The construction of the roof truss system and the subsequent roofing are the most important stages in any construction. This is a very complex matter, involving comprehensive preparation, which includes the calculation of the main elements of the system and the acquisition of materials of the required cross-section. Not every novice builder will be able to design and renovate a complex structure.
Rafter system of a pitched roof
However, often when building adjoining buildings, utility or utility structures, garages, sheds, gazebos and other objects, the special complexity of the roof is not required at all - the simplicity of the design, the minimum amount of costs for materials and the speed of work, which are quite feasible, come first for independent execution. It is in such situations that the rafter system of a pitched roof becomes a kind of “lifesaver”.
In this publication, the main emphasis is on calculations of a pitched roof structure. In addition, the most typical cases of its construction will be considered.
Advantages and disadvantages
Shed roofs are considered the most inexpensive and easiest to install. And this is true, especially with the small width of the building. However, in our country, houses with pitched roofs are very rare. For the most part, this is due to the fact that two or four pitched roofs are more familiar to us - they look more familiar. The second snag is to find a project adapted to our weather conditions. There are a lot of projects on Western resources, but they are designed for a milder climate and, as a rule, have a large glazing area. Finding an architect who will competently change a project you like is very difficult. But if you succeed, and the harmony of the building is not disturbed, the house turns out to be very original.
One of the projects of houses with a pitched roof
Many people are afraid of uneven ceilings in some parts of the building. They are, of course, more difficult to beat than standard ones, but the result is of a completely different level - 100% original. True, this time it is very difficult to find a designer who can develop such an interior in the vastness of our Motherland, but nevertheless, it is possible.
There is another way out - to level the ceilings by overlapping, and use the free space under the roof as technical rooms. Such options have been implemented and the owners are very satisfied. Yes, the technical rooms are on the ground floor and upstairs, but there are no problems with groundwater.
These are, perhaps, all the disadvantages or pitfalls that a pitched roof can bring. There is, however, one more point that can hardly be called a disadvantage. Due to the peculiarity of the structure, the roofing material on such houses is not visible from the ground. If the terrain is flat, without large differences in elevation, there is no point in bothering with the appearance of the roof. It is better to choose simple-looking, but high-quality materials, quiet (the flat surface is large, it makes a lot of noise when it rains) and reliable. One of the popular options is seam roofing. It provides the proper degree of tightness and is not very noisy. Another option is a soft fused roof made from modern materials. Such roofs are even quieter, and modern materials can be used for 20-30 years without repair.
Preparatory work
The walls and floors of the building are prepared, although differences may not be visible visually. The difference in height becomes obvious when the support beam is laid in succession. They try to level the corners of the house. The masonry is leveled with mortar, screeding in the right places, and the wooden frame is prepared with the help of linings, and the bulges are trimmed off.
To correct the frame, a cord is used; it is attached to the two outer beams at the required height. The slabs are cut together so that horizontal areas are formed at the edge of the beams. The control template is applied to three beams simultaneously and the horizon level is checked. If the rail with the device is short in length, tie a long block. Mark the sampling points for the rafter teeth, and place pieces of control slats that indicate the central axis.
Construction of a pitched roof
Organize the required slope of the pitched roof due to the difference in heights of the opposite walls. One wall of the building turns out to be significantly higher than the other. This leads to increased consumption of materials for the walls, but the rafter system is very simple, especially for buildings of small width.
Shed roof
If the load-bearing capacity of the walls is sufficient, the truss system of a pitched roof rests on a mauerlat attached to the wall. To make the load distribution more uniform, the top row of the wall masonry is reinforced with longitudinal reinforcement (for brick walls, concrete blocks) or an armored belt is poured over the last row (for walls made of lightweight concrete, limestone, shell rock). In the case of a wooden or frame structure, the role of the Mauerlat is usually performed by the last crown or top trim.
If the building material of the walls is insufficiently strong, most of the load can be transferred to the ceiling. To do this, install racks (steps of about 1 meter), on which purlins are laid - long bars running along the building. The rafter legs then rest on them.
How to transfer the load from the walls to the floor
When pouring an armored belt or laying the last row, studs are installed into it in increments of 80-100 cm, with the help of which the mauerlat is then attached to the walls of the building. In wooden houses, if you do not make an armored belt, it is impossible to install studs. In this case, installation on pins with a hexagonal head is allowed. Under the pin, through the Mauerlat, a hole is drilled, a couple of millimeters smaller than the diameter of the pin. A metal rod is driven into it, which attracts the wooden beam to the wall. The connection is tightened using a hex wrench of the required size.
