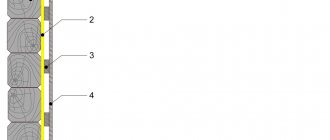Ecowool
Hello, dear blog readers! Today we’ll talk about a method of insulation that is interesting to many...
There has been more and more talk and writing about this material lately, although it has been known for almost 100 years. In Europe, ecowool began to be actively used in the post-war period, and in Russia it began to be used in the early 90s.
Today it cannot be called a frequently used thermal insulation material. For example, we know much more about polystyrene foam and mineral wool. Let's see whether it is possible to insulate your bathhouse with ecowool, and what properties this material has.
Why is it necessary to insulate the floor in a bathhouse?
There is an opinion that insulating the floor in a bathhouse is an unnecessary and even harmful procedure. Proponents of this idea argue that it cannot be cold in a heated bathhouse. An example is a traditional Russian bathhouse, where the floor is an ordinary wooden flooring in one layer with cracks between the floorboards into which water flows.
In addition, installing a heat insulator creates conditions for premature failure of a wooden floor - a lot of water remains on it, mold, mildew, and rot appear.
There is some grain of truth in this point of view. However, the modern design of the bathhouse has changed significantly. In addition, new materials have appeared that are resistant to water and can withstand all biological damage.
Therefore, today floor insulation is a common stage of construction work (or reconstruction of an already finished bathhouse). A correctly performed procedure will significantly reduce fuel consumption during heating and reduce the amount of condensation on the floor after completing bath procedures.
In addition, the floor temperature is one of the indicators of microclimate and comfort - walking barefoot on a warm surface is much more pleasant than on a cold one.
Slag
To produce slag wool, blast furnace slag is used as a raw material, which is previously processed into microfibers. During the production process, additives containing formaldehyde resins are added to cotton wool, which, as is known, release highly harmful substances when heated.
Among the advantages can be noted:
- Low cost.
- Resistance to rodents, fungus and mold.
- Easy installation
The disadvantages of slag wool do not allow its use for insulation in a bathhouse or sauna:
- Sudden temperature changes, which are typical for a steam room, lead to the product losing its thermal insulation qualities.
- The high hygroscopicity of the material will quickly lead to the loss of its function as a heat insulator.
- The increased fragility and thorniness of fibers dictates the presence of a protective mask and respirator when working.
- Slag wool is not able to withstand high loads and is deformed even under the influence of its own weight, sliding down over time if it is mounted in walls.
- Most importantly, slag wool contains phenol and formaldehyde in concentrations dangerous to humans, so using it indoors is extremely undesirable.
Thermal insulation materials
There are many varieties of insulation with high performance qualities. However, not all of them can be used to insulate the floor in a bathhouse. The constant presence of water forces the screening out of permeable materials that tend to absorb moisture and thereby lose their working qualities.
Thermal insulation of the floor in the bathhouse is placed in such a way that all drains fall on it. You can try to protect the material with various films, but it is impossible to achieve one hundred percent effectiveness.
In addition, in hygroscopic types of insulation there is always some amount of water vapor present. It will be locked under the film and cannot be removed, and new portions of water will gradually enter from the outside. Sooner or later the insulation will get wet and stop performing its functions.
Therefore, for floor insulation, the best choice would be moisture-proof thermal insulation materials:
Styrofoam
Penoplex
Foamed polyethylene (these are different materials, about 90 items in total, but they all have the same properties)
Liquid polyurethane foam
These materials are equally resistant to moisture, but their performance properties are different. Let's take a closer look at them:
Styrofoam
The real name of this material is granulated polystyrene foam. The name “foam plastic” was preserved after the name of the company that first supplied this heat insulator to the USSR. However, it caught on and is now used by everyone. Polystyrene foam is an insulator made from sealed polystyrene foam granules.
They are combined in autoclaves in an atmosphere of hot steam. The resulting array is cut into sheets of a certain thickness. The material is light in weight and resistant to water (it has a negligible ability to absorb moisture in the amount of 1% of its own weight, after a day's stay in a container with water).
It is generally accepted that polystyrene foam does not burn. It's a delusion. The granules contain carbon dioxide, which prevents the sheets from burning. However, if the material melts, it can burn and will be very difficult to extinguish.
Of all types of thermal insulation, polystyrene foam is the cheapest. This became the reason for its popularity and demand among users.
Penoplex
This is the proper name for the thermal insulation material; from a chemical point of view, it is extruded polystyrene foam, the closest relative of polystyrene foam. It differs from its counterpart in greater density, strength, and also high cost.
High performance qualities made the material popular. Prices for it are gradually decreasing, increasing the demand and popularity of penoplex.
