Shallow strip foundations (MSLF) are used in the construction of low-rise buildings from lightweight piece building materials. A relatively simple design, low material consumption and a high level of reliability make its use a technically optimal and cost-effective solution.
A structure of this type can be made by digging a pit around the entire perimeter of the house under construction or by digging trenches above the freezing point along the axes of load-bearing walls and partitions. The width and depth of the trench are determined by calculation (presented in gallery form towards the end of the article).
MZLF can be monolithic reinforced concrete or assembled from individual factory-made concrete blocks. It is possible to use rubble stone masonry or solid clay bricks, but the most durable and reliable structure is a reinforced concrete monolith.
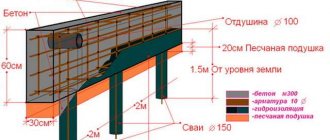
MZLF scheme.
Features of the design of a shallow foundation
A shallow monolithic strip foundation is erected on a flat surface. When building a house on a slope, you will have to combine MZLF with a pile foundation, using supports to level out the height difference. In terms of strength and resistance to deformation, the structure must comply with SNiP 2.03.01-84.
In cross-section, a shallow foundation looks like this:
Features of MZLF that must be taken into account during calculation and construction:
- The depth of the foundation base depends on the depth of soil freezing.
- Be sure to install a cushion made of dry bulk materials: a mixture of coarse sand and gravel.
- When the groundwater level is high, drainage is performed under and around the foundation.
- The base on which the monolithic tape is installed is compacted as much as possible.
- It is necessary to arrange a blind area to drain rainwater and snow.
Sergey Yurievich
Construction of houses, extensions, terraces and verandas.
Ask a Question
Taking these features into account, we can conclude that the backfill and blind area are an integral part of the shallow foundation. Requirements for the blind area are specified in SNiP 2.02.01–83.
Possible mistakes when building a foundation and how to prevent them
Very often, when building a shallow foundation, mistakes can be made and they mistakenly believe that the higher the foundation strip, the better. In fact, this is not the case at all, and there are several reasons for this:
- Increasing the tape will entail the cost of increasing the reinforcement, otherwise the foundation will not be strong and will easily deform.
- When building a frame house on a shallow foundation, it should be taken into account that the structure of the house is quite flexible, and in combination with a flexible foundation they create one single structure that is not afraid of soil heaving. If you make the foundation much higher, then its flexibility is lost and with the pressure of the house on it on the one hand, and the heaving of the soil on the other hand, sooner or later the foundation will not withstand it and will crack.
I would like to note that if you need to raise the foundation higher because its height is not enough, then it is best to do this by laying out the required height with a brick or an additional monolithic tape, which will be separated from the main layer by a layer of waterproofing.
Making a monolithic shallow shallow foundation with your own hands does not require much effort, but it is important to follow all the nuances and rules of construction. Only in this case can the result be a high-quality foundation for any structure
Calculation of a shallow strip foundation
Calculating the MZLF, which is being built on low- and non-heaving soils, is not difficult. During the calculation, three main parameters are determined:
Laying depth
Determined on the basis of SN “Foundations and Foundations”. The document specifies the following minimum depth values for the foundation base:
- when the soil freezes less than 2 m - 50 cm;
- when the soil freezes to a depth of 3 m - 75 cm;
- when the soil freezes more than 3 m - 100 cm.
For most regions of the middle zone, the depth of the MZLF will be 50 cm. For light buildings, such as a frame barn or a small country house, this parameter can be reduced to 30 cm.
Subtleties of construction
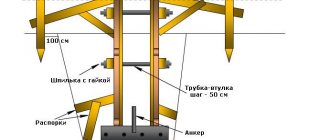
When it is possible to mount support piles below the freezing level of the soil, a shallow strip foundation is built in conjunction with support pillars.
This option is used for damp and marshy areas, on loams, and with close-lying groundwater. This allows you to save on the supporting structure without compromising its reliability.