Basic principles of calculation
To calculate the pitch of the rafters, you can use online calculators. There is also a formula:
N=SxQ , where:
- N - load distribution on the rafter leg;
- S - distance between rafters;
- Q is the total load in kg/m².
The initially selected value of the pitch between the rafters is adjusted in the process according to the formula:
Ls/(Ls/S+1) , where:
- Ls - slope length:
- S - step between rafters.
In this case, the value of Ls/S+1 is rounded up.
For example, the length of the slope is 30 m, the selected rafter pitch is 1 m. After calculation using the formula 30/(30/1+1). We get the exact step length - 97 cm.
Rafter system of a pitched roof
Such roofs are especially popular in the construction of courtyard buildings - sheds, garages. It’s just that the size of the buildings allows the use of not very powerful beams, and beams are required in small quantities. With a building width of up to 6 meters, the rafter system of a pitched roof contains almost no additional reinforcing elements (supports and purlins), which is beneficial. Also attractive is the absence of complex knots.
For Central Russia, for a span of up to 5.5 meters, beams of 50-150 mm are taken; up to 4 meters, 50-100 mm is enough, although in an amicable way, you need to consider the snow and wind load specifically in your region, and, based on this, decide with beam parameters.
Rafter system of a pitched roof with a small span (up to 6 meters)
With a distance between the walls of up to 4.5 meters, the pitched roof consists of two mauerlat bars fixed to the walls, and rafter legs that rest on the mauerlat. Really very simple design.
With a span width of 4.5 meters to 6 meters, a support is also required, fixed to a higher wall at the floor level and a rafter leg that rests on the beam almost in the middle. The slope angle of this beam depends on the distance between the walls and the level of installation of the beam.
More complex rafter systems in a pitched roof with a building width of more than 6 meters. In this case, it is optimal if the house is designed in such a way that there is also a load-bearing wall inside on which the racks rest. With a house width of up to 12 meters, the trusses are still simple, and the cost of installing the roof is minimal.
Construction of pitched roof trusses for buildings with a width of more than 6 meters
For buildings more than 12 meters wide, the system becomes more complex - there are more rafter legs. In addition, manufacturing beams longer than 6 meters is expensive. If an increase is required only by the width of the roof overhangs, the beams are extended along the edges with fillets. These are pieces of beams of the same cross-section, connected to the beam and secured on the sides with two wooden plates at least 60 cm long, fastened with bolts or nails, allowing the use of mounting plates.
Option for splicing rafters
If the total length of the beam is more than 8 meters, they are usually spliced. The joints are further reinforced by nailing boards or mounting plates.
Options for attaching the rafters to the mauerlat: sliding at the top and rigid at the top on the right. Below on the right is a version of a tie-in without overhangs (very rarely used)
There may also be questions about how to attach the rafters of pitched roofs to the Mauerlat. There are no fundamental differences. Everyone also makes a cutout in the rafter leg, with which the beam rests on the mauerlat. In order not to suffer with each rafter leg, leveling its fit, having cut out the first one, a template is made from a piece of board, thick plywood or timber that exactly repeats the resulting “cut”. All subsequent rafters are sawn before installation. A template is applied to them in the right place, a recess of the required shape and size is outlined and cut out.
This was about rigidly attaching the rafter legs to the mauerlat. It is used on all buildings that exhibit low shrinkage. This method of fastening cannot be used on wooden houses - the house always settles or rises slightly, which can cause misalignment. If the roof is fixed tightly, it may tear. Therefore, when installing a pitched or any other roof on wooden houses, a sliding connection of rafters and mauerlat is used. For this there are so-called “slippers”. These are plates, consisting of corners that are attached to the mauerlat and metal strips movably connected to them, which are attached to the rafter leg. Two such slips are placed on each rafter.
Determination of a set of loads
The load on the rafter system directly depends on the number of legs. Even at the planning stage, it is necessary to calculate the total load (including the weight of the roof and snow).
The value of the total load must be divided by the estimated number of rafters . If the final number is large, then it is recommended to reduce the distance between the beams (you can check it using the characteristics table, knowing the material of manufacture).
When increasing the number of rafter legs, it is worth including their weight in the total load when recalculating.
Choosing a roof angle
The roof slope angle is determined by a combination of indicators - wind and snow loads and the type of roofing material. First, the angle is determined according to climatic conditions (depending on the amount of precipitation and wind loads). Then they look at the minimum recommended slope for the selected type of roofing material (in the table below).
| Name of roofing material | Minimum tilt angle (in degrees) |
| Asbestos-cement slate and ondulin | 6° |
| Cement-sand and ceramic tiles | 10° |
| Flexible bitumen shingles | 12° |
| Metal tiles | 6° |
| Asbestos-cement or slate slabs | 27° |
| Galvanized steel, copper, zinc-titanium sheets | 17° |
| Corrugated sheet | 6° |
If the desired angle is greater, everything is fine; if it is less (which happens very rarely), increase it to the recommended one. It is not advisable to make a roof with an angle less than the minimum angle recommended by the roofing manufacturer - it will leak at the joints. To make it easier to navigate, let’s say that for central Russia the recommended slope of a pitched roof is 20°. But it is advisable to calculate the figure for each region, and even for different locations of buildings on the site.
