Bored piles are often used for a strong and functional foundation. This is a type of pile foundation, when concrete is poured into a hole made in the ground, in which a reinforcing frame is placed. On loose soils, special formwork or casing are used for strengthening. This technology is suitable for the construction of country houses and industrial facilities. It is used for work in urban areas, where vibration is contraindicated for surrounding buildings.
Classification and design of bored piles
Bored piles are reinforced concrete structures, the well for installation of which is formed by drilling. A typical bored support structure consists of two elements - a concrete body and a reinforcement cage. For reinforcement of piles, ready-made, factory-produced reinforcement cages are used. The frame type is longitudinal-transverse; it consists of vertical reinforcing bars that are connected by horizontal jumpers. To create a longitudinal contour, corrugated reinforcement is used, produced using the hot-rolled method (class A1-A3). The diameter of the rods is selected based on the size of the pile; it can vary between 12-20 mm.
Fig : Reinforced frame for bored piles
The fixing crossbars are made of smooth reinforcement (diameter 8-15 mm). The frame connection is made by electric arc welding. After joining, the frame is coated with a protective primer to prevent corrosion.
Important : the concrete body of the bored pile is created from a mixture of grade M200-M300, corresponding to strength class B25. The standard frost resistance of the concrete used is 200 cycles, water resistance class is 6.
According to the design features, there are two types of bored piles:
- Cylindrical;
- With widened support sole.
Cylindrical piles have the same cross-section along the entire length of the trunk, while in widened piles the lower part of the trunk has an increased diameter. Due to the increased support area, such supports receive increased stability in the ground and greater load-bearing capacity.
Fig : Installation diagram of bored piles with widening
The widening can be formed by two methods - through the use of special drill strings with folding cutters or the camouflage method, in which an explosive is placed at the bottom of the well and its subsequent detonation is carried out.
Advantages of using cast-in-place piles
This type of construction of building foundations has not yet become widespread due to the specificity of the equipment used for its construction. However, the development of technology and the machines used can significantly increase the economic importance of foundations of this type. Their use has a number of advantages, including:
The possibility of concentrated absorption of significant loads by individual piles, reaching 1000 tons, which allows them to be placed under structures that transfer a large mass to the foundation. In most cases, these are buildings used in industry and production or multi-story buildings.
The possibility of the piles individually accepting enormous loads makes it possible to simplify the design of the grillage or abandon its use in principle. A connecting or transition link, in the form of a grillage, can be mounted without the use of additional parts and reference to depth.
Advantage of cast-in-place piles
One of the main positive qualities that characterize this type of piles is the insignificant absolute and relative values of their displacement in the soil during settlement.
The significant load carried by the design of a single load-bearing element avoids the use of multiple drive-in type parts.
If it is necessary to use small-sized cast-in-place piles, their load-bearing capacity can be increased by widening the lower surface of the structure. An increase in the supporting surface of the load-bearing elements from 7 to 12 times allows the perceived load to be increased several times.
This type of load-bearing elements can be used to strengthen the structure of existing foundation structures.
Bored piles: how it's done
In areas with dense buildings or when there is a danger of soil shifting (during driving piles using the usual method), the bored method of constructing piles is often used. To do this, the following types of work are performed:
- design of a pile foundation based on engineering calculations of the planned load and soil studies on the site
- identification of drilling points on the ground according to the project
- drilling a well and installing casing
- installation of reinforcement cage
- pouring and compacting concrete mixture
- sequential removal of casing pipe.
Fig .: Reinforcement of a bored foundation
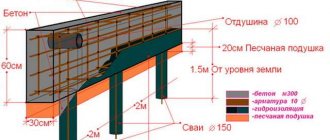
An example of calculating a bored pile foundation
Before starting work, you should determine the required number of support elements and their diameter.
When performing calculations, you should take into account the type and characteristics of the soil on the site, the level of groundwater and the depth of freezing. For a private house, these indicators can be determined independently by drilling a well.
The minimum diameter of bored piles with an element length of less than 3 m should be 30 cm.
Initial data for calculation:
- brick house, external wall thickness 640 mm;
- internal load-bearing wall 380 mm thick, 8 meters long;
- house size 7x8 meters;
- floor height 3 meters.
We calculate the loads on foundations taking into account the specific gravity of the materials and structures used in construction.