The following are used as pillars:
- steel pipes protected by a concrete layer;
- reinforced concrete supports;
- asbestos-cement pipes filled with concrete inside.
It is necessary to consider the arrangement of a high-quality drainage system. Otherwise, the costs of arranging the foundation will not be justified and the structure will collapse over time.
Width of monolithic tape
In order not to make complex calculations, we recommend taking the width of the sole based on the table:
| Wall and ceiling materials | Number of floors | MZLF sole width, m |
| Walls made of lightweight brickwork or aerated concrete with reinforced concrete floors | 1 | 0,6 |
| 2 | 0,8 | |
| 3 | 1,2 | |
| Timber frame walls with timber ceilings | 1 | 0,4 |
| 2 | 0,4 | |
| 3 | 0,6 | |
| Log walls with wooden ceilings | 1 | 0,3 |
| 2 | 0,4 | |
| 3 | 0,6 | |
| Walls made of timber with wooden floors | 1 | 0,2 |
| 2 | 0,3 | |
| 3 | 0,4 |
Height above ground level
The higher the monolithic strip rises above ground level, the better the floors of the house will be protected from dampness and cold. However, the height of the foundation to maintain stability and load-bearing capacity must correlate with its width. The best option: the height of the tape above the zero mark is equal to its width.
Example: The laying depth is 50 cm. The width of the monolithic tape according to the table is 30 cm. This means that the height above ground level will be 30 cm, and the height of the entire monolithic tape will be 80 cm. The height of the ground part of the MZLF should not be lower than the snow level. The snow depth value depends on the region (you can find it on the Internet). For regions of the middle zone, this value does not exceed 8-10 cm.
Calculation of MZLF on heaving soils
When building a house on heaving soils, more complex calculations are performed, the purpose of which is to determine the heaving deformation. It is quite difficult to make such a calculation yourself, so you need to entrust it to professional designers or use a ready-made table:
| Name and degree of soil heaving | Number of floors of the building | Width of foundation base b, m | Thickness of the pillow t, m | Foundation design option | Reinforcement option |
| clays, loams and sandy loams, fine and silty sands, moist - medium sandy | 1 | 0,3 / 0,2 | 0,6/0,7 | G. | 3 |
| 2 | 0,3 / 0,2 | 0,5 / 0,6 | G. | 3 | |
| 3 | 0,3 / 0,2 | 0,4 / 0,5 | G. | 3 | |
| clays, loams and sandy loams, fine and dusty sands, moist - highly heaving | 1 | 0,3 / 0,2 | 0,7 / 0,8 | G. | 4 |
| 2 | 0,3 / 0,2 | 0,6 / 0,7 | G. | 4 | |
| 3 | 0,3 / 0,2 | 0,5 / 0,6 | G. | 4 |
In column 2 “Sole width” and column 3 “Cushion thickness”, the values for heated and unheated rooms are indicated through the sign /. The column “Reinforcement option” indicates the minimum number of reinforcing bars that must be used to reinforce the monolithic strip.
Fill
A shallow foundation can be filled with concrete mortar, having made the appropriate calculations in the required building materials, or ready-made concrete blocks can be installed.
Before filling a wooden structure with concrete, the walls and bottom of the formwork must be moistened with water.
Pipes for water supply and sewerage are laid in the formwork. The pipes must be filled with sand so that concrete does not fall into them when pouring.
You can calculate the concrete solution and then pour it yourself.
First of all, you need to calculate the required amount of mortar for a shallow foundation by multiplying its height, width, length. To prepare the mixture, preferably in a large-volume concrete mixer, you need to mix 1 part cement, 3 parts sand, 5 parts gravel or crushed stone, then bring this mixture to the required consistency with water.
