If you are attentive, then you have probably noticed on some roofs special spherical devices that also spin. These are special ventilation deflectors, which today are indispensable in the ventilation systems of apartment buildings and suburban real estate. They work without electricity, but still do their job perfectly. They also decorate the roof of the house in their own way, introducing a unique dynamic element into the overall design.
Moreover, making such a turbo deflector with your own hands is not at all difficult - the main thing is to carefully study the principle of its operation and select weather-resistant materials. We will now tell you which ones, what to do with them and how to avoid mistakes.
Making a simple device with your own hands
Despite the complexity of the design, every home craftsman can make a deflector with his own hands. You just need to have the necessary tools and materials. To make this device yourself you will need:
- A sheet of thick paper or cardboard.
- Galvanized metal sheet.
- Drawing of a deflector with calculations regarding the diameter of the pipe.
- Rivet gun.
- Metal scissors.
- Drill with a set of drills.
- Marker or scriber.
After preparing the tools, material and personal protective equipment (goggles, gloves), you can begin making a ventilation deflector with your own hands.
- First of all, you should transfer the contours of the product from the drawing to the metal. There must be scans of all the main parts of the device: cap, diffuser, outer cylinder, racks.
- After this, you need to cut out all parts of the device according to the resulting pattern.
- Connect all parts of the device, according to the drawing or sketch, using a rivet gun.
- Connect the two parts of the deflector using stands cut from the same metal.
After manufacturing, you can install the deflector on the head of the pipe, carefully securing it with clamps.
Tip: The deflector will create additional draft in the channels only if all its parts are made to certain dimensions. It should be remembered that the installation should be carried out while working at height, so it is better to do it together and with insurance. If you are not confident in your abilities, contact professionals who have experience in the manufacture and installation of these necessary devices.
Types of turbo deflectors
Varieties of deflectors by shape Many types of deflectors have been developed to select a rotary head model that works effectively in specific conditions. All devices differ in technical characteristics, despite the fact that the commercially available options are almost the same in appearance.
Rotary turbine models vary:
- according to spare parts material;
- according to the size of the connecting ring.
Moving parts of equipment require periodic maintenance. The cost of turbo deflectors is quite high, so many owners can make and install the structure themselves.
According to the material of manufacture
Turbo deflectors made of stainless galvanized steel and polymer-coated The choice of material depends on the preferences and budget of the buyer. Some parts of the turbocharged device are made of plastic. Organic material based on natural or synthetic polymers does not react to humidity or acid precipitation.
The main materials are:
- thin sheets of chrome or galvanized steel with a matte finish are available in budget options;
- Stainless steel has double the cost compared to the previous material and is powder-coated in standard roofing colors;
- Structural metal with a polymer coating does not differ in color from the facade or roof of the building.
Chromium plating saturates the surface of steel with chromium molecules under conditions of electric current or in an electrolyte bath. Processing increases the metal’s resistance to destruction and improves the appearance of products. Stainless steel is used without coating or with a decorative layer; it actively resists corrosion due to the addition of chromium, phosphorus, nickel, and copper during production.
According to the diameter of the connecting ring
The turbo deflector is selected according to the size of the base. The size of the seat is indicated in the labeling and product passport. The diameter increment is 5 mm; sizes are available from 100 to 200 mm. More than 200 mm, sizes are made 250, 300, 315, 355, 400, 500, 600, 680 and 800 mm. Turbine diameters for exhaust 1000 mm and others are manufactured upon request.
The deflector is installed on the outlet section of the ventilation pipe, which can have a cross-section of different shapes. The devices are available with a round or square base. There are turbo deflectors with a box-shaped transition type base. They are installed on ventilation ducts made of bricks or blocks.
How to make TsAGI and a turbo deflector for ventilation with your own hands: drawings, stages of work
The turbo deflector has a rather complex design, so not many people undertake the manufacture of the device themselves.
If you decide to make just such a design, you need to ensure that you have the following tools and materials:
- sheet of stainless or galvanized steel;
- electric or cordless drill;
- regular and metal scissors;
- bolts, screws, nuts and clamps;
- items for drawing up a drawing: ruler, pencil, compass, cardboard and graph paper;
- welding machine.
When making a TsAGI deflector yourself, you will need: a mallet, a drill, a vice and metal scissors.
