What it is
Let us answer the question, what kind of fabrics are these that do not burn? Such materials primarily include the long-known, non-flammable asbestos fabric, used at temperatures up to 500℃. Made from the natural layered mineral asbestos, it does not contain combustible organic substances, therefore, in the full sense of the word, it is non-flammable.
On this topic ▼
Workwear and suits with fire retardant impregnation
The second type of fabric from which fire-resistant workwear for welding and protective suits for working in hot shops are made are high-density natural materials made from cotton and linen.
For example, tarpaulin fabric, additional resistance to direct contact with open fire, the high-temperature thermal effects of which is imparted by fire-retardant impregnation with various types of fire retardants.
This fabric is fire-resistant in its properties, as it is capable of resisting flames and high temperatures for a short period, which makes it possible to reliably protect a person wearing protective clothing made from it in the area of direct contact with negative influence factors.
In addition to these most famous examples, there are many other types of both flame retardant and fire resistant textile materials used in a wide variety of fields.
Fireproof fabric
Where is high-temperature thermal insulation used?
In construction practice, high-temperature insulation finds many applications. Moreover, the necessary thermal insulation characteristics will vary in each specific case.
High temperature insulation of a heating boiler or furnace. This is especially true for models running on solid fuel. Often their surfaces heat up to significant values. Therefore, to insulate them, materials that can withstand the highest temperatures are used (fiber cement boards, mineral wool, etc.
Chimney protection. Here, the insulating materials must be flexible to simplify installation. Rolled materials (metal foil, mineral wool) best meet this requirement.
Types and characteristics
Depending on the component that is the basis for the production of non-flammable or fire-resistant fabric materials, the following types of fabrics are distinguished:
Silica
Also called silicate, quartz. They are made from SiO2 - silica (silicon dioxide), quartz, and other silicates. Such materials work stably up to temperatures of 1250℃, breaking down only above 1700℃. They have a low thermal conductivity coefficient, high electrical insulating properties, and are environmentally friendly.
Fiberglass
These are materials that can withstand short-term heating up to 700℃, sudden cooling down to -200℃, and constantly operated at temperatures up to 550℃. Distinctive characteristics - low weight, high tensile strength, low coefficient of linear expansion, dielectric properties; resistance to ultraviolet radiation, moisture, microorganisms.
Basalt
Made from basalt fibers by melting it. Withstands temperatures up to 700℃. They also produce non-woven fire-retardant basalt material used for structural fire protection of metal structures and filling openings in fire barriers.
Asbestos
Obtained on the basis of fibrous material - asbestos, in combination with various inorganic additives in order to hide and bind the dangerous carcinogenic effects of this natural material when its dust is inhaled.
Carbon
They are produced by weaving from threads made from pure carbon fibers. They are lightweight, stretch-resistant, can withstand temperatures up to 370℃, but are still capable of linear expansion.
Aramid
These are the most innovative fabrics made from polymers - aromatic polyamides. They are extremely durable, even going so far as to make bulletproof vests out of them; resistant to fire, intense heat up to a temperature of 400℃.
Polyester
Made from polyester threads with a high content of phosphorus compounds. When exposed to open fire, they do not ignite, do not melt, and become charred and decrease in size.
As well as various types of sewing and finishing fabric materials subjected to fire retardant treatment by dipping and spraying fire retardants. After such impregnation, it is difficult to set them on fire with low-calorie fire sources; they do not burn, but become charred.
Protective screens near or around the oven
Such a system will need to be implemented when installing a potbelly stove in the corner of the room. You can mount or lay out several screens from brick, installed at a short distance from each other. In this case:
- The first screen protects a person from touching the iron stove and getting burned. It is usually made of refractory or fireclay bricks;
- To protect walls made of flammable material, a second layer of protection is provided. It can be made of brick or covered with a barrier made of sheet steel with a mirror-like front surface. In this case, heat waves will be reflected from the mirror and spread faster throughout the room;
- if the foundation is insufficient in size or it is impossible to manufacture it, it will be necessary to lay a protective screen made of durable fire-resistant material on the wooden floor. This can be a sheet of steel or a decorative layer of heat-resistant clinker tiles or porcelain stoneware. The surface will first have to be covered with a layer of thermal insulation.
