly connected to the pile heads. The result is a durable structure, the installation time of which is minimal, and the result is very reliable. A channel, I-beam or rail is used as beams; they are attached to the tops of the piles by welding. Most often used in combination with screw piles.
- Reinforced concrete . This type of grillage is built using the conventional technology of casting a monolithic strip (floor tile). The only difference arises from the presence of an air gap between the soil and the bottom of the base. In addition, the reinforcement of the piles must be rigidly connected to the reinforced belt of the tape, forming a monolithic supporting structure . This procedure forms a powerful and rigid base that is resistant to all types of loads. The disadvantage is the long hardening time of concrete, which stops work for a month.
Its required height
The height of the grillage is directly related to the material of the walls of the house. If you plan to build a brick (concrete, cinder block) house, then the minimum height is considered to be 15-20 cm above ground level. For wooden houses, the height of the grillage should be slightly increased and be about 40-60 cm .
This will provide the necessary flexural rigidity and will allow the wood to be separated from sources of moisture below.
This refers to the snow cover, the height of which must also be taken into account. If the region has very snowy winters with high snowdrifts, it is necessary to calculate the height of the grillage to exceed their level.
Columnar foundation with high grillage
This design scheme is the most correct and correct, since the grillage in it is located at a certain elevation above the surface of the earth. Usually this distance is at least 15 cm. The gap under the grillage eliminates the pressure on it from rising soil due to frost heaving.
Sequence of work:
1) All foundation pillars are erected. Their elevation above ground level is determined based on two requirements. The first was mentioned above - this is a minimum gap of 15 cm. The second condition is that the pillars must be recessed into the body of the grillage by 5-10 cm.
2) The tops of the pillars are covered with coating waterproofing, which prevents the capillary rise of moisture from the soil and its penetration into the grillage.
3) The base of the formwork is made. There are two ways:
a) With a minimum elevation of the grillage, a poured layer of sand is used as a base. It is moistened, compacted with a tamper and leveled, forming, as it were, the lower surface of the formwork. After filling the grillage, the sand is removed from underneath it.
b) With a higher grillage, the base is made of boards or plywood.
4) The side walls of the formwork are installed. The cross-sectional dimensions of the grillage are selected depending on the material of the walls and their thickness.
For wooden houses, the height is taken to be at least 40-60 cm. At the same time, sufficiently high bending strength will be ensured, and the lower crowns of the walls will not get wet when splashed with rain from the blind area or in contact with snow in winter. The width is selected depending on the thickness of the walls and the design of the basement. The figure below shows that floor beams can be installed on separate pillars (as was generally done before) or placed on a specially formed grillage extension.
For stone houses, the height of the grillage is taken to be at least 20 cm, and the width corresponds to the thickness of the wall. The low height is due to the absence of large bending loads. Stone walls themselves have great bending strength and bear the main load.
5) After installing the formwork, the reinforcement cage is knitted. The working reinforcement is located in the lower and upper parts of the belt, going deeper into the concrete by at least 5 cm. The number of rods is selected depending on their diameter: ∅10 mm - 8 pieces; ∅12 mm - 6 pieces; ∅14 mm - 4 pieces. Reinforcement of large diameters is not used; it begins to work worse in conjunction with concrete.
6) Concreting is in progress. Do not rush to remove the formwork and remove the sand from under the grillage. You can start building walls and even a roof with them already on the 4-5th day after pouring. And you’ll remove all the unnecessary stuff later, when you need to finish the base and build a blind area.
Laying depth - what it depends on
The depth of placement depends on the condition of the soil on the site.
All related factors are taken into account:
- Groundwater level.
- Availability and volumes of soil water.
- Possibility of flooding in spring.
- The presence of seasonal changes in hydrogeology, an increase or decrease in the degree of filling of all aquifers.
To select the correct depth, it is often necessary to collect information from local geological and meteorological departments, consult with experienced builders, and refer to various SNiP applications.
It must be taken into account that all values indicated in various sources are minimum, i.e. it is allowed to increase the lifting height, but it is impossible to reduce the gap height .
Preparatory activities for the construction of a bored foundation
In order for the foundation in which bored piles with a grillage are used to have high strength and reliability characteristics, it is necessary to calculate the permissible loads.