When making it yourself, it is important to correctly make the landing part, which will correspond to the required pipe diameter. After this, plates with a tube located in the middle, into which the dynamic part of the device is inserted, are welded to the finished part. Then steel blades are formed using the finished template, which are attached to the structure and form a turbo deflector
To understand how the execution process goes, it is better to refer to the videos available on the Internet
Then steel blades are formed using the finished template, which are attached to the structure and form a turbo deflector. To understand how the execution process goes, it is better to refer to the videos available on the Internet.
Most craftsmen prefer to make a TsAGI device at home, because making a deflector is quite simple. To do this, you will need to take galvanized steel no thinner than 0.5 mm, from which the necessary parts are then cut out. Rivets, bolts and nuts are used to assemble the structure. To work you will need the following tools:
- hammer or mallet;
- drill;
- vice;
- metal scissors;
- tape measure and pencil.
After cutting out the necessary parts from sheets of tin, they are connected to each other using rivets.
Due to the fact that a large number of ready-made drawings are available on the Internet, it will not be difficult for anyone to draw a diffuser. The main thing is to determine the size correctly. The most popular parameters are ventilation ducts with a diameter of 10-11 cm, especially if the hood is made of a plastic pipe.
So, after the necessary parts are cut out of sheets of tin, they are connected to each other using rivets. Then the finished deflector is put on the head, and the lower pipe is tightened using a clamp. If the shaft is square, an adapter is additionally made or purchased, the flange of which is attached to the end of the pipe.
Properly designed ventilation will help maintain a normal microclimate in your home, and a deflector installed on the roof will provide draft that will quickly clear the room of exhaust air. Despite the fact that most appliance models are not very expensive, they still guarantee productive hood and preserve the health of residents.
Selection rules
You can select the optimal deflector based on the goals and tasks assigned to it. It is also worth considering the conditions in which it will operate.
A simple chimney is a cap on a wood-burning chimney, made in the form of a regular umbrella, and has the following advantages:
- maintains the necessary traction both in calm conditions and in the movement of air masses with a power of up to 10 points;
- does not create excessive pressure on the pipe, due to which even in a severe storm the chimney remains in its place; rather, the umbrella itself can break off and fly away;
- has a simple and understandable design;
- practically does not coke or clog, and is quite easy to clean;
- due to the imperfection of the aerodynamic structure, it is insensitive to the shape of the umbrella; if the building is located in the wind, then the chimney can be made in the form of a tent, this greatly simplifies its use and opens up great opportunities for the implementation of design ideas.
At the same time, there are serious disadvantages, such as:
- in weak winds it reduces draft, and the stronger the heating element works, the weaker it is. This is quite dangerous, since in cold winter weather, in the absence of wind, the stove can “choke” and breathe fumes into the living quarters;
- in strong winds, on the contrary, it creates too much draft. This significantly reduces the efficiency of indoor stoves and fireplaces;
- in gusty winds it can cause blowing into the pipe and creating a reverse draft effect.
The aerodynamic open model maintains sufficient draft in any wind for efficient operation of stoves and boilers using liquid fuel and gas. Such deflectors can freeze, they easily become littered and quickly become covered with soot and soot, however, they are easy to clean.
The disadvantages include the following:
- complex body of rotation;
- as a result of the load created by air masses, the umbrella itself can easily fly off the chimney, and at the same time, the direct mechanism of the device can collapse the pipe itself;
- with strong gusts of wind from force 8, the lateral pressure on the structure increases significantly and further increases in accordance with the power law;
- open structures are quite poor at reducing strong dynamic loads resulting from gusts of wind, which is why in no case should such a model be placed on pipes made of brick;
- the modification cannot be used for pyrolysis heat-generating mechanisms, otherwise, when wind occurs, all pyrolysis gases will be sucked out and the stove or boiler will simply go out;
- not suitable for creating design elements, since it is unsuitable for decoration; all kinds of blotches and figures only worsen the overall aerodynamic status of the structure as a whole.
By the way, an interesting study was conducted in the USA. There, at one time, they studied issues related to open deflectors and installed them on locomotives to check the degree of increase in efficiency at low speed. At the same time, the result was the most depressing - at mid-speed, fire began to burst out of the pipe and not a single train was able to reach its maximum speed. In general, the open version of the deflector should be recommended for all types of heating devices, with the exception of pyrolysis ones. At the same time, it must be checked and cleaned at least once a quarter. It is optimal for a chimney with low draft force, it is most effective for wood-burning sauna stoves; not a single case of people burning out due to the ventilation deflector in saunas has been recorded.
The closed or as it is called “perfect” type has such advantages as:
- provides stable draft, which is sufficient for stoves and boilers of any type;
- not prone to freezing and clogging from the inside;
- Dust and ice formed on the outside do not significantly change the operation of the device.
