builds bathhouses and houses from hand-cut northern logs. It is selected according to GOST; when laying crowns and building a log house, all technology requirements are observed. One of the main rules is observing the shrinkage time and its correct compensation. Let's consider what the process is, how long it lasts and what to provide to make the house warm and durable.
Shrinkage is a natural process in which, due to a decrease in wood moisture content, the linear dimensions of a wooden structure change. Porous material absorbs and releases moisture, and if this is not taken into account during construction, the building will “lead”, the geometry of the walls will be disrupted, and cracks will appear in them. In addition to the “shrinkage” of the log, all joints are compacted - under the own weight of the elements. If the shrinkage of the log house proceeds correctly, the gaps “close” and the building becomes strong and windproof.
Wooden, log houses change geometry in two directions. With mechanical shrinkage, the upper links put pressure on the lower ones, and with natural shrinkage, the diameter of the log changes due to drying out. However, this is not only shrinkage, which increases internal stress in the elements. The two concepts are often confused, but it is important to differentiate them in order to understand what causes cracks to appear on logs. They are caused not by shrinkage of the house, but by shrinkage of the logs, and it differs for different species - pine, for example, has a higher risk of cracking than cedar.
Reasons for log shrinkage
The main reason for shrinkage is changes in wood humidity. Wood contains water:
- capillary - it is located in cell cavities and intercellular space;
- hygroscopic - it fills the cell walls;
- chemically bound - water contained in the substances that make up wood.
The tree decreases in size due to the loss of hygroscopic water; capillary moisture does not cause shrinkage. All three types evaporate, changing the moisture content of the material. In freshly cut trunks it ranges from 50%, in a tree that has reached the fiber saturation point (in the absence of capillary water) - about 22%. Thus, shrinkage is caused by the shrinkage of the log, but, in addition to it, the compaction of the joints under the own weight of the structure. In this case, the natural process does not cause distortion. The log house may “lead” due to settlement. This is another concept that shrinkage is often confused with. Settlement occurs due to the wrong choice of foundation type, errors in calculation of connections, foundation strength, insufficient quality of wood or other reasons. Because of it, the structures become distorted, the house can “sink” into the ground, and the crowns can bulge. To avoid problems due to settlement, you need to be meticulous in choosing a construction organization.
Errors in the operation of a newly built house
The desire to quickly move into your home can result in the appearance of cracks, deformation of the timber, mold and other problems. At best, the situation can be corrected by plating. How not to spoil a tree:
- Do not turn on the heating for at least 6 months after completion of construction. Radiators will warm up the wood, but unevenly. The walls will remain damp on the outside and dry on the inside. Internal cracks, deformations will appear, and fungus will develop.
- Ensure good ventilation, do not block windows and doors. This increases the humidity inside, and the walls outside continue to dry, resulting in uneven drying. In the first few months, no matter how many years the house shrinks, it must “breathe.”
- Pay careful attention to the choice of builders and materials.
Specialist Dmitry Bagrov tells more about the peculiarities of moisture loss in wood:
Shrinking a house made of timber, no matter how long it takes, brings fewer problems than correcting mistakes. Therefore, if you don’t want to live with wide cracks or redo the interior decoration, you shouldn’t rush to move in.
Log shrinkage time
There is a stereotype that shrinkage takes a very long time, and the process is actually endless. This is only partly true. Wood is a living material, and natural changes in humidity occur constantly, thanks to which an optimal microclimate is maintained in the house. However, the main processes affecting the strength, geometry, and thermal insulation of a log house end in the first year or two. Logs release moisture most actively during the first three to five months, when about 70% of shrinkage occurs. Over the next few months, the joints in the structure are sealed, and in general the initial intensive stage takes about a year. Over the next couple of years, minor changes in height or geometry may occur that do not significantly affect the performance characteristics of the log house. Experts talk about almost imperceptible shrinkage within a year and a half from the moment of construction. The exact time of completion of the process also depends on seasonality. If the house is built in the summer, it will “settle down” in about a year. For “winter” log houses, as a rule, eight months of shrinkage are sufficient, after which further work can begin. Therefore, builders consider the cold months to be the most favorable season for the construction of log houses. Due to the low temperature, all metabolic processes in wood, including moisture evaporation, slow down, and the log house shrinks evenly and efficiently. When winter is over, it will be possible to install window and door units and begin finishing. The exact time for the processes must be determined by builders, taking into account all the nuances. It is very important not to artificially accelerate shrinkage. The house should not be heated so that the elements do not begin to crack. This is especially true for timber and rounded lumber. Hand-cut logs are more resistant to temperature changes. It is advisable not to light the stove in the house for about a year from the date of construction. Heating can only be turned on after finishing the final finishing, and the temperature must be increased smoothly and gradually.
