The strip foundation occupies the main place among all supporting structures for buildings and structures.
It is able to work effectively on the most difficult soils and has an optimal set of performance qualities.
Monolithic tape structures do not lose their performance qualities for up to 150 years, which exceeds the service life of the walls of a house.
Such high possibilities arose due to the high rigidity and strength of the tape, which is ensured by the joint work of concrete and metal reinforcement.
Each of them performs its own function, together providing reliability and high load-bearing capacity of the strip base.
How does reinforcement work in a strip foundation?
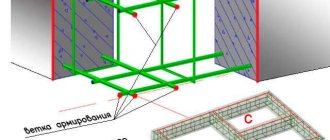
The reinforcement cage is necessary to compensate for axial counter-directional (tensile) loads that arise in the tape when deforming influences appear - bending or twisting forces.
The peculiarity of concrete is its ability to take gigantic pressures without any consequences.
At the same time, it is practically defenseless against multidirectional efforts, quickly becomes covered with cracks and collapses .
Therefore, any forces applied at one point are extremely dangerous for the tape - for example, lateral or vertical heaving loads. Reinforcing bars are designed to absorb these forces.
There are horizontal (working) and vertical reinforcement . The main loads are taken by horizontal rods.
They have a larger diameter and a corrugated surface that has good adhesion to concrete.
Vertical rods serve two functions:
- Fixation of working reinforcement in the required position until concrete is poured.
- Partial compensation of twisting forces.
The first task is the main one, and the second one is additional, since the presence of such specific loads is observed quite rarely.
In most cases, vertical (smooth) reinforcement serves only as a supporting structure that holds the working rods in the required position until pouring.
They are quite thick, since pouring is a process with fairly intense impacts on the frame, concentrated at one point (the place where heavy material falls into the formwork), and also distributed along the entire length (bayoneting, processing with a vibrating plate) .
How to connect
When laying reinforcing belts, the longitudinal and transverse components must be connected in some way. This is done in two ways: welding and knitting with wire.
Welding is a quick way, but not the best. The fact is that in places exposed to high temperatures, steel is more susceptible to corrosion. This is a very poor quality when laid in concrete.
The reinforcement can be connected by welding or wire
If there is one more disadvantage of a welded connection of reinforcement, there is a fairly real chance of breaking the connection during pouring or compacting the solution. It is usually pinpoint in nature and can be broken off.
The frame elements connected by welding have greater strength, but such a base is unable to respond to soil movements. And this leads to the formation of stresses in the concrete and the appearance of cracks. Therefore, we conclude: on heaving and loose soils it is better to use knitting.
Knitting of reinforcement using wire is done manually. There are some devices that make the process easier - hooks, flares, guns. But the process still takes a decent amount of time.
Read more about how to knit reinforcement for the foundation here.
Instructions for using the calculator
There are many online calculators on the Internet that help calculate the parameters of strip foundations for all important positions . Calculating reinforcement with their help takes literally a couple of minutes.
For example, on the website you only need to enter your own data into the appropriate windows of the program and click the “calculate” button.
A reinforcement diagram is given, in which the main parameters must be indicated - the number of working rods in one row, the total number of rows, the distance between vertical bars, etc. The cost of fittings per unit is indicated in a separate window.
As a result, the program displays the quantity of reinforcement and the total price. The calculation is simple and quick; in addition to the reinforcement, the resource provides the parameters of all elements of the tape - formwork , amount of concrete, etc.
The disadvantage of this calculator is the need to know in advance the reinforcement scheme, the diameter of the rods and the market value of the material.
If you need to determine the number and cross-section of rods, the resource is useless. It provides only quantitative information, without touching on qualitative aspects, which is sometimes not quite what is needed .
IMPORTANT!
Not all online calculators work using this algorithm. There are others that determine exactly the dimensions and general parameters of the reinforcement frame, which will be useful for obtaining primary information . The cost of the material should be found out directly from the sellers, since there are many specific factors in this matter.
Bookmark scheme
Section 8.3 allows you to accurately calculate the reinforcement for the foundation. Code of Rules.