Foamed polyethylene
This is a relatively new material with advanced functionality and capabilities. There are about 90 types of polyethylene foam - isolon, penofol, isospan, tepofol, energyflex, porileks, etc. The abundance of names can be confusing, but in terms of quality and properties, many types are almost identical.
Polyethylene foam is produced in rolls, in the form of shells for pipes and in the form of bundles for insulating gaps. There are varieties with a foil surface that can reflect thermal (infrared) rays back into the room, improving the heating mode.
Expert opinion
Lovkachev Boris Petrovich
Bath master who knows everything about steaming
Polyethylene foam does not absorb or allow water to pass through at all, is lightweight and relatively thin. The potential of this insulator is great and has not yet been fully exploited; experts predict a great future for it. The popularity of the material is enhanced due to its relatively low cost and availability for the mass buyer.
Liquid polyurethane foam
This is a material that is a two-component liquid. When applied, it foams and increases in volume, resembling polyurethane foam. Applied by spraying using specialized equipment.
The advantage of the material is the ability to create a sealed insulation sheet applied to any surface - curved, convex or concave, with a mass of small parts, etc.
Virtually no preparation is required before application; even a wet surface can be coated (only without ice or frost). In addition, you can apply a layer of any thickness as required.
The disadvantages of liquid polyurethane foam are the high price and complexity of application. The need to use special equipment significantly limits demand, although all material indicators are very high and harmonious.
Insulation for a steam room: types
There are different types of insulation used for installation on walls, ceilings and floors. Separate articles are devoted to materials used for thermal insulation of the roof and insulation of the attic floor.
For walls
All wall insulation can be divided into two categories:
- - natural;
- - artificial.
Natural
Natural materials are made from natural raw materials:
- sphagnum (field of application: sealant between crowns);
- tow (field of application: eliminating cracks);
- building moss (insulation of steam room walls).
Artificial
Popular artificial materials for wall insulation include:
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- Styrofoam.
These insulation materials are characterized by high resistance to damage, have a long service life and a high degree of thermal insulation.
- basalt wool.
Basalt wool is often used as insulation for steam rooms in frame baths
It is distinguished by high quality, ease of installation and low cost.
For the ceiling
Traditional
Various materials can be used to insulate the ceiling. For example, clay, as insulation for steam rooms, is still used to insulate the ceiling; it is used to coat the ceiling of the steam room on the attic side
It is common to use bulk materials such as expanded clay, sawdust, slag, etc. A layer of earth must be poured onto the sawdust to ensure fire safety. And the expanded clay layer should be at least 30 cm.
Modern
For ceiling insulation, the following are better suited:
- basalite (slabs of low-density basalt fiber);
- isospan (there are 2 types):
- — isospan A (barrier type against wind and condensation, installed outside the insulation);
- — isospan B (barrier type against steam, installed indoors, protects the insulation).
The ceiling can also be insulated with regular foil, the layers of which must be overlapped.
For floor
To insulate the floor in a steam room you can use:
- — expanded clay synthetic slabs (easy to install);
- — loose expanded clay (also easy to install, but hygroscopic);
- — penoplex ( IMPORTANT ! The brand you choose must have high compression loads).
Which thermal insulator to choose?
The choice of suitable insulation is made taking into account various factors:
- subfloor material;
- design of the subfloor and water drainage system;
- room area;
- personal preferences of the owner and his financial capabilities.
Choosing a heat insulator is not so complicated, but requires careful consideration of operating conditions and possible loads. In principle, the main subject of consideration is usually the strength of the insulation, the ability to withstand possible loads. In this regard, all types of insulators behave differently.
Polystyrene foam under prolonged mechanical action crumbles and crumbles into individual granules. Penoplex wrinkles. Foamed polyethylene turns into a thin dense layer, and liquid polyurethane foam becomes denser and loses its porous structure.
In terms of the combination of price and performance qualities, penoplex is in the lead, and polystyrene foam is in second place.
Of all the factors, the material of the subfloor has the greatest influence. The most common types of floors are concrete and wood floors. Let's take a closer look at the ways to insulate them:
Insulation of a wooden floor
Most owners prefer wooden floors, as they correspond to the traditional idea of the design of bathhouse elements. Insulation of such a floor is carried out by laying a heat insulator over the subfloor.
In this case, you must first make a plank flooring and sew a vapor barrier underneath to protect the boards from contact with water vapor from the ground. In addition, it is necessary to think over a water drainage system and organize its drainage into the sewer or to a discharge point.
Thermal insulation is laid between vertical strips laid on edge. They act as joists for the finished floor and at the same time serve as sides for thermally insulated compartments. Penoplex slabs are laid tightly next to each other, the joints are glued with aluminum tape or filled with polyurethane foam.
