What is the best foundation for a bathhouse, choosing the best option, tips for saving money and quality construction. A bathhouse made of logs or solid timber is a relatively light-weight building that requires a reliable foundation raised above ground level. With the right approach, the type and parameters of its foundation are justified by calculations that take into account the nature of the site's topography, the bearing capacity of the soil, groundwater level and other factors influencing the durability of the foundation. The optimal characteristics for such buildings are pile and strip foundations, which can be built on your own if desired.
Depending on the bearing capacity of the soil
This indicator is considered the main one and depends on the composition and size of soil particles, the degree of its compaction and moisture saturation.
Soils with high bearing capacity (coarse and medium sands, dense gruss, gravel and rocky soils) are suitable for the construction of any type of foundation for a bathhouse, including budget columnar and prefabricated strips of concrete blocks. If there are small and weak particles in the soil (water-saturated sandy loam, plastic clay, fine sand, peat), the foundation under buildings swells and moves during periods of freezing and thawing. The requirements for the stability of the foundation for a timber bathhouse in such cases increase significantly. In particular:
• When constructing on clay soils that are stable only in a dry state and have a bearing capacity of no more than 1 kg/cm2 when saturated with moisture, the lower part of any type of foundation must be buried below the freezing level. • When constructing a bathhouse on peat bogs with high humidity and silty-clayey soils, only pile types of foundations resting on stable and dense layers have suitable characteristics. • When laying buildings on sandstones, the type of foundation depends on the size of the sand fractions and the density of the soil layers. Sandstones with particles of about 1-2 mm have a load-bearing capacity of at least 4 kg/cm2 and are suitable for the construction of any type of foundation; less than 1 mm require a slab or pile foundation.
Of particular danger are quicksand soils , consisting of a mixture of flakes of plastic clay and fine suspensions of clay. Due to the strong risks of horizontal soil shifts in such areas, the construction of residential and commercial buildings is not recommended in principle. The problem can only be solved by a stable pile-screw foundation with a support length of at least 3 m or a complete replacement of the soil in the pit.
Block subtype
The type of such base differs in its manufacturing technology and raw materials. Cement mortar is poured into the finished trench, and brick or rubble blocks are placed in it, held together with cement mortar. This subtype of foundation makes it possible to use a smaller volume of solution.
Due to the fact that the blocks can be laid with gaps, an intermittent foundation is created, which has noticeably lower shrinkage rates. This leads to the fact that the mass of the bath can be increased by 20-30%. Thus, a shrink-wrapped bathhouse made of timber will be more reliable and durable.
It is worth noting that all types of strip foundations should not be laid in heaving and watery soils. They are also more difficult to install than pile foundations.
From the terrain of the site
When constructing on flat areas, the type of foundation can be any; in other cases, the method of laying it depends on the angle of inclination.
In areas with a slope of no more than 20 cm on one side of the bathhouse, it is advisable to lay prefabricated or monolithic tapes - after simply leveling the bottom or local deepening of the trench. According to the technology, such tapes must be protected from precipitation and ground moisture using drainage pipes and water collection and drainage systems. The structures are heavily reinforced, and the soil for backfilling, if necessary, is changed to a more dense and frost-free one.
For medium and high slopes, the lowest point of the site is taken as the base level. The costs of excavation work and pouring a solid monolithic tape in such cases are too high; the problem is solved in two ways:
• laying stepped shallow structures (permissible only when constructing on stable, non-heaving soils); • construction of a pile foundation.
The last option is considered the only possible one if it is necessary to build a timber bathhouse on uneven areas with weak soils.
If necessary, piles are used as additional supports and combined with strip or stepped structures. In particular, such a need arises with a complex configuration and large weight of the bath.
But in most cases, the problem of an uneven area is solved by laying ordinary piles resting on dense layers and tied with a channel or reinforced concrete grillage.
Preparing the site for the foundation
The choice of location for a bathhouse directly depends on the conditions of water supply and sewerage. A convenient place to build a bathhouse will be a flat area with a slight elevation relative to the outbuilding at a distance of 15-30 m from an artificial or natural reservoir. Regardless of the type of foundation, the site must be carefully marked and leveled, having previously assessed the density of the soil.
After preliminary marking and leveling of the site, you can determine on which foundation it is better to build a bathhouse. If the soil is strong enough with a low level of groundwater, then the choice of foundation type is determined only by the material used to make the walls of the building and their weight. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the weight of the roof and seasonal snow load.