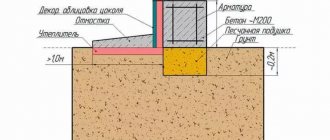
Protective layer In reinforced concrete foundations, a protective layer is provided for steel parts, which provides:
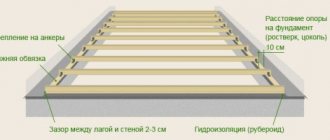
collaboration of all parts; protection of rods from aggressive environmental influences (moisture), chemicals; fire resistance. In soil, the layer thickness (the distance from the rods to any outer edge of the concrete) is chosen to be at least 40 mm. Outdoors, the distance is reduced to 30 mm.
Calculation procedure
Let's look at how to calculate the reinforcement cage of the tape yourself.
First of all, it is necessary to determine the number of working rods in one row. To do this, you will need to use the requirement of SP 52-101-2003, which limits the maximum distance between adjacent rods to 40 cm.
Considering that depth of the working reinforcement should not exceed 2-5 cm, we obtain :
- For tapes less than 50 cm thick - 2 working rods.
- For tapes wider than 50 cm - 3 rods.
In cases where it is possible to use both 2 and 3 rods in one row, they usually try to play it safe and take a larger value, since the foundation is a responsible and important section of the building.
The second stage is to determine the diameter of the working rods. To do this, you will need to calculate the cross-sectional area of the working part of the tape by multiplying the width by the height.
The total cross-sectional area of the reinforcement is 0.1% of the cross-section (this is the minimum possible value, it can be increased, but cannot be decreased).
Having received this value, you need to divide it by the number of working rods. Using the table of diameters of reinforcing bars, the most successful option is found, which is accepted for work.
The diameter of the vertical reinforcement is selected based on the height of the tape:
- For heights up to 60 cm - 6 mm.
- From 60 to 80 cm - 8 mm.
The diameter of the transverse rods is usually taken to be 6 mm.
To calculate the number of working rods, you need to multiply their number in the lattice by the total length of the tape, after which the resulting value is divided by the length of the working rod (usually 6 m, but it is better to find out exactly this value from the sellers).
Vertical reinforcement is calculated by multiplying the number of clamps by the length of the unit.
The quantity is obtained by dividing the total length of the tape by the pitch of the clamps (usually 50-70 cm).
Statement of consumption
| ø12 | ø8 | ø6 | |
| total length | 95.23 m | 153.42 m | 98.6 m |
| Weight of 1 meter according to the assortment | 0.888 kg | 0.395 kg | 0.222 kg |
| total weight | 84.6 kg | 60.6 kg | 21.9 kg |
| Number of rods 11.7 m each | 9 | 14 | 9 |
Careful calculation of materials for construction will save time and money.
An example of calculating the required parameters
Let's consider the calculation of reinforcement for a strip foundation using an example.
Let's assume that the height of the tape is 100 cm and the width is 40 cm (a common version of a shallow foundation).
Then the cross-sectional area will be:
40 • 100 = 4000 cm2.
Determine the total cross-sectional area of the reinforcement (minimum):
4000: 1000 = 4 cm2.
Since the width of the tape is 40 cm, 2 rods need to be placed in one grid, and the total quantity is 4 pieces.
Then the minimum cross-sectional area of one rod will be 1 cm2. Using SNiP tables (or from other sources) we find the closest value. In this case, you can use reinforcing bars with a thickness of 12 mm .
Determine the number of longitudinal rods. Let's say the total length of the tape is 30 m (6: 6 m tape with one 6 m jumper).
Then the number of working rods with a length of 6 m will be:
(30 : 6) • 4 = 20 pcs.
Determine the number of vertical rods. Let's say the pitch of the clamps is 50 cm.
Then, with a tape length of 30 m, you will need:
30: 0.5 = 60 pcs.
Determine the length of one clamp.
To do this, subtract 10 cm from the width and height of the section and add up the results:
(40 - 10) + (100 - 10) = 120 cm. The length of one clamp is 120 • 2 = 140 cm = 2.4 m.
Total length of vertical reinforcement:
2.4 • 60 = 144 m. The number of rods with a length of 6 m will be 144: 6 = 24 pcs.
NOTE!
The obtained values should be increased by 10-15% in order to have a margin in case of errors or unexpected material costs.