Drawing with the names of the elements of a bored pile. This makes it possible to optimally select the diameter of the pile base and the required quantity for a specific construction site and the type of building material used. When carrying out calculations, the following data is used:
- approximate weight of the future building with a larger tolerance;
- the design of the building being constructed, the presence of internal walls, extensions, areas with additional removal;
- type of soil and its features;
- soil freezing point and groundwater rise height;
- planned pile diameter and cement strength indicator;
- length and safety factor of reinforcing elements;
- coefficients of standard longitudinal loads of earthen soil on piles.
It should also be noted that, in accordance with building codes, the following must be taken into account when placing piles:
- the maximum distance between piles is 2 m;
- the minimum allowable distance can be at least 3 diameters of the pile itself.
Device
The grillage is a supporting structure located under all load-bearing walls, both external and internal.
It is assembled into a single strip; the beams are assembled into a single structure using conventional technologies specific to this material.:
- Wooden beams are connected half-timbered with a jute tape sealing the joint.
- Metal beams are welded to the ends with reinforced connections with threaded elements.
- The concrete grillage is cast in the form of a monolithic element, rigidly connected to the piles by a common armored belt.
Each beam is rigidly connected to all the supports located under it . The distance between them must correspond to the magnitude of the load; excess will contribute to the deflection of the beams and the deformation of all adjacent elements. Longitudinal connections of beams can only be located above the pile head; joining them in the span is prohibited.
How to calculate a monolithic base
The calculation of a pile-grillage foundation is carried out by experienced and competent specialists .
This is a complex and responsible engineering task that is beyond the power of outsiders and those without special training (the work is carried out using diagrams and formulas).
If you don’t have the opportunity to contact specialists, you can use online calculators , which give a fairly correct answer within a few seconds and completely free of charge.
If for some reason you need to calculate the supporting structure yourself, perform the following steps::
- The weight of the house is calculated along with the property, wind and snow load, and additional elements. This point is the most difficult, since it is necessary to take into account absolutely all the factors influencing the foundation from the side of the building. Some values can be found in SNiP tables, for example, the magnitude of wind and snow loads characteristic of a given region .
- The resulting value is multiplied by the structural strength coefficient. Usually it is taken equal to 1.1, but in some cases an increased coefficient of 1.2 is used.
The value of the safety margin is relevant only for this configuration of the house.
All additional elements, decoration, furniture or extensions will increase its weight and load the foundation beyond its design value.
Therefore, it is quite acceptable to take a much higher strength coefficient in order to avoid future deformation or destruction of the foundation.
After the load is determined, the number of piles is calculated.
The total weight of the house is divided by the permissible load per unit and the result is rounded to the nearest whole number.
The permissible load on finished supports is indicated in the product passport; for bored piles it is calculated independently, using the methodology specified in SNiP or other sources.
Step-by-step DIY installation instructions
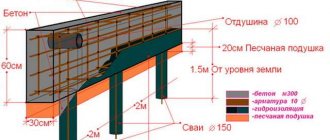
Let's consider the procedure for installing a reinforced concrete grillage located at a height of 30 cm above ground level (one of the most difficult options).
Procedure:
Preparation
The site is cleaned and leveled (if necessary). Remove all foreign objects, plants and other obstacles.
Pegs are used to mark the area . For driven piles, it consists of installing one peg on the axis of the supports; for bored piles, the lines of the outer and inner perimeter are marked. They also require preliminary drilling of wells, which is carried out based on the results of test drilling.
It determines the depth of dense layers of soil and is carried out in any case, as it makes it possible to determine the length of the trunks.
Installation of piles
Piling is driven using special machines .
It is necessary to draw up a driving plan so that the finished piles do not cut off the installation points of the next supports.
Typically, installation is carried out in a spiral or snake , sequentially moving from one point to another.
For bored piles, wells are lined (immersing a pipe made of rolled up roofing felt or a piece of plastic pipe of the required diameter). Then an armored belt is assembled and lowered into the well, the dimensions of which must be selected so that it easily fits into the hole.
The length of the reinforcement must exceed the length of the well, so that it can subsequently be rigidly connected to the reinforced belt of the grillage. Then the well is filled with concrete and kept for the required time (28 days).
Construction of formwork
To build formwork, it is not necessary to wait for the concrete to harden in the wells . If driven piles are used, they usually wait about a week for the shaft to “suck” (a construction term for restoring the soil and sealing it tightly to the side walls).
The formwork is a kind of long wooden tray , the internal dimensions of which repeat the shape of the future grillage.