By the way, keep in mind that different manufacturers of the same type of roofing material may require different minimum slopes. For example, laying metal tiles of one brand can be done on roofs with a minimum slope of 14°, another - 16°. And this despite the fact that GOST defines a minimum slope of 6°.
It is also worth remembering that with a slope of up to 12°, in order to ensure the tightness of any roofing material, it is necessary to coat all joints of the material with a liquid waterproofing compound (usually bitumen mastic, less often - roofing sealant).
Summary
It’s not enough to know how to install rafters and secure them to the walls of the house. First you need to calculate the loads and choose the optimal fastening method, taking into account the length of the spans, the possibility of shrinkage and other factors affecting the stability and durability of the structure being created. And most importantly, you need to have experience working with wood and be a perfectionist in order to achieve the perfect identity of each pair of rafters and install them in the same plane.
You can take on such work yourself if you have a detailed project in hand and an experienced assistant nearby. Otherwise, it makes sense to turn to professionals.
Ratings 0
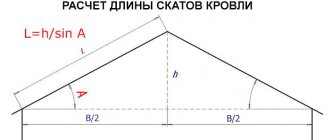
Determine the height to which you want to raise the wall
To ensure the found slope angle of the pitched roof, it is necessary to raise one of the walls higher. How much higher we will find out by remembering the formulas for calculating a right triangle. Using them we also find the length of the rafter legs.
How to calculate the parameters of a pitched roof
When calculating, do not forget that the length is obtained without taking into account overhangs, and they are needed to protect the walls of the house from precipitation. The minimum overhang is 20 cm. But with such a small protrusion beyond the building, the pitched roof looks short. Therefore, overhangs of at least 60 cm are usually made on one-story buildings. On two-story ones they can be up to 120 cm. In this case, the width of the overhang is determined based on aesthetic considerations - the roof should look harmonious.
Example of a drawing in ScratchUp
The easiest way to determine how much the roof needs to be extended is in design programs that allow you to draw the building to scale and “play” with the overhangs. Everything should be displayed in 3 dimensions (the most popular program is ScratchUp). Twist through different sizes of overhangs, decide which one looks better (if there is no project), and then order/make rafters.
What does the step depend on?
The pitch of the rafter system is the distance between the beams that form the roof frame. Typically the value varies from 70 cm to 2 m. The specific step depends on :
- the chosen design (layered, hanging rafter system);
- material (concrete, wood);
- beam section and length;
- roofing material;
- slope length.
Other factors may also influence. When constructing yourself, it is recommended to use a calculator to accurately calculate the distance between rafters or a ready-made project for a pitched roof.
Photo report from the construction site: a pitched roof on a house made of aerated concrete
A house was built in St. Petersburg. There was no project, there was a general idea, which is presented in the photo. The house is made of aerated concrete, the finishing is plaster, the roof is seam, chosen on the basis of low cost, reliability, and ease of installation.
Idea of a house with a pitched roof
After the walls were removed, an armored belt was poured into them, into which studs (Ø 10 mm) were installed every meter. When the concrete in the armored belt reached the required deterioration, a layer of waterproofing (“Gidroizol”, cut lengthwise into strips of the required width) was laid on the bitumen mastic. A mauerlat - 150-150 mm timber - is laid on top of the waterproofing. All lumber used for roofing is dry and treated with protective impregnations and fire retardants.
Beginning of installation of a pitched roof - laying the Mauerlat
First, they put it in place (lying on the pins, held by assistants), and walk along it, hitting with a hammer on the places where the pins are. The places where the studs stick out are imprinted in the timber. Now they drill holes and simply push it onto the studs.
Since the span turns out to be large, supports made of timber (150-150 mm) were placed on which the purlin was laid, which will support the rafter legs.
Installation of racks and purlins
The width of the roof is 12 meters. This takes into account a 1.2 meter offset from the front side. Therefore, the Mauerlat bars and the purlin “stick out” beyond the walls exactly at this distance.
To ensure the removal of the roof, the mauerlat and purlin stick out from the walls
At first there were doubts about such a large offset - the rightmost beam hangs 2.2 meters. If this offset is reduced, it will be bad for the walls, and the appearance will deteriorate. Therefore, it was decided to leave everything as it is.