Installation of metal screens
This is the easiest way to make surface protection. It is better to use sheets with a polished front surface. Before fastening, the wall surface at the required level along the height of the screen is covered with a layer of thermal insulation. In this way, we protect the surface of the walls from the effects of heat.
You can lay a layer of thermal insulation or fasten the metal with self-tapping screws with inserted ceramic spacers. But it is better to attach the screen to strips or a metal profile treated with a layer of protection. In this option, the air gap will not allow heat to pass freely to the walls, and reliable insulation of the stove from the wooden wall is ensured.
A special gap is made at the bottom of the wall for the passage of cold air, ventilation of the wall and screen. When arranging a wall with a layer of thermal insulation, a number of longitudinal guides are installed on the surface. The space between them is filled with a layer of mineral wool or other material. Then sheets of metal are installed and screwed to the sheathing with self-tapping screws.
In this design, there is no need to leave a gap at the bottom. The air will not be able to pass through calmly, but the wall will be reliably protected from high temperatures. To protect the floor of the house, a slab made of non-flammable durable material can be used.
Brick screens
This protection option is usually installed near the stove. Thus, you can protect not only the wall, but also the person from burns. By installing a brick wall, you can reduce the distance from the stove to the wall. For laying, it is better to use ceramic or fire-resistant bricks.
The work is carried out in several stages:
- you will need to make a small foundation or remove boards from the floor along the marking lines for laying the screen and, by drilling holes in the concrete of the base of the building, insert metal rods to fasten the bottom of the wall and the foundation;
- Having leveled the floor surface, lay out a layer of mortar and lay the first row of bricks; you need to place the bricks in the same plane without distortions. This determines how level your entire wall will be. Do not forget to make small grooves for ventilation; for this you can move several bricks of the bottom row.
- checking the level and pulling the twine for laying each subsequent row, all bricks are laid on a mortar of clay and sand. Having raised the wall to the required height, the top is sealed with a layer of mortar or covered with a board. This way you can make a shelf for decorative ornaments and all sorts of little things.
The brick is laid no higher than the top of the furnace at a distance of at least 40-100 mm from it.
Using both types of protective screens, you can reduce the distance from the oven to 500 mm.
Examples of installation of protective brick screens in the photo:
Photo 1
Photo 2
Photo 3
Requirements
At the time of writing, there are no national standards defining the production of non-flammable, fire-resistant fabrics that do not burn well. Therefore, companies that produce this group of textile materials themselves develop technical specifications that regulate the entire production process.
In addition, specifications are a mandatory document provided by the manufacturer for certification fire tests of serial products, necessary to obtain a fire safety certificate.
Testing non-flammable fabric for flammability
Requirements and test methods relating to the main characteristic - the flammability of fabrics - are set out in the following fire safety standards:
- GOST R 50810-95, which classifies decorative textile materials based on the flammability test method.
- NPB 257-2002. This document regulates testing methods for flammability, smoldering, flame sustained and residual combustion of textile materials - curtains, drapes, bedding, upholstery.
Such tests involve exposing selected tissue samples to the flame of a laboratory gas burner or a smoldering cigarette; and the results obtained objectively show how well their fire protection treatment was carried out with fire retardant solutions.
Oxygen index
The oxygen index is a fire safety characteristic of a material, which shows the minimum amount of oxygen per unit volume of insulation. According to the oxygen index, there are several flammability thresholds:
- 40% - composite polymers;
- 31% - fibrous and cellular non-flammable insulation;
- 20% - materials that burn well in air.
Purpose
Fabric materials based on asbestos, due to its carcinogenic properties, are practically no longer used in the production of fire-retardant elements of overalls for firefighters and metallurgists, but are widely used as asbestos-technical, fire-resistant heat-insulating products, including in aggressive chemical environments.
