Home » Building a house
Alexander Korovaev 05/12/2020
997 Views
A properly made foundation of a building is the key to its long-term operation. The key to a good foundation for a building is formwork. For a country house or cottage, you can make the formwork for the foundation with your own hands.
Purpose of formwork
The design is designed to prevent liquid material from spreading. Due to the limited space, concrete maintains its given geometry and position in space, dries evenly and acquires the required strength.
Basic requirements for formwork for strip foundations:
- high strength, resistance to the pressure of the liquid mixture inside a given volume and external influences;
- stability of the dimensions of the internal space (the geometry of future base elements);
- the possibility of unhindered pouring of the liquid mixture into the mold, reinforcing the monolithic foundation.
Technical requirements for formwork are collected in GOST 52085-2003, but they relate to industrially used auxiliary structures. For self-installation of formwork, only basic conditions must be met.
Polyethylene film
Used as a waterproofing material. The film is not equivalent, it can be replaced with roofing felt, roofing felt.
Film
It is recommended to use polyethylene film in several cases:
- If after dismantling the formwork you do not plan to throw away the boards. If new lumber was used, it can be used again in building a house. But if traces of cement are found on the surface, it is better to abandon the boards; when cutting, you can significantly dull the knives on the surface planer.
- If a waterproofing layer is installed on the surface of the formwork, it will not be deformed, which means that dismantling will be easier.
Features of different types of structures
There are removable - removed after hardening - and permanent formwork.
Removable formwork for foundation
This name refers to auxiliary structures that are removed after the concrete mixture has gained partial strength. Removable elements consist of panels (solid or plank) and fastening and fixing elements connecting them. If reinforcement is provided (almost always for strip bases), supplies and spacers are added to the standard set to prevent contact of the reinforcement grids with the soil and the inner surface of the pouring forms.
Important: the removal of the formwork occurs before the final curing of the concrete, therefore, when carrying out further work, you should focus on the “maturation” time frame of the foundation, depending on the grade of concrete, weather conditions and the dimensions of the structural elements.
Permanent formwork
Fixed forms are considered to be pouring molds that remain in the building structure after the mixture has cured. This type of structure provides additional strength to the building, its heat, sound and waterproofing properties, and other characteristics. Typically, special blocks made of polystyrene foam, fiberboard and other materials are used as material for permanent structures.
Important: constructing a house using permanent forms significantly speeds up construction, improves the operational characteristics of the building, but at the same time increases the cost of the work.
Tool
You will need regular carpentry tools and some extra ones. Marking tools - marker, water level, building level, plumb line, cord. Hand tools: hammer, hacksaw, carpenter's hatchet, mallet, small sledgehammer, nail puller, crowbar (used for removing formwork), wide “priming” brush (for coating with a water-repellent composition). A small sapper blade will come in handy, but you can also use a regular bayonet blade. If you use self-tapping screws, you definitely need a good screwdriver. Having a chainsaw, electric saw, circular saw or even a jigsaw will greatly facilitate the work.
Calculation of formwork for the foundation
In this case, calculation means the calculation of the required thickness of the boards or boards of the structure, taking into account the distance between the supports, the specific gravity of the mixture being poured and the resistance ability of the mold material. The traditional, simplest formwork design consists of panels installed at the bottom of a pre-dug trench, held in a vertical position by special supports.
The choice between stakes or braces depends on the volume of the mixture being poured and the type of soil: for small foundation strips (250...400 mm) and dense soil that is not prone to shedding or sliding, stakes are sufficient. If in doubt, it is better to give preference to braces, since they are able to hold the panels in place even with increased load.
Formula for calculating the thickness of shields (minimum)
h = √((0.75×G×n×l^2)÷T)
Here
- G is the load of the liquid mixture on the formwork, it is assumed to be maximum and is defined as the product of the specific weight of concrete and the thickness of the poured layer G = qx H. The specific gravity is q = 2500 kg/m3, H is the height of the foundation strip in meters;
- n is the compaction coefficient of the concrete mixture. If vibration compaction is not used, the coefficient is equal to one;
- l – distance between shield supports, in meters;
- T – load resistance of the board material; for wood it is assumed to be 8 x 105 kg/sq.m.
Taking into account the difficulty of independently determining the grade of concrete, respectively, its density, as well as the lack of accurate data on the resistance of the material of formwork panels, calculations are carried out approximately, for average values. Typically, the thickness of the board is taken to be 25 mm.
The second part of the calculation is determining the required number of boards of a given thickness and the number of fasteners. For these calculations, it is necessary to know the length of the foundation strip and the height of the fill. The length of the tape is multiplied by two, since the shields are located on both sides. When installing a strip foundation with a step, the calculation is carried out twice - for the first and second stages of pouring. The amount of lumber is determined based on the data on which board for the foundation formwork will be used (dimensions).