Laying rafters
Rafters are laid from two spliced boards 200*50 mm, with a pitch of 580 mm. The boards are nailed together in a checkerboard pattern (top-bottom), with a pitch of 200-250 mm. Nail heads are sometimes on the right, sometimes on the left, in pairs: Two on top/bottom on the right, two on top/bottom on the left, etc.). We space the joints of the boards by less than 60 cm. The resulting beam is much more reliable than a similar solid beam.
The rafters are laid
Method of fastening the rafters
Next, the pie of a pitched roof for this case is as follows (from the attic to the street): vapor barrier, 200 mm stone wool, ventilation gap (lathing, counter-lathing), moisture insulation, roofing material. In this case it is dark gray pural.
An example of a roofing pie for a pitched roof (it’s actually standard)
We will carry out insulation from the inside later, but for now we are laying a Tyvek Solid hydro-windproof membrane (vapor-permeable) on top of the rafters.
We lay a waterproofing windproof vapor-permeable membrane
The membrane is laid from bottom to top and secured with staples. The fabric that is rolled out higher overlaps the one already laid by 15-20 cm. The joint is sealed with double-sided tape (bought together with the membrane). Then the planks are placed on top of the membrane, and on them is a sheathing for a standing seam roof.
Lathing made of boards 25*150 mm
First, the sheathing was made from 25*150 mm boards in increments of 150 mm. After installation, walking around the roof, it was decided to strengthen the sheathing. To do this, we fill 100 mm wide boards between the already laid boards. Now there is a gap of 25 mm between the boards.
Sheathing a pitched roof as a result
Next, hooks were placed on the lower gable for installing the drainage system. They are filled unevenly, since due to the large length of the pediment, it was decided to make two receiving funnels at a distance of 2.8 meters from the edge. To ensure drainage in two directions, such a relief was made.
Filled hooks for the drainage system
Next, you need to bring in pieces of metal (pictures) 12 meters long. They are not heavy, but they cannot be bent, so the “sled” disappears. For lifting, a temporary “bridge” was built connecting the ground and the roof. The sheets were lifted along it.
Lifting sheets along the bridge
Next comes roofing work, which differs depending on the type of roofing material. In this case, it was necessary to solve the problem of thermal expansion of the material - galvanized steel (pural) significantly changes its dimensions when heated/cooled. To ensure freedom of expansion, it was decided to fasten the material to the sheathing by the seam using movable clamps with a freedom of movement of 15-20 mm.
Installation of clamps for seam roofing
Laying seam roofing from pural
After laying the roofing material, what remains is the lining of the overhangs, and they are no different.
The roof needs to be brought to perfection - the overhangs need to be hemmed, but basically it is already ready
Well, the photo below shows what happened after finishing. Very modern, stylish and unusual.
House with a pitched roof - finishing is almost finished
DIY installation features
Method of laying rafters on the mauerlat
Nests for supporting rafters should always have horizontal platforms and vertical walls. Violation of the rule leads to loss of stability and displacement of load-bearing elements.
Making a truss template:
- Two boards 25 mm thick, 10 cm longer than the rafters, are fastened at the top with a bolt to allow rotation.
- The estimated height of the system is measured on the rail in the center of the tenon.
- The fastened boards are placed on the end gaps so that their edges rest against the notch.
- Combine the attachment point and the marks on the rail to determine the length of the rafter.
- The size of the tooth is marked on the lower edge, the template is lowered to the ground and the tenon is cut out.
- They try on the workpiece on site, inserting the tenons into the designated notches.
If after installation the vertex does not coincide with the mark on the rail, it is corrected by releasing the bolt, and the new position is marked on the rail. Measure the dimensions of crossbars, racks, fillies, tie rods and other elements of the truss truss. After the required products are manufactured, they are placed in the installation position.
Projects and photos of houses with a pitched roof
As has already been said, it is difficult to find interesting designs of residential buildings with a pitched roof. So far, these buildings are unpopular with us. Perhaps just because of its originality. This section contains several projects or photos of already built houses. Maybe it will be useful to someone, at least as an idea.
Project of a small house with a pitched roof
This house exists. Pitched roofs are especially good in areas with height differences
One-story house with a large pitched roof
Two-storey house with terraces on two floors
Natural tiles require a large roof angle
Large windows are beautiful, but irrational in our climate
Multi-level house - an interesting completed project
This is a prototype of what is located above
Original house. Under one pitched roof there is a house and outbuildings, and part of it is a canopy over the yard between two buildings
Same project as above, on the other side
Two pitched roofs at different levels