To level and pre-mark the site for the construction of a bathhouse, the following tools may be required:
- marking pegs;
- marking cord or wire;
- theodolite;
- rail;
- shovels and bayonet shovels;
- scrap;
- ax or chainsaw;
- roulette.
From the height of groundwater
Saturation of the soil with moisture, in addition to the obvious negative impact on building structures (corrosion, increased aggressive effects of mineral substances, erosion and freezing of the sole, dampness in basements and underground) sharply reduces its load-bearing capacity.
The only exceptions in this regard are coarse and gravelly sands with a constant resistance to weight loads of at least 4 kg/cm2. The high degree of moisture saturation of the soil in the areas is usually explained by the close occurrence of aquifer veins and is leveled in one of the following ways:
• Placing a drainage system around the perimeter of the bathhouse with a shallow strip foundation. • Installation of a pile-screw foundation with piping above ground level. • Laying an insulated Swedish slab with a high base.
The latter option is rarely chosen when building log baths due to the high cost of materials and the large amount of work. Investments in a pile-screw foundation (if necessary, with enhanced anti-corrosion protection of the supports) and systems for draining water from the building, on the contrary, always pay off when the groundwater level is high.
Design features of the bathhouse
The bathhouse is an auxiliary outbuilding and has a number of design features. In particular, when building a bathhouse, the issues of water supply, sewerage, power supply and heating should be taken into account. The mode of operation of the bathhouse should also be taken into account - year-round or seasonal. A summer bathhouse requires lower costs for its construction and operation, and for year-round use of the bathhouse, special attention must be paid to the thermal insulation of the building, as well as protecting the water supply and sewerage from freezing.
The material used to build a bathhouse is timber, logs, brick, stone or foam block. For a summer bath it is permissible to use a frame base with lumber covering the walls. Internal partitions can be made of timber, thin logs, boards or fibreboards. When installing a bathhouse, special attention should be paid to fire safety rules and waterproofing of wooden walls. Another extremely important point is the organization of proper ventilation to remove fuel combustion products in the furnace.
Based on the size of the bathhouse, the weight of the walls and stove, location, soil quality and climatic characteristics of the region, the foundation for the bathhouse is laid. Which foundation is better, cheaper and easier to make is determined during the development of the project, carrying out engineering surveys and drawing up estimates.
You can determine on which foundation it is better to place a bathhouse after deciding on the size of the building and the material for its manufacture. Particular attention is required to checking the quality of the soil, determining the groundwater level and freezing depth. The depth of foundation laying, in addition to soil density, is also determined by the groundwater level and the depth of freezing of the ground in winter.
Depending on these parameters, the foundation depth can range from 50 cm with dense soil, low groundwater levels and shallow freezing depth, to 100 cm or more with large freezing depths and high groundwater levels. The groundwater level and freezing depth can be determined by laying a test pit in summer and winter. To prevent swelling of the foundation, the foundation is laid below the freezing depth of the soil.
Metal and concrete screw piles
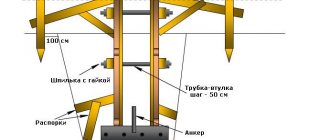
On weak, wet, uneven and prone to crumbling soils, the only correct solution is to lay a pile-type foundation under a timber bath. Such work is carried out using special equipment (in case of high soil density and long supports) or independently using devices for screwing metal piles or hand drills for preparing holes for concrete pillars. The technology for constructing a foundation from screw piles is recognized as the most effective and fastest. When implementing it, a simple algorithm of actions is carried out:
1. The pile field is marked according to a pre-drawn diagram , with pegs driven in in the right places and the level checked using a cord and a laser pointer. Supports are laid in the corners and under all load-bearing structures of a wooden bathhouse, including stove foundations, in increments of no more than 2 m. If the bathhouse is heavy and the soil has low load-bearing capacity, the piles are screwed in not only around the perimeter, but also under the building itself, followed by tying it with metal or timber .
2. In the marked places, pits up to 50 cm deep are prepared. After this, piles are screwed into them using a screw device placed on the top of the metal support. Thanks to special blades or pointed ends, problems with twisting metal piles under a bathhouse do not arise; the need to use special equipment arises only in extreme cases (the presence of large debris in the ground or construction on peat bogs).
3. After screwing in and checking the evenness, the piles are cut to a height of 20-40 cm and filled with concrete. At the same stage, threaded rods with a cross-section of at least 15 mm are installed in their upper part to hold the timber frame, or metal caps are welded for subsequent fastening of the channel.