Construction of a shallow foundation: construction technology
The technology for constructing MZLF is not complicated; filling can be carried out according to SNiPs 3.03.01-87, 2.02.01-83 or according to our instructions. The foundation for a frame house 10 x 10 m can be poured in 1-2 days. Before you start pouring, you need to decide where you will take the concrete solution. There are two options:
- 1order concrete class B22.5...B17.5 at the nearest RBU. In this case, the mixture will be delivered to you at the specified time by a concrete mixer truck. If the ABS cannot reach the pouring site, then a special hose is used through which the concrete solution will be supplied to the formwork. Ordering a sleeve will slightly increase the cost of ABS services. In addition, you will have to pay for every hour of downtime of the special vehicle.
- 2 prepare concrete yourself. At the same time, you will not depend on RBU and will spend significantly less money, however, the quality of the concrete mixture will be slightly lower. When mixing concrete, the recipe must be strictly followed. To prevent concrete from starting to set ahead of time, you can use special additives. You can begin preparing concrete immediately after installing the formwork.
Installation of MZLF: step-by-step instructions from A to Z
Preparatory work and marking
The installation of a shallow foundation begins with site preparation, which consists of removing debris and uprooting stumps. The top layer of soil with vegetation is cut off. If necessary, leveling and filling of soil is carried out, followed by compaction.
The marking is carried out as follows: the perimeter of the future foundation is established, beacon pegs are driven into the corners. Ropes are stretched along the future monolithic tape.
The diagonal between the corners must be strictly 45 degrees. You can check the evenness of the markings using a tape measure and a building level.
Construction of trenches and cushions
The depth of the trench depends on the depth of the foundation and the thickness of the cushion. The width of the trench is made 10 cm wider than the calculated thickness of the monolithic tape. This is necessary for installing the formwork. When constructing MZLF on loose soils, the trench slopes can be strengthened with boards. Pillowing is necessary to reduce the impact of frost heaving forces on the foundation. The thickness of the cushion, as a rule, is 20-30 cm for slightly heaving and non-heaving soils. For heaving ones - determined according to the table given above.
Correctly backfilling means making 2 layers: the first is coarse sand, which is poured, and then moistened and compacted, the second is fine crushed stone or gravel. Blast furnace or boiler slag can also be used as a second layer. If the groundwater level is high, it is recommended to put a layer of waterproofing under the cushion: roofing felt or geotextile, and fill it on top.
Installation of formwork and reinforcement
The formwork is made from planed boards, the thickness of which is no more than 3 cm. The formwork is mounted in a trench, and its height is 5-10 cm greater than the height of the monolithic tape. A reinforced frame is installed into the finished formwork. Reinforcement of the monolithic tape is carried out in accordance with SNiP 52-01-2003 and SP 52-101-2003. The reinforced frame can contain from 3 to 6 longitudinal reinforcement bars connected to each other by vertical jumpers.
The reinforcement scheme is determined based on the width of the foundation strip. The reinforced frame is assembled from corrugated reinforcement with a cross section of 12 mm, class A3. For a small structure, you can use A500C class reinforcement, the cost of which is much cheaper. The frames are interconnected with an overlap, forming a reinforcement unit. The length of the overlap should not exceed 20 diameters of the rods (20 x 12 = 24 cm). The connections are secured by welding.
For corners where the walls of the future house intersect, it is necessary to strengthen the reinforcement frame by installing additional vertical rods, which are welded to the longitudinal rods. This reinforcement allows the strip foundation to withstand critical loads acting at the intersections of the walls.
You can lay the reinforced frame on a prepared cushion, but it is better to do it on the starting layer of concrete. The thickness of the starting fill should not exceed 20% of the entire height of the tape. Concrete pouring helps create a more even surface on which the reinforced frame is laid. If you decide not to fill the starting layer, then support fungi should be used to raise the reinforced frame above the surface of the pillow by 5-7 cm.
The reinforced frame should be located in space, nowhere in contact with the bedding and formwork.
Pouring concrete
Filling should be done at a temperature of +10 C and above. Before pouring, the formwork must be moistened, then the concrete will lie more evenly. The mixture must be poured in layers, the layer thickness should not exceed 40 cm, optimally 20-30 cm. Each layer is subjected to 5-10 minutes of vibration compaction. This technology does not allow voids to form inside the concrete. To supply the concrete mixture to the formwork, you must use an elastic sleeve or chute.