Table 2. Specific gravity of basic materials.
| Material | Weight kg/m3 |
| Brick | 1800 |
| Reinforced concrete | 2400 |
| Pine lumber | 500 |
| Metal tiles (kg/m2) | 70 |
Load collection
- Walls:
Wall mass = 7 m (length) × 2 + 8 m (width) × 2 × 3 (height) × 0.64 (wall thickness) + 8 × 3 × 0.38 (inner wall) × 1800 kg/m3 (brick density ) × 1.2 (K – correction factor) = 116,294.4 kg.
- Monolithic floors:
Floor mass = 7 m (length) × 8 m (width) × 0.12 (thickness) × 2400 (specific gravity of monolithic reinforced concrete) × 1.3 (K) = 20,966 kg.
- Gable roof made of wood:
Roof mass = 7.5 m3 lumber × 500 kg (specific weight of wood) = 3,750 kg.
- Roof:
Roof mass = 7 × 8 × 1.3 (slope slope) × 70 kg (weight of 1 m2 of metal tiles) = 5,096 kg.
- Reinforced concrete grillage:
For brick walls 64 cm thick, we accept a grillage made of monolithic reinforced concrete with a section of 60 cm × 50 cm. The length of the grillage is equal to the length of the load-bearing walls
Grillage mass = 7 × 2 + 8 × 2 +8 × 0.6 × 0.5 × 2400 (specific gravity of reinforced concrete) × 1.2 (K) = 32,832 kg.
Weight of the house with grillage = 116,294 + 20,966 + 3750 + 5096 + 32,832 = 178,938 kg.
Calculation of the bearing capacity of the pile
To construct the foundation of a private house, we make piles with a diameter of 30 cm and a length of 2 meters.
Sectional area of the pile S = πR² = 3.14 × 15² = 706 cm2.
To fill the piles we use B12.5 concrete, with a strength of 261.8 kgf/cm2.
Load-bearing capacity of one pile = 706 × 16.05 = 11,331 kg.
Required number of piles = 178,938 / 11,331 = 16 pieces.
Pile pitch = 38/16 = 2.37 m.
When calculating, you should be guided by the joint venture “Pile foundations”
For a more accurate calculation, the specific gravity of all building materials and structures should be taken into account.
Technologies for constructing bored piles
Depending on the construction technology, all bored piles are classified into three types:
- Supports formed without shell;
- Supports with removable and permanent shell
As a shell, casing pipes are used - cylindrical steel structures connected to each other by means of a threaded or anchor connection.
Drilling wells for piles without a shell is not accompanied by their use, which is only possible in stable conditions (not prone to landslides) with a minimum groundwater level. Important : if necessary, in the process of drilling without casing, a bentonite solution can be used, which is fed into the well being developed, washes out soil masses from it and settles on the walls of the cavity, forming a crust that prevents soil shedding.
Fig : Casing pipes for drilling under piles
The technology for creating bored piles with a removable shell is implemented when working in problematic, moisture-saturated soils. The casing pipe, in this case, prevents the collapse of the well walls and isolates the cavity from groundwater. Dismantling of the casing occurs after filling the well with concrete. The creation of piles with a permanent shell is practiced when working in clayey soils, sands and sandy loams with a high level of groundwater, which can destroy the body of the pile at the stage of hardening of the concrete solution.
What are drilling rigs used for?
Drilling rigs for bored piles in modern construction are the primary equipment, without which not a single civil engineering project can do. These drilling machines have one goal - to erect a bored pile, on which the foundation of a building will then stand, a bridge support will rest, or the pile will serve as a kind of hook (soil nail) to prevent landslides and mudflows.
Piles can be of different diameters and depths, this is determined by the design organization, and then the builder is faced with the question: which drilling rig to choose and buy in order to build bored piles as quickly and as cost-effectively as possible.
Technology for installing bored piles with casing
The process of installing bored piles begins with the relocation of special equipment to the site. Three types of installations are used for arranging supports:
- Drilling machine;
- Jib crane;
- Concrete mixer truck.
After marking the pile field (drilling points for piles), the drilling machine is placed at the well development site. The drilling rig is brought into working condition and the cavity is drilled to a depth identical to the length of the first casing section. Next, the auger is removed from the well, the installation fixes the pipe in the supporting unit and places it in the cavity. The second casing section is installed in a similar way, the sections are joined using a threaded connection, after which the well is deepened until the upper contour of the casing is equal to the ground level and the process is repeated again.
Fig: Drilling using casing
Important : during the drilling process, the auger string rotates inside the casing. The casing itself is deepened by excavating soil from under its walls, under the influence of its own weight and the applied effect of a vibration unit, which exerts reciprocating loads on the pipe.