Advice! When pouring concrete into a pile, it is best to additionally reinforce the pile with reinforcement (three rods connected to each other)
Advice! The most problematic node in a metal pile is the point of contact with the ground, this is where corrosion begins, so additionally treat this place with an anti-corrosion compound.
Advice! After welding, paint all welded areas to prevent corrosion.
Advice! Choose only high-quality piles. The blades of the piles play an important role, they are the ones who transfer the load to the ground, so when twisting, make sure that the blades do not damage. This will be indicated by easier twisting of the pile; such a pile definitely needs to be replaced, as it will sag under the weight of the structure.
An alternative to metal piles are driven or vibrating reinforced concrete supports . This option is considered reliable, but expensive due to the need to use special equipment.
When constructing on wet soils, supports need enhanced protection from corrosion or the aggressive effects of groundwater. Under such conditions, metal piles are pre-treated on the outside with protective compounds, while concrete piles have a higher water resistance grade or are coated with bitumen.
Attention! No matter how much you might think that driven concrete piles are a more reliable solution, this is not the case at all. I’ll explain why: the concrete pile has a point at the end and the area of contact with the soil under the pile is much smaller. The likelihood of such a pile subsiding is much higher than a screw pile made in compliance with installation technology.
Screw piles bath
Monolithic base.
This is a floating base, poured with concrete over the entire area of the building, a good option for rectangular structures on heavy soils of heaving, weak-bearing or bulk nature. This is a reliable and durable foundation, the thickness of which should be from 30 cm.
A trench 60 cm deep is dug for it and filled with crushed stone and sand, which are repeatedly watered with plenty of water to allow them to shrink. After installing the waterproofing, reinforcement and formwork are done to strengthen the base.
What is the best foundation for a bathhouse?
After pouring concrete, the monolithic foundation is held under wet sawdust or burlap.
Poured piles when working independently
The function of supports for this type of foundation is performed by:
• thick-walled metal or asbestos-cement pipes, immersed in dug holes with a depth of 2 m or more and filled with sand or lean concrete; • sleeves made of roofing felt with the same depth, filled with good quality mobile concrete and reinforced with metal.
The preparatory work is practically no different from the previous ones: the areas are cleared, leveled as much as possible and marked. The main difficulties arise at the stage of drilling holes, which, according to technology requirements, are laid below the freezing level.
When constructing a foundation yourself, this work is carried out using a hand or gasoline drill, with the obligatory protection of the edges of the holes from crumbling. After this, pipes coated with mastic or fake roofing felt or rolled up sleeves made of dense rolled waterproofing with a reinforced frame are carefully immersed into the holes.
Concrete pouring begins after checking the accuracy of the supports. But according to technology standards, this work is carried out in the warm season and dry weather.
The solution is poured in small portions, without interruptions, with the obligatory removal of air using long pins. At the final stage of concreting, scraps of strong steel wire or anchor bolts are placed in the upper parts of the supports.
Advice! Such a foundation, when executed independently, is the most reliable and inexpensive. But at the same time, it is labor-intensive, since drilling wells is not an easy process and depends on your soil.
Attention! The most reliable solution for this design would be to create extensions at the end of the pile (the so-called TISE foundation) to increase the foundation support area. Such a foundation is suitable even for building a house. But I’ll say right away that it’s easy to say, but in reality, such a foundation is difficult to implement due to soil crumbling, and the Tise drill will not help here.
Poured piles
conclusions
In each individual case, it is very important to take into account the characteristics of the soil, the size of the structure, the quality of the materials used, as well as other factors that significantly affect the reliability and durability of the object. The width also affects the strength of the foundation,
In any case, taking into account such characteristics, you can easily and confidently make one or another type of foundation with your own hands, as a result of which you will get a truly beautiful and reliable bathhouse and enjoy your vacation.
Attention! If you are not confident in your abilities, it is recommended to turn to specialists with experience who will carefully analyze what kind of soil is on the territory and choose exactly the type of base that is most suitable for you.
Regardless of the depth of the bathhouse foundation you choose, the main thing is to use high-quality materials and follow construction technologies.
Shallowly buried belt with floors on the ground
Monolithic reinforced reinforced concrete tape is laid around the perimeter and under the load-bearing structures of a bathhouse made of logs with any number of storeys and successfully withstands movements of heaving soils when the design parameters are justified by calculations. On average, under low-rise bathhouses made of solid wood, strips with a width of 25 cm are laid (10 cm is added to the thickness of future walls made of lumber), a laying depth of at least 50 cm (including the obligatory 15-20 cm sand and gravel cushion), and a height above the level soil from 30 cm.