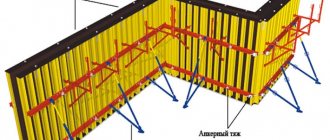
Drawing up a plan similar to that shown in the illustration will help you navigate a more accurate calculation of the required length of the form, the number of connecting and supporting parts.
Step-by-step instruction
Do-it-yourself installation of foundation formwork should only be done on a flat, well-prepared surface - the area should be cleaned to remove all debris. The formwork must be positioned strictly vertically so that the panels are flush against the ground. The inner surface of the boards, which will come into contact with the concrete mixture, must be flat and smooth. If you can’t sand the material, you can stuff plywood sheets onto it - the main thing is that the distance between the parallel panels exactly corresponds to the designed width of the future foundation wall.
When knocking down panels, the boards need to be adjusted to each other in such a way that there are no gaps between them, especially if it is planned to vibrate the concrete mixture with special devices for better shrinkage.
Cracks measuring 3 mm or less will go away on their own after the material swells during preliminary wetting. If the configuration and quality of sawing the boards do not allow the boards to be knocked down without significant gaps, then gaps of more than 3 millimeters must be caulked with tow, and distances of more than 10 millimeters will need to be additionally filled with slats.
Correctly assemble the formwork for a strip foundation up to 0.75 meters high by fastening the guide boards. They are fixedly fixed in the ground using fastening pegs. To make an accurate installation, you should first stretch a rope around the perimeter of the future foundation and secure it at both ends. Having installed the guide boards, you should make sure that they are installed correctly - use a level to check that they are level and there are no deviations. Then you can begin installing the formwork panels, and the plane of the panels must exactly coincide with the edge of the guide boards.
Formwork, as a rule, is driven into the ground using pointed bars, which connect the boards to each other, forming shields. It should be taken into account that the concrete mass will exert strong internal pressure on the structure, therefore, to prevent the shields from moving apart at the bottom, additional pegs must be driven into the ground. Their exact number will depend on the width and height of the foundation, but in general, experienced builders recommend using pegs at least every meter.
If the height of the future foundation does not exceed 20 centimeters, then pegs from connecting bars alone will be enough. When the foundation is higher, it is necessary to use additional external stops - bars of a certain length, which are set diagonally at an angle.
One end of such a block rests on the upper part of the formwork wall or on a peg and is secured there with a self-tapping screw. The second end rests firmly on the ground and is slightly dug in (in these places you can hammer in another pegs that will hold back the persistent bars so that they do not jump off and bury themselves in the ground).
Step-by-step instructions for assembling and installing foundation formwork with your own hands:
- on a prepared, level base, the boards are laid close to each other;
- transverse slats or bars are placed on top, which will connect the boards to each other, and are fixed with self-tapping screws (the distance between the slats is at least 1 meter);
- You need to screw in the screws from the inside so that their heads are buried in the board, and the ends stick out on the other side by at least 1-2 centimeters; these ends should be bent;
- the finished panels are mounted on the edge of the trench - they are driven into the ground using pointed connecting bars and attached to the guide boards with wire twists;
- Additional vertical stakes are driven close to the shields, which are connected to the shields with self-tapping screws;
- horizontal (laid on the ground) and diagonal struts are attached close to the stakes, which on the other side are fixed with the help of another peg driven into the ground;
- Experts recommend connecting the panels to each other, using additional jumpers in the upper part, they will not allow the structure to move apart when pouring the concrete mixture.
To learn how to make wooden formwork for a strip foundation with your own hands, see the following video.
Do-it-yourself formwork for a strip foundation
In order to correctly form the base of the building, it is necessary to correctly install the base for pouring. We will analyze two design options, based on removable wooden and permanent foam formwork.
Regardless of what type of form is used, part of the work performed is carried out according to a single scheme.
- Site marking. It is done using stretched cords or fishing line (in the illustration “cast-off strings”) according to the building construction plan.
- Digging a trench. In this case, it is necessary to dig out a ditch according to the depth of the future foundation, taking into account the cushion under the foundation and the depth of soil freezing (you can read in more detail about the principles of constructing a foundation and preparing a place for it in the article). Since creating strictly vertical walls is practically impossible, they try to create a slope with a minimum slope, about 15...30 degrees to the vertical.
- Compaction of soil at the bottom and walls of the ditch. Tamping is done manually or using special mechanisms. This process is especially important for loose soils. Tamping can be replaced by the use of geotextiles - a special material that prevents soil shedding.