Favorable conditions for quick drying
To make the construction of a wooden house take less time, you can help the house made of timber to shrink as quickly as possible.
How to provide a tree with favorable conditions:
- use dried materials;
- maintain indoor humidity levels less than 70% but more than 40%;
- treat the ends with a compound that prevents the release of moisture, insulate the seams;
- cover surfaces that can accumulate snow with film.
Regardless of how long the shrinkage of the house takes, it is important not to begin interior decoration until it is finished.
What affects shrinkage
It is quite possible to calculate the percentage and end time of shrinkage. To do this, you need to collect data on all the key factors influencing the process. Among them:
- log house materials - species, percentage of humidity, type of wood drying;
- wood processing method;
- climatic conditions in the construction region and location of the site;
- technology for constructing a log house and the method of connecting elements.
Only experienced builders who are well aware of all the features of the natural process can accurately calculate shrinkage and monitor its progress.
Construction materials
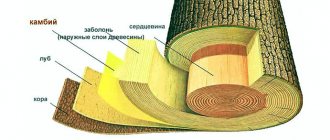
Shrinkage is primarily affected by the physical and mechanical characteristics of wood. A denser material evaporates moisture more slowly, so the process takes longer. The densest species are larch, oak, beech, maple and other hardwoods. Most conifers have a lower density (below 1.55 g/cc) and shrinkage occurs faster in them. It is important how the wood dries - naturally or in special chambers. In the first case, you need to know exactly how the logs were dried - the room should be dry, cool, with adequate ventilation. Otherwise, the elements will remain damp inside, which will lead to cracks. They will have to be sealed, covered with sealant, wood chips, caulked or puttied so that the wood does not rot.
Log processing method
The scale of shrinkage directly depends on how the wood was processed. Hand-cut logs release moisture the most - 10-11 cm per three meters of wall. Thanks to this, the shrinkage is stronger, but the changes are smooth, so there is less risk of cracks. At the same three meters in height, other materials decrease in size:
- rounded log - up to 10 cm;
- lumber of natural moisture and profiled (undried) - 4-6 cm;
- profiled timber for chamber or condensation drying - up to 3 cm;
- laminated veneer lumber - up to 2 cm (double up to 3 cm).
Climate and site features
Wood is characterized by active moisture exchange with the external environment, so shrinkage is affected by the amount of precipitation, sun intensity, and wind load in the region. If the climate is hot and dry in summer, the outer layer of the log will dry faster than the inner layer, which can cause the wood to warp and the structure to deform. It is important where and how the log house is located. In a lowland or among tall trees, shrinkage will take place more slowly, in a dry place, or in a windy field - faster. Therefore, it is also necessary to choose the right site for the construction of a log house. On the sunny side, shrinkage will occur faster than on the shady side, but not so much that the house noticeably warps.
Method of constructing a log house
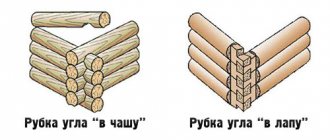
To determine the amount of shrinkage, it is important how exactly the crowns are connected in the log house. There are many ways - dovetail, paw and bowl, Canadian cut, etc. A competent choice of connecting elements, material for inter-crown sealing and other nuances helps to reduce the negative consequences of the process, which is why it is so important that the log house is cut by an experienced and professional team.
Eliminate twisting, skewing and sagging of logs
The walls of a wooden house made of logs, during the shrinkage process, in addition to drying out, also tend to change their shape. The log twists and bends. This occurs along the axis of the load-bearing walls, and not only in the vertical and horizontal planes.
To compensate for the above-mentioned processes and to prevent the structures from shifting from the design level, a log house is assembled on wooden dowels. Without it, during drying due to internal forces, deformation of the log will be inevitable.
A dowel is a dowel made of wood, which during shrinkage prevents the logs from twisting along its axis.
Complete absence, incorrect installation or insufficient number of dowels will ultimately lead to distortions and logs falling out of the walls.
The dowels are installed, taking into account the length of the log and the location of the doors and windows, in a checkerboard pattern relative to each other. Holes for dowels are made strictly vertically and in the center of the log every one and a half to two meters.
The diameter of the hole is made slightly larger than the diameter of the dowel itself. Its depth should also be greater than the length of the dowel by about 3-4 cm, this provides space for its advancement for shrinkage of the log house. Otherwise, the top log will hang on the dowel when it shrinks, resulting in a gap forming between the logs. The best material for dowels is birch.