After drilling the cavity to the required depth, the auger column is removed from the well and a reinforcement cage is loaded into the cavity using a jib crane. Upon completion of the installation of the frame, a concrete pipe is installed at the wellhead, through which the excavation is filled with concrete. During the process of pumping the mixture, the well casing is sequentially dismantled.
Fig: Installing the reinforcement cage in the well
To increase the strength characteristics of a bored pile, the mixture is compacted using deep electric vibrators, which remove air cavities formed in the concrete. The support is suitable for subsequent use (tied with a grillage) 25-30 days after pouring (this time is necessary for the concrete to gain its design strength).
Fig : Filling a hole for a bored pile with concrete
Disadvantages in arrangement
The use of drilling injection technology also has certain disadvantages. Thus, during the construction of these piles, unlike cast-in-place and bored supports, there is no artificial soil compaction. That is, their carrying capacity is at the level of the natural state.
The use of drill-injection supports is often impossible due to the threat of squeezing out the concrete composition from the soil by groundwater until it dries completely. This process can occur during the construction of foundations in sandy, water-logged soils with a high filtration coefficient, as well as active movement of groundwater.
The technology of their arrangement may also raise some doubts about the quality of already manufactured foundations. Difficulties often arise during the immersion of the reinforcement cage into concrete, which, at low pressure, sinks to a depth of no more than 75-85% of the length of the support. Subsequent immersion of the reinforcement, which occurs under increased pressure, leads to a violation of the integrity of the reinforcement and its protrusion from the support walls. That is, the lower section of the pile is almost without reinforcement.
Technology for installing bored piles with a grillage
The configuration of the grillage of bored supports is selected based on the arrangement of piles in the foundation:
- Tape grillage tying is used in a sequential arrangement scheme, which is used for arranging foundations for low-rise buildings (the supports are placed under the contour of the walls of the house);
- A slab grillage is used to tie the pile fields of the foundations of high-rise buildings, in which the piles are located along the entire perimeter of the structure.
Important : at the stage of forming bored piles, the supports are reinforced with a frame, the length of which is 30-50 cm longer than the length of the concrete body of the pile. The protrusions of the reinforcement are necessary for subsequent connection with the reinforcement frame of the harness.
Depending on the level of elevation above the ground, 3 types of grillages are classified:
- Low (lowered into the soil below its freezing level or so that the upper contour of the piping is flush with the ground);
- Elevated (laid on the ground surface);
- High (raised above the ground to a height of 20-30 cm).
Fig : Types of bored pile grillages
The sequence of installation of the grillage of bored piles is as follows:
- A layer of sand and crushed stone bedding 20-30 cm thick is laid around the perimeter of the piping; if necessary, the soil level is lowered by digging;
- A formwork is formed on top of the bedding, made from planed boards. The formwork is fixed by means of side struts;
- The internal walls of the formwork are covered with waterproofing material (oilcloth, roofing felt);
- A reinforcement frame is assembled from reinforcing bars, which is placed in the formwork and welded to the protrusions of the reinforcement of bored piles;
- The grillage is filled with concrete. Filling the formwork is carried out simultaneously, without pauses. After pouring, the mixture is compacted by vibration.
Fig : The process of arranging a grillage of bored piles
Important : upon completion of installation of the grillage, a 30-day pause is maintained for the concrete to gain strength, after which time the foundation of bored piles becomes suitable for further construction.
Bored pile driving technology
In construction practice, the injection method of constructing bored piles is often used. The essence of the method is to use hollow drill columns to develop wells for piles, while the concrete mixture is supplied immediately upon completion of their penetration through a channel inside the auger. This technology is called CFA drilling.
Fig : Column of hollow augers
The process of constructing piles using CFA technology is as follows:
- The well is developed to the designed depth (if necessary, under the protection of the casing);
- Concrete is pumped into the well through an auger, and the column is systematically removed as the cavity is filled;
- A reinforced frame is installed into a well filled with concrete using a vibrating hammer.
When implementing this method, the time spent on installing bored piles is significantly reduced.