A polyethylene film is laid on top of the insulation, which forms additional moisture protection for wooden parts. After this, you can begin laying the final floor covering (finish wood flooring).
Insulation of concrete floor
Insulation of a concrete floor is carried out according to the usual method for concrete floors and screeds. A waterproofing sheet (polyethylene or waterproof membrane) is laid on the rough concrete floor.
Then slabs of polystyrene foam or penloplex are placed tightly next to each other, immediately filling all the gaps with polyurethane foam.
After this, the pipes of the water drainage system are laid and the embedded parts of the drains are installed. Now you can start pouring the screed. Its thickness must be at least 50 mm to ensure sufficient strength. After the screed has hardened, the tiles are laid.
Price list for finishing a bath
| 1 | Treating floor beams with a protective compound from a spray gun | sq.m. | 40 | 0 rub. |
| 2 | Floor joist installation | sq.m. | 190 | 0 rub. |
| 3 | Leveling and strengthening the floor beams to the level (if they were installed previously) | sq.m. | 140 | 0 rub. |
| 4 | Installation of subfloors from edged boards | sq.m. | 195 | 0 rub. |
| 5 | Installation of vapor barrier | sq.m. | 40 | 0 rub. |
| 6 | Insulation (per 1 layer 50 mm) | sq.m. | 45 | 0 rub. |
| 7 | Laying floor boards | sq.m. | 270 | 0 rub. |
| 8 | Plywood flooring 6-22 mm thick | sq.m. | 180 | 0 rub. |
| 9 | Parquet flooring | sq.m. | 280 | 0 rub. |
| 10 | Laminate flooring | sq.m. | 230 | 0 rub. |
| 11 | Linoleum flooring | sq.m. | 180 | 0 rub. |
| 12 | Sanding floor boards | sq.m. | 240 | 0 rub. |
| 13 | Installation of floor plinths, layouts, corners | m. linear | 70 | 0 rub. |
| 14 | Painting the floor with paints and varnishes (per 1 layer) | sq.m. | 60 | 0 rub. |
www.tvoidom-tver.ru
Heated floor system
Warm floors in the bathhouse are a relatively recently used technique. Similar solutions were known back in the days of Ancient Rome, they were used in Turkish baths, but then were forgotten for a long time.
Today, heated floor systems are successfully used in bathhouses as a source of main heating, or as an additional element of comfort in “dry” sections (rest room, locker room, etc.). At the same time, the traditional heater is not canceled.
Only a water heated floor is suitable for a bathhouse - electric systems are not suitable either in design or in terms of economy. It should be connected to a boiler (gas or solid fuel), and a temperature control system (heating manifold) should be installed.
The system installation proceeds as follows:
- A waterproofing layer and a layer of heat insulation (foam plastic or penoplex) are laid on the floor.
- Place polyethylene film and reinforcing mesh. A polyethylene tube is fastened to it with nylon clamps - underfloor heating loops. The laying pattern is chosen so as to evenly cover the entire area of the room and bring the ends of the loops to the collector.
- The loops are connected to the collector, the functionality of the system is checked, and a concrete screed is poured to hide the tube. At the time of pouring, there must be water under pressure in it so that the screed does not flatten the hinges of the heated floor.
- When the screed has hardened, lay the floor covering.
Warm floor screed is the most effective design option. However, if the tube is damaged, you will have to break the screed and then refill it.
Frequently asked questions
Some questions that users have can be answered immediately, without waiting for them to arise:
If the floor is wet, is it necessary to install a waterproofing layer over the moisture-proof insulation?
Despite the properties of the heat insulator, it is recommended to cover it with a film to cut off waste water. Over time, the film will develop a layer of slime and can simply be replaced without much expense or labor. It is not practical to change the insulation every year.
If mineral wool is chosen as insulation, how to protect it from water?
The usual technique is used - laying a waterproofing sheet, then mineral wool, on top of which is another layer of polyethylene.
If foil insulation is installed as thermal insulation, will the polyethylene sheet interfere with the passage of reflected infrared rays?
Polyethylene does not interfere with IR rays. However, it is not recommended to use black film; it can cut off some of the rays.
Is it possible to insulate a wooden floor with a layer of expanded clay backfill?
There are no fundamental objections to this matter. Many sources even recommend this option. However, you will have to carefully protect the backfill from water, which is technically difficult and ineffective.
How to lay drain system pipes?
As a rule, they are laid even before the installation of the heat insulator. When laying the pipes, they are covered with pieces of insulation and all cracks and joints are filled with foam, eliminating the possibility of cold bridges.