Final stage of work
After pouring the foundation, the reinforced concrete strip is closed from above to prevent it from drying out and left to harden for at least two weeks.
During cold weather, special additives are used, since at subzero temperatures water turns into ice, which prevents concrete from hardening even after the temperature rises above zero again. In hot weather, concrete that hardens is watered because when it evaporates excessively, it stops the hardening process and turns into dust. A strip foundation is poured for a low house, a bathhouse, or a panel house. It is attractive because you can simultaneously cover all four sides of the house with a foundation. Before starting construction work to install the foundation, the ground is cleared and markings are carried out for it. Construction cords mark the location of the future formwork, after which earthworks begin. A trench is dug, the bottom of which is filled with crushed stone drainage and compacted. Then formwork is installed from boards, into which concrete is poured. To make the foundation stronger, concrete is reinforced by installing a lattice of metal rods in the formwork. The poured concrete is kept for at least a month, then the formwork is removed and work is carried out to waterproof the upper part of the foundation.
Insulation of a shallow foundation
Professional builders recommend be sure to insulate the MZLF. It is recommended to do this immediately at the time of construction of the structure. An insulated foundation will protect the floors of the house from dampness and cold, which is especially important when arranging the floor “on the ground”. In this case, in the absence of thermal insulation, all the heat from the floor will go into the ground.
There are external and internal thermal insulation MZLF. External - when the insulation is attached to the outside of the monolithic tape, internal - from the inside. External insulation is considered mandatory, but internal insulation is usually done if the house has a basement. What insulation should I use? There are a lot of options. The most popular are:
- Penoplex. Dense thermal insulation, excellent heat conservation. Its service life is significantly longer than that of conventional foam. Penoplex is resistant to rodents, mold and practically does not absorb moisture. In terms of price/quality ratio, this is the best material for thermal insulation of a shallow foundation.
- Expanded polystyrene. The extruded material is slightly inferior to penoplex in terms of physical and mechanical properties. However, the price of polystyrene foam boards is 20-30% cheaper. It can be used in dry and dusty soils with minimal moisture.
- Polyurethane foam. Liquid spray thermal insulation is an expensive option, but it has many advantages: no joints between slabs, a service life of at least 50 years, minimal water absorption and resistance to aggressive environments.
The use of insulation based on mineral wool for thermal insulation of the foundation is strictly prohibited! Mineral wool absorbs moisture well, so the insulation will quickly become damp and lose its heat-insulating properties.
The insulation technology depends on the selected material. The heat insulation slabs are attached to the monolithic tape using glue, and then reinforced with a special mesh. A layer of plaster is applied on top. The finishing of the base is carried out together with the installation of the blind area.
Features of construction of MZLF on heaving soils
Heaving soils do not allow moisture to pass through, preventing it from going deeper, so precipitation accumulates near the surface of the earth. When erecting a building made of blocks or wood on heaving soils, drainage must be done, and the backfill must be at least 30 cm. When building houses, a set of protective measures is taken for the foundation:
- The backfill is made from non-heaving soil. Waterproofing must be installed under the sand and gravel cushion. It is better to use geotextiles, which prevent siltation well.
- Drainage is installed at the level of the sole of the monolithic tape. Drainage pipes are laid at a distance of at least 1 m around the foundation. The slope of the pipes depends on their diameter: the smaller the pipes, the greater the slope should be.
- Installation of insulated blind area. The blind area helps drain water from the MZLF. A layer of insulation under the scaffold prevents freezing of heaving soils around the house.
- Storm sewer installation. The main purpose of a storm drain is to effectively remove precipitation from the site. For a shallow foundation, a well-executed storm drain will avoid flooding and subsequent freezing of heaving soils.
If these conditions are met, a shallow foundation built on heaving soils can last for many years without problems. To avoid mistakes during construction, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with SP 45.13330.2012, which describes all measures to protect MZLF on difficult soils.