- Creating a foundation cushion. For it, sand of large (1...3 mm) fractions, fine crushed stone or granots, pre-washed and dried, is used. To enhance the load-bearing capacity of the base, the cushion is poured with a liquid cement mixture; in especially critical cases, concreting is performed.
- The formwork is being installed. Slots and gaps between structural elements should not exceed 2 mm, the strength of the structure should correspond to the required one, taking into account the thickness of the poured layer.
- The fittings are being installed. The installation of rod systems and meshes is planned with the obligatory preservation of the protective layer of concrete from the metal to the external environment. You can read more about the rules for tying reinforcement and its protection against corrosion in the feature article.
- Pouring concrete mixture.
- Vibration compaction (if possible).
Depending on what type of forms is used, the nuances of the technological process of installing the formwork and, in the removable version, its removal change.
Installation of formwork from boards or plywood
Due to the successful combination of load characteristics and price, edged boards for foundation formwork are the most popular and popular option. The wood used is water-resistant species (pine, alder, birch) with an initial moisture content of 18...25%. Boards made from boards are assembled using bars on nails or self-tapping screws. In this case, the points of the fasteners should extend to the outer (facing the ground) side of the boards.
The knocked down panels are installed on the prepared cushion, reinforced with braces or stakes with a pitch of 800...1000 mm. To prevent the structure from spreading under the weight of the poured mixture, the opposite panels are connected by spacers.
As an option, first a box is mounted on the base of shields and cross braces, after which the finished structure is laid in a trench and fixed with stakes.
Important: there should be no gaps between the boards! Otherwise, the solution will begin to flow into the gaps, and the consumption of concrete will noticeably increase. Possible formation of voids inside the poured form, violation of the strength calculations of the foundation.
Proper formwork can easily withstand the pouring of concrete mixture and is easily separated from the hardened base after initial curing. The period for stripping (removing formwork), depending on temperature and humidity conditions, is 8…20 days. At subzero temperatures, it is undesirable to disassemble the form-building structure, since the time it takes for concrete to gain design strength slows down in proportion to the decrease in temperature.
How to assemble formwork for a foundation from foam blocks or panels
Industrially produced foam blocks or panels are manufactured with their own tongue-and-groove fastening system. Thanks to this, connecting the elements of the future form is not difficult:
- the first row is laid according to the markings so that the line is perfectly straight;
- the second and subsequent rows are mounted taking into account the location of the reinforcing bars - they must pass strictly through the cavities in the blocks. For panel options, displacement is allowed;
- concrete is poured only by hand, after installing every three to four rows of foam blocks.
Important: low-quality (crumbling, irregularly shaped) blocks are only suitable for low-impact buildings with low loads.
If you want to create permanent formwork with your own hands, you should choose the option with a two-layer structure. The outer layer is a sheet material that defines the geometry (as is the case with removable formwork), the inner layer is sheets of foam plastic or expanded polystyrene. Concrete is poured into the cavity between the internal heat-insulating layers, which are not subsequently removed. The outer layer is dismantled after the mixture has cured.
Telescopic stands
Vertical timber supports can be replaced with telescopic racks. A formwork system using height-adjustable racks significantly saves formwork installation time. Telescopes are simple and easy to use.
This stand is based on a metal pipe that extends like a telescope in increments of 10-17 cm. The stand contains:
- outer and inner pipe;
- threaded element for tensioning;
- staples;
- thrust bearing
Telescopic racks are used to create formwork at a height of up to 5 m. Operating principle: first, the thrust bearing is firmly fixed, then the inner pipe is raised to the desired height and fixed. The larger the diameter of this kind of jack, the higher its load-bearing capacity.
The optimal solution for a small house is to rent a fully equipped telescopic formwork system. The landlord will always help you correctly calculate the need for all formwork elements.
The cost of materials for rent is usually determined by the floor area. For a small construction site not very far from the lessor, the cost per square meter of fully equipped telescopic formwork varies in the range of 10-15 rubles per day of rental. With a non-standard floor configuration, the developer may have to purchase additional materials for the flooring.
Important! The installation step of timber supports is 50 cm, telescopic posts can be located in increments of 1 meter. This small nuance gives a good economic effect when using “telescopes” - they require half as many.
In addition, when using timber, illiquid scraps will certainly be formed - metal racks are not damaged and do not lose value after dismantling.
Nuances of formwork installation for different types of foundations
In low-rise private construction, a strip base is the most common option. However, he is not the only one. Slab and columnar foundations are also used.
Formwork for columnar foundations
In this case, in addition to the general trench, deep holes are dug for columnar supports. They are located along the perimeter of the future building so that there is a support at each corner or intersection of the walls.