Shrinkage compensation methods
Compliance with compensation technologies helps “take control of shrinkage.” Among its main methods:
- break in construction - at least six months must pass between installation under the roof and finishing;
- temporary roofing for the period of shrinkage - it is installed if the roof has a complex shape;
- “sliding” fastening of wall sheathing and structural elements of the roof (to log gables);
- connecting the crowns vertically with wooden dowels;
- installation of compensators for vertical parts on the porch, veranda, terrace, balconies;
- fastening and passages through the roof when installing chimneys;
- filling a gap for shrinkage when installing window and door blocks in the casing;
- treatment of logs with water antiseptics, compounds to reduce moisture evaporation, etc.
When laying logs, you can reduce shrinkage by properly installing a high-quality seal and providing ventilation to the structure during the drying period under the temporary roof. To prevent elements from twisting or falling out, and to prevent the locking joints from moving, wooden dowels are used. For them, holes are made in the logs, strictly maintaining the verticality of the walls. To control the process, special compensators are used - screw jacks with an adjusting anchor, beams for the casing of windows or doors. Longitudinal grooves and tenons in the logs relieve pressure and improve the fit of the elements. There are other ways to compensate for shrinkage - specialists will tell you more about them.
Chain link
To prevent the gables from hanging, a dormer window (15 x 15 or 20 x 20 cm) is made in their upper part, stretching a galvanized chain through it and the lintel of the window (or door) opening. The ends of the chain outside the house are connected with a special screw tie, which is tightened from time to time, creating a load on the pediment. When tightening the chain, it is important to take into account the uneven settlement of the log house and avoid bending. Instead of a dormer window, you can drill a small hole in the pediment, closing it with a wooden insert.
The need to comply with assembly technologies
In construction, the combination of quality materials and professionalism in work is important. Therefore, the construction of a timber house for shrinkage should be entrusted to experienced, qualified specialists. The method of assembling the material is of great importance; the more densely it is folded, the less distortion there will be. The profiled beam has a tongue-and-groove design that is advantageous in this regard, which ensures good joining. Metal or wooden dowels are used to fasten the elements.
Due attention should be paid to the choice of inter-crown insulation when caulking a building. Flax fiber is most often used; it gives less loss in volume, unlike moss. Good sealing is provided by jute fiber. After the walls settle, you need to repeat the run of the insulation between the links. This will prevent cracking of the timber structure due to insufficient density. To speed up the process, use a wooden mallet, with which you can help seal the box without damaging the material, reducing the gaps.
How wood of different species can be changed
Its shrinkage depends on the density of the wood structure. Each type of wood dries out differently. In housing, coniferous trees are most often found, since due to the concentration of resins in the structure and greater hardness, they are less susceptible to deformation. More details about the indicators can be found in the table:
Having studied the information about the influence of wood density on the deformation of structures, it becomes clear why larch cottages are in special demand in the construction industry. While houses for living are not built from birch, a soft and loose material.
Advantages of profiled timber
The main advantages of profile timber include:
- environmentally friendly material - the beams are not chemically treated, which will protect any family from further exposure to artificial materials;
- the material allows enough oxygen to enter the room, the walls “breathe”;
- additional insulation is needed only in certain cases, since the beams fit tightly due to their special profile;
- walls made of this material are smooth, which eliminates the need for additional processing and finishing of walls;
- due to the correct profile geometry, wall assembly takes a short time;
- the structure is lightweight, so the foundation is not expensive;
- the price of such a house is low.
Protecting an unfinished log house in winter
In winter, an unfinished log bathhouse needs additional protection, which ensures the stability, strength and safety of the erected structures. If the conservation work on the construction site is carried out correctly, then the resumption of construction work in the spring will take place without problems.
The structure itself, communications (provided they are connected) and building materials need to be protected. All work is carried out in several directions:
- Installing insulation between the crowns to protect against excess moisture;
- Covering surfaces – horizontal and vertical, where snow accumulates;
- Protecting wood with antiseptic agents.
Rubemast, stekloizol or polyethylene film on a reinforced base are used as covering materials. They provide the log house with high protection from increased moisture, wind and cold. For a wooden structure, it is not recommended to use roofing felt and heat-resistant film, which have low moisture resistance.
To protect surfaces, it is necessary to prepare strips of covering material of a certain length, rolling them along the joists and crown, securely fixing them at the edges.
For fixing, you can use thin slats with a cross-section of up to 2.5 cm or edged boards. To secure the slats, ordinary screws or nails are suitable. The film is fixed to the base using construction staples.