Introduction to the topic
Construction experts say that to build a small house with several rooms, there is no point in laying a deep foundation. For this type of building, there is no point in spending the budget by burying it in the ground. The unreasonable use of deep strip structures has a negative impact on the environment: it inhibits the normal course of soil processes and changes the topography. Therefore, when calculating the parameters of a building, it is necessary to take into account not only practicality, but also the environmental friendliness of the process.
Shallow foundations come in several types:
- Tape - preferably used on heaving soil;
- Columnar – applicable on hard, stable soils;
- Slab - monolithic structure on subsidence type soil.
FMZL with heaving soil should be buried at the freezing level. This is due to the principle of water expanding when it freezes. That is, when the water in the ground freezes in winter, it pushes out everything that is above. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that such a foundation is immersed at a level where the temperature is not negative, then it will withstand all impacts.
There is an option: a shallow foundation with a slab. That is, a concrete screed is poured to the floor level above the foundation. It is the basis for future construction. A structure placed on a foundation of this type should not be very heavy, since the base already puts significant pressure on the soil.
Prefabricated MZLF on sandy soils
Most sandy soils are classified as slightly or non-heaving. In areas with such soils, shallow prefabricated foundations can be erected from ready-made reinforced concrete blocks. Installing ready-made blocks is much easier, and their cost differs minimally from the cost of concrete mixture and formwork. For prefabricated MZLF, the following types of blocks are used:
- FBS - rectangular solid structures;
- FL - trapezoidal pillow blocks with increased load-bearing capacity.
FL blocks are excellent for frame houses and outbuildings made of aerated concrete, and FBS are considered universal and have a wide range of applications. The sizes of finished reinforced concrete products are used small so that you can install them yourself without the involvement of a construction crane. The technology for installing a prefabricated shallow foundation is described in detail in SNiP 3.03.01-87. Just like a monolithic tape, the blocks are mounted on a prepared cushion. It is necessary to deepen the FBS in accordance with the calculations performed. To strengthen the base, the blocks are connected to each other with reinforcing mesh at the intersection of the walls.
It is not recommended to make a prefabricated foundation on heaving soils. The forces of frost heaving will push out individual elements, which will lead to the destruction of the foundation.
If all work on the installation of FBS is carried out correctly, a small prefabricated foundation will last 70-80 years. This is exactly the service life that reinforced concrete blocks have.
You can ask your question to our author:
Video description
This video shows the construction of a shallow foundation with piles and filling of the internal space of the tape:
Slab
A base in the form of a monolithic slab is more expensive, but it is more reliable. Such a foundation is often called floating and compared to a raft, whose entire plane follows the movement of the waves.
Work on its construction also begins with cleaning the construction site, removing the loose layer of soil, marking the outer corners and excavating the pit to the depth of the slab. If the groundwater level is high, then drainage trenches are dug and equipped along the outer perimeter to drain water.
Then the bottom of the pit is lined with a cushion of sand and crushed stone with a tamper. Waterproofing material is spread on the pillow with the joints glued, on top of which dense thermal insulation boards made of extruded polystyrene foam are laid. This substrate protects shallow foundations from water and freezing.
After installing the formwork along the perimeter of the future slab, a steel frame of two grids made of reinforcing bars is mounted in it. And this structure is filled with concrete with mandatory compaction using an in-depth vibrator.
Slab MZF device diagram Source smetadoma.com
It is important! Before concrete work begins, all communications must be laid and outlets made.
Columnar
The columnar type of foundation, especially with a slight depth, is the most unreliable, and therefore is not used in the construction of critical structures. But it is quite suitable as a foundation for sheds, gazebos and other small light buildings.
To construct it, holes are dug along the perimeter of the marked tape, surrounded by formwork, mounted in each frame and filled with concrete. Alternatively, only the underground part of the pillars is made of concrete, and the upper part is made of brick or small blocks.
Columnar foundation Source sdelai-lesnicu.ru
The pillars are connected to each other by a grillage, which is the basis for the construction of walls.