The formwork itself is also made from boards, plywood or other sheet materials using the technology described above. The difference is the arrangement of the limiting elements in the form of a vertically located tetrahedral prism (a column of rectangular or square cross-section) or a cylinder. Filling is done from above. Reinforcement of a columnar foundation is carried out separately for each support, followed by piping.
In this case, the column has either the same cross-section throughout its entire height, or an enlarged lower step.
It is mandatory to place a cushion under the foundation supports; the lower step can be poured into the ground without formwork, but at the same time reinforced. Formwork is installed for the upper part of the support, and the reinforcement of the upper and lower parts is tied together. Supports that are simple in shape and have a limited load can be concreted without reinforcement.
If it is planned to install a monolithic grillage on top of a columnar foundation, the formwork for it is carried out separately, in the form of a box.
Formwork for foundation slab
The main difference between this type of limiter is its one-sided arrangement: the shields outline the shape of the future slab along the outer sides.
Important: when installing this type of formwork, you should be more careful when calculating the strength of the structure, since the load on the panel stops increases in proportion to the size of the slab.
Foam blocks are not used as permanent formwork for slab foundations. If it is necessary to make the limiters non-removable and at the same time use them to insulate the base, use flat sheets of foam or polystyrene.
Installation work
It is convenient to mark the formwork on the building site using pegs and stretching a construction cord or fishing line along them
It is very important to remember that the foundation should be 10-15 cm wider than the walls. Each action should be checked with a level and a laser level - this way you can ensure the most even placement of the formwork panels
It is possible to position the formwork correctly only by using a level, which should be used to periodically check for possible displacement of the panels during installation.
You can start installing the boards only on level ground, securing each board with scraps of reinforcement and wooden support pegs. The panels are secured from the inside with reinforcing rods - after concreting, the reinforcement will serve as an additional reinforcement element to impart vertical rigidity. Watch the video on how to install formwork without mistakes.
The lower edges of the formwork panels should rest completely on the upper surface of the ground, and adjacent elements should have the closest possible fit to each other.
The side panels are tightened using special ties made of timber, which are strengthened on top of the formwork panels from above. Screeds are installed every 0.5 - 1.0 meter.
Materials
For foundation formwork, different building materials are used. They affect the quality of the building’s foundation and the speed of its construction. They also determine whether the concrete form can be reused.
Removable formwork for the foundation is dismantled when the concrete density reaches 50%. Usually it is used repeatedly. The number of fills that a set of panels can withstand depends on the characteristics of the building material from which they are made. Homemade structures perform their function well 3 to 8 times. Industrially produced formwork does not lose its strength after several dozen pours.
The permanent structure cannot be dismantled after the concrete solution has hardened. It turns into part of the base. The use of such models in construction began several years ago. The material for the production of parts is extruded polystyrene foam.
Note! An alternative material for the production of a non-dismantled structure is concrete blocks with voids inside. They can be corner, radius, or wall. Each part consists of two or three walls, fastened together by jumpers. They are connected in pairs with locks. To make the base strong and rigid, reinforcement is placed in the concrete solution.
Metal
This design is universal. It is suitable for formwork of monolithic construction and construction of the foundation for a private house. The structure is assembled from metal sheets 1-2 mm thick. This form is used to create a strip or slab type base. To increase rigidity, the reinforcement is welded directly to the formwork sheets. If necessary, metal sheets are bent to give them the desired shape. The main disadvantage of the metal version is the high price.
Reinforced concrete
Here, concrete slabs are used to form the base. It turns out to be inseparable. When a structure is constructed from parts of large thickness, the consumption of cement mortar is reduced. The strength of the base and other important characteristics do not deteriorate. Installation of concrete slabs is impossible without the involvement of a construction crane due to their heavy weight.
Made from polystyrene foam
The shape of the blocks varies. The formwork of the future foundation is assembled from them, as from parts of a construction set. They are connected to each other with metal pins or locks. This design is convenient in that it simultaneously provides hydro- and thermal insulation of the base. Expanded polystyrene blocks are expensive, but they reduce the time for constructing the foundation of a building and simplify subsequent finishing.
Made of wood
The easiest way is to make formwork for the foundation with your own hands from wooden boards or sheet plywood. These building materials are always on sale and inexpensive. To install the foundation form, you do not need complex tools or construction equipment. But sometimes a homemade structure needs to be reinforced due to the different sizes of wooden panels.
Available materials
To pour the foundation for a small private house or summer gazebo, a form is assembled from any suitable materials. Slate, profiled sheet and other items are suitable. They are used to make a solid structure without gaps. The only advantage of such collapsible formwork is its low price.
The disadvantages of using improvised materials include:
- complex installation;
- high probability of leaks;
- low load-bearing capacity;
- the need to install additional supports.