There are also disadvantages, however, users claim that they are not so significant, namely:
- when exposed to strong winds, it gives maximum pressure on the pipe, and then increases linearly, so the chimney under the deflector should be further strengthened with guy wires;
- has rather complex design and technological parameters;
- cannot be used as a design element, since any additional elements significantly reduce the overall level of aerodynamics.
Models may differ in appearance, purpose and material. Most often, plastic, stainless steel or aluminum are used to produce deflectors. In rare cases, copper may become a raw material for production. Many users prefer the sandwich model.
Instructions for assembling the deflector
The Grigorovich deflector is the simplest and most popular type of protective device. It has a simplified and reliable design that you can make yourself.
Tin or galvanized steel with a thickness of at least 0.5 mm is suitable for making a chimney.
For assembly you will need the following set of working tools:
- Scissors for cutting metal.
- Hammer.
- Electric drill and drills.
- Welding machine.
- Roulette.
- Pencil and felt-tip pen.
- Thick cardboard.
- Self-tapping screws.
- Bolts and nuts.
The basis for the device is a 0.8 mm galvanized steel sheet and steel strips.
A homemade deflector is assembled according to the following scheme:
- Calculation of the dimensions of the future device. To simplify, you can use a ready-made formula.
- Each structural element is marked on cardboard. The finished templates are cut out and connected to each other to check that the sizes match the required parameters.
- The templates are placed on steel sheets and outlined along the contours using a felt-tip pen. The blanks are cut with scissors strictly along the contours.
- A cylindrical diffuser is formed from the central part. Holes for self-tapping screws are made at the edges.
- The outer cylinder is created in a similar way. A cone-shaped cap is assembled from two blanks.
- 6 cuts are made along the edges of the upper cone for fixing posts. Stands 21 cm long and 5 cm wide are cut out of steel strips. Next, the lower cone is fixed to the upper cone with an edge using stands.
- The finished cap is connected to the diffuser and installed in the outer cylinder.
Area of use
Where exactly can turbo deflectors be used? The products have proven themselves excellent in rooms and facilities where air exchange is extremely necessary. Scope of use:
- For private and apartment buildings. In addition, it should be noted that increased demands are placed on the operation of ventilation ducts in a high-rise building. Often in such houses the quality of ventilation is not the best, since they were made in the Soviet Union. But thanks to the use of a deflector, this problem is solved.
- Turbo deflectors are good for livestock farms and agricultural buildings such as stables, poultry houses, granaries and haylofts. They help ventilation more effectively remove odors, fumes and gases generated when keeping livestock. In addition, the humidity in the room is controlled, it is optimal.
- For processing enterprises. Since the turbo deflector does not require electricity to operate, the savings on the device are corresponding. The exception is enterprises that produce or process substances hazardous to humans.
- Public buildings such as sports complexes, swimming pools, shopping centers and cinemas.
Important! The turbo deflector is also used to ventilate the under-roof space.
But how to make turbo ventilation deflectors with your own hands? Let's find out.
Advantages and disadvantages of turbodeflators
What will a user get if he makes a turbo ventilation deflector with his own hands or buys one? A lot of advantages and only positive impressions about his work. Here are the advantages that a product for ventilation or chimney has:
- The turbo deflector head, which rotates, enhances air exchange in the ventilation or chimney pipe. No backdraft is formed, and the under-roof space does not accumulate condensate. In addition, the rotary device works much better than a regular deflector.
- The product runs exclusively on wind energy and does not consume electricity. Therefore, there will be no extra costs, unlike using electric fans.
- If you properly care for the equipment and perform correct installation, the service life will be 10 years, or 100 thousand hours of operation. If we take stainless steel turbo deflectors, their service life is 15 years. In comparison, fans work 3 times less.
- Snow, hail, rain, leaves, and rodents will not enter the ventilation duct. The turbo deflector is used in areas with strong and frequent gusts of wind.
- The design of the equipment is light, convenient and compact. Turbo deflectors with a diameter of 20 cm or more weigh slightly less than the TsAGI deflector. The large size product, which is 680 mm, weighs approximately 9 kg. To understand the difference, let’s say that a TsAGI deflector of the same diameter weighs up to 50 kg.
- Easy to install. Even a beginner can cope with this task. All you need is instructions and a standard set of tools.