The assembly is made from edged boards, trying to prevent the formation of cracks and gaps.
The height of the formwork should slightly exceed the height of the grillage . To provide rigidity to the lower section, a series of supports are installed on the ground to prevent deflection of the bottom of the formwork. The inner part is covered with polyethylene, which prevents water or material from escaping from the formwork.
Creation of an armored belt
The reinforcement frame is created using conventional technology - working rods with the help of smooth auxiliary reinforcement are installed in the desired position according to the design diagram and general rules.
An important point is the rigid connection of the pile reinforcement and the reinforced belt of the tape, for which it is best to use welding. The remaining elements are connected by knitting with soft wire.
Pouring concrete
Concrete is poured after the concrete has completely hardened in the piles.
This is important, since the weight of the reinforced concrete grillage is very large and can deform uncured concrete.
The pouring must be done as quickly as possible, without interruptions, in order to obtain an absolutely monolithic support with a high degree of rigidity. The concrete is leveled and covered with burlap or polyethylene, and periodically watered with water for the first 10 days.
After 10 days, the formwork is removed , after which the tape is kept until it hardens completely, which occurs 28 days after pouring.
Advantages and disadvantages
The piles of the supporting structure in question, due to their large immersion depth, provide excellent stability to the entire mini strip foundation on top. And they cost much less than a reinforced concrete monolith of the same height. Moreover, if the support pillars are tied on top not with a concrete tape, but with a metal grillage, then you can save a little more. This option is one of the most inexpensive ways to create a support for a private home.
In terms of device speed, a pile foundation with a grillage is inferior only to an analogue made only of screw supports. Plus, a foundation made of wall foundation blocks will be ready to give a head start to the structure in question. In both cases, the high speed of work is due to the lack of concrete work, when it is necessary to wait several weeks until the concrete completes its strength.
If the building site has a slope, then pouring a monolith on it is problematic and expensive. It will be difficult to do without this type of foundation on such a site. Only with the help of piles will it be possible to create a stable and horizontally level base for the structure. This is one of the main advantages of the foundation. All other options are immediately inferior to him on construction sites with complex terrain.
Another undeniable advantage is the extreme simplicity of execution. It’s not difficult to make your own pressed supports from asbestos-cement pipes and concrete inside. It’s even easier to make a reinforced concrete strip of small size and weight on them.
Minor difficulties here can arise only when installing the formwork suspended. It cannot be immersed in the ground. The pillars must raise the grillage part above the ground by at least 30 cm, otherwise, if there is severe heaving, it may “float” from the supports along with the building on top.
The underground space of a cottage on a pile foundation with a grillage must be closed from the wind, otherwise constant drafts under the floor will blow all the heat out of the building. To do this, you can use facade panels from various materials or make masonry from beautiful facing bricks. Plus, the floor in such a house will definitely have to be insulated. It is better to immediately include these expenses in the overall estimate for housing construction.
Floors on the ground
Floors on the ground are used to create a grillage structure immersed in the ground. If there is an air gap, creating a ground floor becomes too difficult, ineffective and impractical.
The inside of the tape is covered with a layer of sand cushion . Then a layer of geotextile is laid on it and crushed stone is poured, onto which a layer of crushed stone is poured through an additional layer of geotextile.
The entire backfill is compacted sequentially, achieving the best possible result. Then a layer of screed is poured on which the heat insulator is laid.
A screed is again poured on top of it, inside which a heated floor system is installed.
A finishing coating can be applied to this screed . The floor cake is quite multi-layered, but it provides high-quality heating and prevents heat loss due to contact with the ground.
Waterproofing technology
The grillage is waterproofed using one of the most common materials:
- Hot bitumen.
- Bitumen mastic.
- Pasting with roofing felt.
- Application of impregnating compounds.
The simplest and fastest option is to use bitumen mastic, which performs its tasks perfectly and is sold in ready-to-use form. Apply by roller or brush, usually in one or two coats.
Insulation scheme
Waterproof materials are used for insulation:
- Liquid polyurethane foam.
- Extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex).
- Styrofoam.
- Expanded clay.
- Foam glass, etc.
The most convenient and effective option is considered to be penoplex, which is glued in a dense layer to the entire surface of the grillage, both internal and external.
It is somewhat worse, but much cheaper, to use polystyrene foam , which is also resistant to moisture and is an excellent heat insulator, but has the ability to crumble and is excessively brittle.