To avoid errors, the width of the tape is checked by calculation. All expected weight loads, including the mass of both the walls, roof and stove of the bathhouse, and the foundation itself, are compared with the bearing capacity of the soil. If the soil resistance is sufficient, the width of the tape is considered optimal, otherwise this parameter is selected again. After receiving all the dimensions, calculations and preparation of materials, the following are sequentially performed:
1. Clearing, leveling and marking the area . At this stage, the fertile layer of soil under the future building is removed, and the place of the future tape and the trench itself is marked with pegs and a cord.
2. Excavation work, with removal of soil to the design depth, compaction of the bottom, backfilling and compaction of at least 10 cm of gravel and sand.
3. Installation of removable or permanent formwork , taking into account the locations of drain pipes and similar underground communications.
4. Knitting and lowering 2 or 3 contour frames made of ribbed reinforcement with a cross-section of at least 10 cm, installed on special plastic cups to protect the metal from below and a distance from future edges of at least 5 mm.
5. Continuous concreting , with layer-by-layer pouring of the solution, forcing out air every 20 cm and laying bolts for attaching the lower beam to the upper layers. The poured mixture is carefully leveled and covered with polyethylene film, the tape is left alone until the formwork is removed (at least after 10 days) and the concrete has completely hardened (28 days according to technology standards). When carrying out work in dry weather, the foundation is periodically watered with water.
6. Waterproofing the walls of the strip foundation and backfilling the soil.
The method of tying the lower crown is thought out in advance; bolts with bent or expanded bases, embedded in concrete when pouring it, are best suited for these purposes. At the tying stage, the tape is leveled, if necessary, with mortar or a grinder and covered with at least 2 layers of rolled waterproofing. Corner and stressed areas are additionally reinforced with metal, the final screwing of the studs is carried out after checking the level and tightening all weak points.
The installation of floors in a wood-burning sauna usually begins after the walls have been erected. In the simplest version, a ventilated board flooring (ideally insulated) is installed in the bathhouse. But when planning to lay floors with tiles or high requirements for durability, the floors are poured with concrete over the ground, with a multi-layer insulated screed laid. There is no need for lags in such cases, but the work as a whole becomes more complicated.
Mandatory technology conditions include:
• Removal and removal of fertile and unstable soil layers. • Thorough compaction of the soil base. • Backfilling and compaction of layers of gravel and coarse sand with a thickness of at least 5 cm. • Ensuring a mandatory 10° slope of concrete floors in the washing room using special frames, beacons and a dry ladder. • Protecting the screed from leakage and freezing in winter using rolled materials, expanded clay, foam glass or compacted polystyrene foam boards. • Use of high-quality concrete with a grade of at least B12.5 and reinforcement of the floor screed with metal mesh. • Installation of a thin damper layer around the perimeter of the bathhouse in order to eliminate the risk of cracking of the floors. • Covering the screed with moisture-resistant flooring materials, impregnations or removable wooden flooring.
Shallow recessed tape
Let's start construction
Having become familiar with a certain lyrical digression, you can begin to study the practical nuance. It must be said right away that if you still want to make a foundation on a strip basis for a greenhouse from a bar, then you can skip the moment of reinforcement. This is due to the fact that this building does not exert a significant load.
So, we perform the operations in the following order:
- First of all, the axes are broken down using a theodolite. For example, if such a device is not available, use a cord and stakes.
- Further along the lines that were pre-planned, a ditch is being driven. If the building area is large, it is recommended to use a mini excavator.
The ditch must be perfect, otherwise the entire structure will become distorted
- The dug ditch needs to be filled with sand and compacted tightly. Next, gravel is poured, and both layers must have a thickness of at least 15 cm.
We invite you to read: Advice on how to arrange a relaxation room in a bathhouse
It is important to know: the ratio of sand to gravel must be 1 to 2.
- A small layer of cement mortar is poured onto the resulting crushed stone (this is called “concrete footing”). Its thickness should be 8-10 cm. A solution of this type will harden in 4-5 days.
- After this period of time, installation of the fittings can begin. It would be better to lay a layer of waterproofing before carrying out the permitted stage. Roofing felt or special insulating compounds are suitable for this.
Important! Water, sand and gravel must be used without any impurities. Otherwise, the strength of the system may be lost.
- To lay the reinforcement, longitudinal and transverse reinforcement should be made using reinforcement rods. They will need to be fastened with wire specially designed for this purpose. Don’t forget to treat the reinforcement with anti-corrosion substances - this will extend its “lifetime”.