Polyester, as well as some varieties of aramid fire-resistant fabrics, serve as the starting material for curtains used for the stage of theaters and clubs; for restaurants, hotels. Wherever there are a lot of people constantly or regularly, there is a possibility of draperies, drapes, curtains coming into contact with ignition sources.
On this topic ▼
Fire retardant impregnation: requirements and procedure for processing materials
Furniture manufacturers also use these types of fire-resistant fabrics as furniture upholstery, which cannot be set on fire by a fallen smoldering cigarette.
For mittens included in the sets of special clothing for firefighters, workers in hot shops of metallurgical and energy production, carbon, silica, basalt fire-resistant materials are used, as well as fiberglass, which is the surface layer of both hand protection means and workwear in general.
Special clothing and suits with fire-retardant treatment are also made from linen and cotton fabrics of high density and thickness of the material.
They are used by gas and electric welders, blacksmiths, boiler house workers, hot shop workers of other industries.
Technology for installing refractory materials for finishing walls around the stove
Let's consider the technology of lining the stove in the bathhouse.
Flamm mineralite fireproof board
The principle by which wall cladding is carried out near the heater is the sequence of actions:
- Initially, a layer of vapor barrier and waterproofing is fixed to the wall made of combustible material. As the first, you can use a three-layer film, which consists of foil, polyethylene, and kraft paper. These materials provide strength. The film is fixed using a metal profile.
- At the next stage, insulation is placed, for example, you can use mineral wool. It needs to be placed inside the sheathing so that the foil layer is on top. The joints of the wool boards must be sealed with aluminum tape.
- Using self-tapping screws, fire-resistant boards, for example, made of fiber cement, are attached to the sheathing. An alternative option is to install the plates on self-tapping screws through a sleeve. This creates a space between the wall and the slab.
- After the slabs are fixed, they can be faced with ceramic tiles. So, the appearance will be more attractive. To do this, a metal mesh is screwed to the plates with self-tapping screws, onto which heat-resistant glue is later applied. This is how the tiles are attached.
Thus, finishing the walls around the stove or fireplace with fireproof materials will protect your home.
Application area
Fire-resistant fabrics/mats are made from fiberglass and asbestos fabrics, which are an effective means of extinguishing small-area fires in fire-hazardous industries during hot work.
Silica, basalt fabric, non-woven materials are used:
- For thermal insulation of heat-generating units, pipelines, including those transporting flammable liquids. For example, for a pipe for supplying heating oil to a boiler in a thermal power plant.
- For flow filtration, as a filler for fire arresters when transporting flammable liquids.
- As fire-resistant heat shields in metallurgical shops and gas-electric welding production areas.
- In the production of roller fire curtains, screens, curtains.
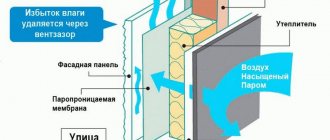
- In construction, as non-flammable breathable membranes, floor insulation coatings; wind protection, vapor barrier of roofs, building facades.
Aramid, hydrocarbon fabrics, being less resistant to fire, more expensive compared to silica, basalt fiberglass materials, are less common, but are also used as inserts, elements in the production of workwear, and for technical production purposes.
Texture of fire-resistant fabrics for curtains
Right choice
The choice is based on the scope of application of the insulation. Thus, basalt wool is relevant for insulating roofs, walls, ceilings and facades, as fire protection for ventilation and building structures, pipelines, baths and saunas. Foam glass is an excellent non-flammable insulation for chimneys; it is appropriate to use it for insulating roofs, walls, ceilings and fire-resistant structures.
If you want to insulate an apartment with foam glass, then you need an L-shaped bracket, an anchor, which will help secure a layer of blocks to the plastered wall (ceiling). Fiberglass is applicable for insulating attics, roofs, walls, floors along joists, partitions and interfloor ceilings, saunas and baths, walls behind radiators of central heating systems.