This is why turbo deflectors are so often used. But along with the advantages, the products also have some disadvantages:
- When compared with other types of deflectors, the turbo deflector is somewhat more expensive. True, if you do it yourself, it will cost less;
- under unfavorable atmospheric conditions, for example, if there is no wind, low temperature or high humidity, the device may simply not work and stop. But if the deflector is constantly in motion, then it is less susceptible to icing;
- The use of a deflector for rooms with increased ventilation requirements, such as a medical laboratory, industrial premises, buildings with chemical substances, cannot be considered the only solution. You still need to install fans.
Depending on the material used, the price of the device can be quite high. Still, these disadvantages are very few, so many people prefer to use a deflector for their ventilation system.
Area of use
Where exactly can turbo deflectors be used? The products have proven themselves excellent in rooms and facilities where air exchange is extremely necessary. Scope of use:
- For private and apartment buildings. In addition, it should be noted that increased demands are placed on the operation of ventilation ducts in a high-rise building. Often in such houses the quality of ventilation is not the best, since they were made in the Soviet Union. But thanks to the use of a deflector, this problem is solved.
- Turbo deflectors are good for livestock farms and agricultural buildings such as stables, poultry houses, granaries and haylofts. They help ventilation more effectively remove odors, fumes and gases generated when keeping livestock. In addition, the humidity in the room is controlled, it is optimal.
- For processing enterprises. Since the turbo deflector does not require electricity to operate, the savings on the device are corresponding. The exception is enterprises that produce or process substances hazardous to humans.
- Public buildings such as sports complexes, swimming pools, shopping centers and cinemas.
Important! The turbo deflector is also used to ventilate the under-roof space. Number of blocks: 18 | Total number of characters: 23820 Number of donors used: 6 Information on each donor:
Number of blocks: 18 | Total number of characters: 23820 Number of donors used: 6 Information on each donor:
Number of blocks: 18 | Total number of characters: 23820 Number of donors used: 6 Information on each donor:
- https://ventkam.ru/ventilyatsiya/rotatsionnyj-deflektor: 3 blocks out of 7 were used, number of characters 2861 (12%)
- https://trubanet.ru/sistemy-ventilyacii/deflektor-na-vytyazhnuyu-trubu-princip-raboty.html: 3 blocks out of 6 used, number of characters 2191 (9%)
- https://oventilyacii.ru/ventilyaciya/deflektor.html: 4 blocks out of 6 were used, number of characters 6964 (29%)
- https://www.stroy-podskazka.ru/ventilyaciya/montazh-turbodeflektora/: 3 blocks out of 5 were used, number of characters 6282 (26%)
- https://proventilation.ru/ventilyatsiya/turbodeflektor-svoimi-rukami: 1 blocks out of 5 used, number of characters 2510 (11%)
- https://ProRoofer.ru/aksessuary/turbodeflektor-dlya-ventilyacii-svoimi-rukami.html: 3 blocks out of 8 were used, number of characters 3012 (13%)
Varieties
Many users constantly wonder: which deflector is best for a chimney? To answer this question, you need to study existing models and, based on their characteristics, select the most optimal option.
Today, there are several types of deflectors that have gained popularity due to their practicality and reliability.
Disc Astato. This deflector is open, but at the same time it is very effective. Its main distinguishing feature is that it is able to provide good traction, regardless of which direction the wind blows. Material of manufacture: galvanized/stainless steel.
Disc chimney deflector Astato
TsAGI deflector. This model is recognized as one of the most popular and in demand. It is made in the shape of a cylinder. The manufacturing material is stainless or galvanized steel. Connection type: flange.
Round Volper. In terms of design features, this model resembles the previous one. The main distinguishing feature is the top of the device. Typically, such deflectors are made of stainless steel or copper. Most often they are purchased for installation on the chimney of a bathhouse.
Grigorovich deflector. This type is a more modern and improved version of TsAGI. It is installed in places where the winds are generally not very strong.
H-shaped. This model is highly durable and reliable, regardless of the direction of wind movement - it is effective. The H-shaped deflector is made of stainless steel. The connection is made through a tap on the device pipe.
Deflector-weathervane. It is a rotating body with a weather vane on top. Made from stainless steel or carbon steel.
Types of chimney deflectors
Basically, chimney deflectors differ in shape and component elements. As can be seen from the examples, products are usually made from stainless steel and galvanized steel. Models are round, square, in the form of an open and closed cylinder. The “top” of the device also varies. In some it has the shape of an umbrella, in others the lid can be gable or hipped, and in others it is completely flat or with decorative figured elements.