- Don't forget that welding areas are mostly susceptible to rust. And so finish these details very carefully.
- The load produced by the building affects the lifespan of the system. So, using, for example, a foundation on a strip basis for a gazebo made of timber, it will be possible to forget about this component for a long time. But, if we are talking about a heavier structure (for example, a bathhouse), then it is recommended to monitor its condition every year.
The planks must be firmly attached, otherwise the formwork will fall apart
- Now it’s time to create the formwork. To do this, they make a system in the middle of the ditch using some materials (plywood, sheets of metal, slate, etc.). A mixture of concrete will be poured into it.
- When pouring in cool weather, it is necessary to use cement of at least M300 grade. In acceptable conditions, the M200 brand will be sufficient. If you live in a region with a cool microclimate, then it would be better to use specialized frost-resistant additives, which will extend the life of the system.
- The ideal ratio of crushed stone, sand and cement is 5x3x1, and the amount of water should be almost half the amount of solution.
Important to know: remember the golden rule: in cool weather, use warm water and vice versa. This kind of measure will ensure the speed of hardening is favorable.
- Pour the prepared solution into the niche. Then we make several holes in it using a probe. This is necessary to remove air.
- Also, do not forget to tap the formwork using a wood hammer. The concrete mixture is compacted using a specialized vibrator. This makes it possible to proportionally place the binders.
- After three to four days, the formwork is removed. Then it is necessary to wait in the same way so that the concrete acquires the required strength in order to carry out further operations.
The frame is fixed to the foundation using specialized metal plates
- Do not forget that attaching the beam to the foundation involves a significant load on it. And therefore there is no need to proceed to this stage until the composition has completely hardened. Otherwise, you can harm the system.
If the site has weak soils, a rubble concrete foundation may be a good choice. The construction of a shallow rubble foundation is carried out in the following order.
First, a trench is dug around the perimeter of the walls of the bathhouse, 60-70 cm deep, after which stones and crushed stone are laid in rows with a solution of 1 part M400-M500 cement mixed with 3 parts sand.
Do not forget that the foundation cannot be left unloaded for a long time. Otherwise, it may become deformed under the influence of soil processes. Therefore, if you decide to start building a foundation in the summer, you cannot leave it unloaded throughout the winter.
The construction of the foundation and building frame must be completed within one season. Otherwise, by spring the foundation may be so chalky that you will have to start all over again.
When building a rubble concrete foundation, you should not take long breaks in pouring. If there is a need to interrupt work for 1-2 days, the already completed foundation should be covered with a film to prevent it from drying out and periodically shed with water (3-4 times a day).
What influences the choice
The location of the building for the bathhouse, for which the foundation is being installed, must preserve the landscape. But this is not the most important thing:
- the type and composition of the soil is taken into account;
- nature and direction of groundwater;
- soil freezing;
- state of the landscape.
For natural gravity flow of water, it is advisable to make the foundation on an elevation, taking into account the side - from the north there may be a reverse outflow in the spring. To prevent snowdrifts from accumulating in winter, the best choice can be made in favor of the south side. For a comfortable stay, it is beneficial to place a bathhouse building near a pond. What could be more beautiful than a hot dip into the water! And of course, take care of the fence to feel private.
Design and other factors
When deciding on a location, we take into account the material from which the bathhouse will be built. If these are lightweight materials, such as a frame and foam block, then the task is simplified, but if it is timber or, for example, a log, then the location and type of foundation must be appropriate. The walls are made of wood, the stove, the mass load on the support is more than a ton, so the foundation must be heavier.
That is why we talk in detail not only about the material for the base of the building, but also about the preparation for its construction. You can learn about foundation construction technology from this article. The level of soil freezing is also important. The depth of the foundation depends on this; it should be an order of magnitude deeper than soil freezing.
Recommendations
There is a large selection of foundation base designs, each of which has a number of advantages and disadvantages. It is impossible to choose the best option, because the choice of foundation depends on the characteristics of the territory. When constructing the foundation, consultation with professionals is necessary, because the length of the service life of the bathhouse depends on the proper construction of the foundation.
The layer of sand and crushed stone must be protected with a layer of geotextile. This material can be laid between layers of soil, bending the edges upward. Textiles will protect the pillow from silting and erosion. The material allows moisture to pass through well, and due to its composition it is not subject to destruction for a long time. Geotextiles are produced in special rolls, which makes them easy to use.
Water must be drained from the bathhouse. For this purpose, a special drain is installed that goes into the ground.
You will learn further where to start building a foundation for a bathhouse.