Statement of consumption
For purchase and transportation, it is necessary to combine all values into one table.
| ø14 | ø8 | ø6 | |
| Length | 216.7 m | 388 m | 207.5 m |
| Weight of 1 meter according to the assortment | 1.21 kg | 0.395 kg | 0.222 kg |
| total weight | 262.2 kg | 153.26 kg | 46.07 kg |
| Number of rods 11.7 m each | 19 | 34 | 18 |
To obtain the number of required rods, the total length of the required reinforcement must be divided by 11.7 meters (standard rod length).
Types and sizes
There are two main types of fittings:
- Metal.
- Composite.
The metal bars used to assemble the reinforcement cage have a ribbed or smooth surface.
Ribbed rods are used for horizontal (working) reinforcement, as they have an increased adhesion force to concrete, which is necessary for the high-quality performance of their functions.
Vertical rods, as a rule, are smooth, since their task is to maintain the working rods in the desired position until pouring. The diameter of the rods ranges from 5.5 to 80 mm. For private house construction, working rods of 10, 12 and 14 mm and smooth rods of 6-8 mm are used.
Composite reinforcement consists of different elements:
- Glass.
- Carbon.
- Basalt.
- Aramid.
- Polymer additives.
Fiberglass reinforcement is the most widely used.
It has the greatest strength, the most rigid and resistant to tensile loads of all other options.
Like all types of composite rods, fiberglass reinforcement is completely resistant to moisture.
Manufacturers claim constant performance throughout the entire service period, but in practice the validity of this statement has not yet been verified. The problem with composite reinforcement is the complexity of the technology, due to which the quality of the material differs markedly from different manufacturers .
In addition, composite rods are not able to bend, which is inconvenient when assembling frames and reduces the strength of the corner joints of the frame.
IMPORTANT!
Among builders, the attitude towards composite reinforcement is complex. Without denying the positive qualities, they do not put too much trust in little-studied building materials that have not gone through a full cycle of use. In addition, metal reinforcement has very specific technical characteristics, while composite types have a fairly wide range of properties . All these factors limit the use of composite rods.
Range of metal products
Classes of reinforcing steel For reinforced concrete structures, the following reinforcement is used:
hot rolled, smooth or with a periodic profile (ring or crescent) with a diameter of 6 to 40 mm; thermally and mechanically strengthened with a periodic profile, 6–40 mm; cold-deformed periodic section (3–12 mm). It is recommended to use smooth reinforcement with a class not lower than A-240 (A-I). For ribbed (periodic profile) choose class A-300 and higher. In areas where the temperature drops below 30°C, class A-300 is prohibited from use.
It is preferable to use products with a periodic profile - with tides in the form of rings or a sickle. Irregularities increase the adhesion area of the rods to the concrete and the strength of the entire structure.
Recently, composite reinforcement has appeared on sale. The manufacturer recommends using it instead of steel products.
SP 295.1325800.2017 does not allow the use of composite products for foundations.
How to make the right choice
The choice of reinforcing bars is based on design data and builder preferences.
Typically, metal rods are chosen, although composite reinforcement is increasingly used every year in the construction of strip foundations. Preference is given to metal rods due to the ability to give them the necessary bend, which is impossible to do with fiberglass rods .
This is especially important when constructing belts with curved sections or when there are fracture angles other than 90°.
In addition, metal reinforcement is more economical, as it allows you to make clamps from a single rod, without the need to create several connection points .
The diameters of the rods have long been worked out in practice; they are often chosen without preliminary calculation - for a tape width of about 30 cm, a 10 mm rod is used, for tapes 40 cm wide, 12 mm rods are chosen, and for a width of more than 50 cm, 14 mm. The thickness of the vertical reinforcement is determined by the height of the tape; up to 70 cm, 6 mm is chosen, and for heights above 70 cm, 8 mm or more .
Purpose of reinforcement
The reinforcement resists loads on the foundation from the soil and the building itself. Strip foundations are a monolithic foundation structure made of reinforced concrete. The base is made directly at the construction site.
Reinforced concrete is concrete, inside of which there is a metal frame made of reinforcement. Metal allows you to withstand lateral loads that create:
from bottom to top - soil heaving processes; from top to bottom the mass of the building. Pure concrete resists lateral loads poorly. Steel embedded inside the structure can make the foundation tens of times stronger.
Under load, each meter of concrete can stretch by 2–4 mm, while steel can stretch from 4 to 25 mm. Concrete withstands compression many times better.