STROYPROEKT LLC performs the following types of work:
— Installation of bored piles Ø 600-2000 mm up to 65 meters. — Installation of drilled injection piles Ø 250-500 mm. CFA Ø 250, 300, 350 , 400 , 450, 500, 550, 600, 700, 750, 800 mm up to 25 meters. — Construction of soil-cement piles and consolidation of soils using jet grouting using Jet-grouting technology and Ø 600-4500 mm. and a depth of up to 40 m. — Installation of ground anchors for fastening enclosing structures up to 40 m long. — Construction of fencing a pit using the “wall in soil” method with a depth of up to 24 meters — Fencing of a pit using reusable telescopic support E+S (Germany) with a depth of up to 12 m. — Vibration loading/extraction of sheet piles and pipes up to 40 m deep. — Closed laying of communications Ø 350 – 1420 mm. — Installation of piles by drilling in a casing inventory pipe; — Construction of piles using the continuous hollow auger method (NPSH, CFA); — Construction of piles using soil rolling method (DDS, FDP); — Installation of piles using the Double Rotary method; — Installation of piles by screwing the casing; — Installation of piles using the method of vibro-immersion of the casing pipe; — Construction of piles under the protection of clay mortar;
tel.,
+7 (929) 549-38-00,
+7,
The email address is protected from spambots. Javascript must be enabled in your browser to view the address.
Bored piles: pros and cons
If the construction site is located in an area where the use of technologies that cause the slightest vibration of the ground, as a rule, it is impossible to do without bored piles.
However, the technology for their manufacture, although proven, is quite labor-intensive and requires precise adherence. The level of professional training and experience of the employees performing this work must be appropriate, since this process, depending on the condition of the soil on the site, has a lot of nuances. Bored piles, photo :
In weak, sandy, dusty soils, on peat bogs and in some other cases, the surface of bored piles turns out to be uneven. Such a surface is more susceptible to the destructive effects of moisture and heaving forces when the soil freezes than the smooth surface of finished driven piles. See also:
- How to close a pile foundation
- Strengthening the pile foundation
Engineering calculations
The technology of a suspended foundation is quite complex and requires careful calculations at the planning stage. These calculations differ from those for rack piles - they take into account many more direct and indirect values and parameters. This is due to the unreliability of weak subsidence soils as a load-bearing support.
The required bearing capacity of the foundation can be determined using the formula given in section No. 2-02-03-85 of SNiP. Engineering calculations are quite complex, and they should be carried out by specialists with appropriate education. For accurate calculation you will need the following parameters:
- The outer perimeter of the pile section (u).
- Area of the lower end of the support (A).
- Length of the recessed part of the hanging support (Hi).
The formula also includes a number of tabular values:
- Soil resistance under the bottom of the support (R).
- The resistance of all layers of soil through which the pile passes (Fi).
- Conditional coefficient of work of the structure under the tip and on the side surfaces of the support. Depends on the method of deepening and is given in the corresponding SNiP tables.
The compressive load of each individual support is calculated according to the following formula.
This is the basic formula for pendant piers driven by the hammer method. There is another formula that allows you to calculate the bearing capacity of a pile. It is performed to determine the minimum pull-out load.
The parameters used in this case are similar to those previously given, with the only difference being that the operating conditions coefficient has a different meaning.
An alternative to bored piles - leader drilling for piles
An excellent alternative to the production of bored piles is leader drilling of wells for piles. The cost of drilling one linear meter of a well starts from 200 rubles, and depends on the condition of the soil.
Our equipment allows us to immediately immerse piles into drilled holes without changing position. What is the advantage of this method?
- Such immersion does not create a high level of vibration impact on neighboring buildings.
- Allows you to build reliable pile foundations even in urban areas with dense buildings.
- Provides accurate calculated driving of piles in complex soils (permafrost soils, areas with high groundwater levels, soils with quicksand and lenses, etc.).
In addition, we carry out leader drilling for screw piles and their installation. Contact us, our specialists know and love their job!
Benefits of foundation design
Bored piles allow construction to be carried out close to existing buildings, since when constructing such foundations there are no shock and vibration effects.
The main advantages of a pile foundation with a grillage include:
- high load-bearing capacity;
- versatility and efficiency;
- simple technology;
- small amount of excavation work;
- affordable price;
- durability.
The absence of dynamic effects on soils makes it possible to install bored foundations in close proximity to existing buildings, utilities and main pipelines.
The costs of constructing pile foundations are significantly lower than those of installing slab and strip foundations, due to the smaller amount of reinforcement and concrete used.
Pile technology has both advantages and disadvantages:
- Complexity of calculations. To accurately calculate the parameters of the foundation, you should perform a geological survey of the site, study the regulatory requirements, and take into account all possible nuances for each structure.
- Impossibility of constructing a basement or ground floor. When excavating the soil, the adhesion of the soil to the piles is disrupted, which entails a decrease in the bearing capacity of the entire structure;
- Significant heat losses due to raising the structure above ground level. To reduce heat losses, floor insulation is required.
Errors in foundation calculations can lead to deformations due to uneven settlement of structures and excessive consumption of building materials.
House on screw stilts.