Trade marks
There are many types and brands of both completely non-flammable and fire-resistant fabrics on the market:
- Tend building fabric is a non-flammable material that corresponds to group NG, hazard class KM0. It is used as a steam-, wind-, and heat-insulating material for ventilated facades, roofs, and floors of buildings. The material is resistant to moisture, aggressive environments, sudden temperature changes, and exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- Thermally resistant silica fabric KT-11 . SiO2 content – up to 99%. The main qualities are fire resistance up to 1200℃ (long-term), strength, dielectric, environmental properties, which makes it a multifunctional material.
- Basalt fabric TBK-100 coated with metal foil. The operating temperature range is from – 200 to + 650℃, melts at 1100℃. Used in the production of rolled roofing materials as thermal insulation.
- Izoltex fabric is made from fiberglass. Operating temperature – up to 560℃, maximum short-term – 700℃. It has excellent thermal insulation properties, is chemically inert to strong organic and mineral acids, concentrated solutions of alkalis. An excellent substitute for asbestos fabrics, used in construction and various industries.
- Kevlar, Arcelon, Terlon, Kermel, Nomex are various trademarks, names of types of aramid fabrics that are thermally resistant in the range from 250 to 400℃.
For fire-retardant treatment of natural fabrics, the following impregnations are used: “Negorin-fabric”, “OGNEZA-PO”, “Nortex”, “ANTAL TM”, which do not change their appearance, do not reduce strength, and do not have an unpleasant odor.
Important: for each batch of such products, regardless of the volume of the batch, the customer (buyer) has the right to demand a fire safety compliance certificate, which specifies all the necessary characteristics.
Types of high-temperature thermal insulation
The division into types of high-temperature insulating materials is carried out according to the method of their production and the composition of the ingredients. Currently, on the market you can find both thermal insulation with a long history of use, as well as new products.
- Expanded clay. Bulk material has a rich history of use. Currently, it is most often used only as a filler for composite materials.
- Mineral wool. It is obtained by melting threads from mineral raw materials. It is gradually disappearing from the market due to its fragility and hygroscopicity.
- Foamed concrete. Due to the porous structure, it has a small thermal conductivity and weight.
- Basalt thermal insulation. Universal material. With good fire resistance, it also has sound insulating properties.
Basalt high temperature thermal insulation
There are also less common types: foam glass, high-temperature foams, etc. The specific choice of one or another type of high-temperature insulation should take into account operating conditions and economic feasibility.
Fire rated wall cladding with cladding
If the sophisticated interior does not allow the use of stainless steel cladding, fire walls can be made from cladding with cladding. In this case, the following materials are good camouflage: terracotta or clinker tiles, tiles, porcelain stoneware, soapstone.
Despite the excellent fire-resistant qualities, tiles laid on the wall will not act as a heat insulator. Therefore, it is used as a finishing layer in a thermal insulation “pie”:
- wall;
- ventilation gap (2-3 cm);
- fire-resistant material (minerite, glass-magnesium or fire-resistant plasterboard sheets);
- tile.
The distance from the tile to the stove body must be at least 15 cm.
Finish options
It is necessary to create heat-insulating structures or apply coatings of this type when the distance from the walls of stoves or fireplaces to the protected surface is less than the established standards. They are as follows: from the walls to the surface of the stove made of brick there should be at least 32 centimeters, to the heating device made of metal - at least a meter, and to lined metal fireboxes - at least 70 centimeters. In other cases, fireproof material is needed to decorate the walls in the place where the stove is located and underneath it. You can complete the design with the following types of coatings:
- Reflecting heat into the room. As a rule, this role is played by a stainless steel sheet or a special heat-insulating screen made of the same factory-made stainless steel.
- Protecting the surface due to its characteristics - physical and chemical. There is more choice here - fire-resistant gypsum plasterboard, mineralite, glass-magnesium sheet, various ceramics and porcelain stoneware slabs.
Both finishing options are quite effective, but mixed-type structures are often used, including both a reflective coating and an internal fire-resistant layer. These are the solutions that are used most often and provide the highest degree of insulation.