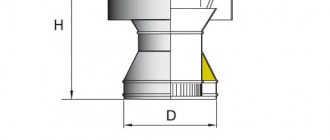
The diameter of the deflector on the chimney pipe can be 100-500 mm, the width of the diffuser varies from 240 to 1000 mm, and the height of the device is 140-600 mm.
The deflector is connected to the chimney using brackets, bolts and sealing tape. It is made of steel, the thickness of which is 0.5-1 mm. You can also install a spark arrester. Typically, the equipment is equipped with such parts in case of risk of a possible roof fire.
Weather vanes
Pipe deflectors - weather vanes are also called weather vanes. Sometimes all chimneys in general are called this, but this is incorrect, because... A weather vane is, by definition, a rotating device.
The deflector on the pipe - weather vane can be made rotary, self-orienting and rotating. The latter are also called turbo deflectors, and self-orienting smoke teeth, which is also incorrect. The smoke tooth is part of the chimney of an English fireplace. The weak point of all weather vane deflectors is the bearing. It becomes very easily clogged and covered with soot, and the seals are subject to increased wear. Therefore, you need to inspect the weather vane deflector at least once every 2 months. But the weather vane deflector itself almost never becomes overgrown with the main enemy of all fixed deflectors - icicles.
Pipe deflectors - weather vanes
A multi-bladed weather vane deflector (items 1 and 2 in the figure) provides stable draft in winds of up to 9-10 points with minor loads on the pipe, so it can be installed on sandwich, ceramic and glass chimneys. A single-blade weather vane deflector puts a lot of stress on the pipe in a strong wind, so it must be strong and the house must be located in a place where the storm wind will not blow up. But a single-bladed weather vane deflector can easily be designed in the shape of a bird (items 3 and 4).
Turbo deflector (item 5) – remember and don’t trust anyone – not smoke! It is ventilated or for gas boilers with electric ignition. The turbine rotates both by the wind and by the air current in the pipe, and a correctly made turbine, as in some types of wind engines, is self-spinning: the weakest initial thrust or a light breath of breeze is enough for the turbine to spin and draw air, and it will stop only when the thrust , and the wind will stop completely. In a house ventilation system with turbo deflectors, you have to turn on the fans in the vents, as they say, once a year, not every year. Unfortunately, the turbo deflector is easily filled with dust and debris from the air, so it also needs to be checked at least once every 2 months.
The technical properties of the turbo deflector are the same as those of a multi-bladed self-orienting one, but it loads the pipe even less. It is quite possible to make a turbo deflector with your own hands, see the video below.
How to make a turbo deflector with your own hands
DIY turbo deflector
The simple design of the turbo deflector is easy to assemble yourself. First a drawing is made. A cardboard pattern is cut out for each element. The paper is applied to a metal sheet and outlined with a marker. Then the part is cut out with a grinder or metal scissors. Holes for bolted connections are drilled at the required points.
Part size calculation:
- product height = 1.6 pipe width;
- the diffuser diameter is 1.2 times larger than the pipe width;
- The cover is equal in width to 2 pipe diameters.
The Grigorovich deflector or a regular weather vane model is best suited for self-assembly.
First, the landing part is made. A vertical tube is fixed in the center of this part into which the bearing is inserted. She is responsible for the rotation of the deflector. The tube is fixed to the seating part with 4 metal plates. Then you need to insert a metal rod into the bearing. The thread is cut on the top of the rod. The upper fairing is installed on top of the rod. This is a round metal plate that should be several centimeters wider than the landing part. A hole for mounting is drilled in the center of the fairing. The part can be fixed with a regular nut. Riveting or welding are also suitable, but when making your own, it is more convenient to use bolted connections.
Then identical blades are made. To cut parts of a suitable shape, you need to find a drawing. After this, holes are made along the edges of the blades for fastening. Next, you need to bend the blades so that they are all the same. To do this, it is better to make a template.
The blades are attached to the fairing at the top, and at the bottom to a metal ring, the diameter of which is slightly larger than the landing part.
Features of device installation and useful tips for proper installation
To correctly calculate the deflector, you need to measure the diameter of the exhaust shaft. If there is a rectangular exhaust shaft, you should select a device with a round cross-section, the value of which is equivalent to the size of the channel. That is, you need to calculate the cross section of the rectangle and take a circle with a similar area. It is also necessary to remember that in this case, an additional adapter will be required for installation.
As for the installation of the deflector, they are guided by SNIP standards governing installation rules
So, first of all, you need to pay attention to the height of the ventilation pipe and hood, which is determined depending on the location on the roof:
- The height is 50 cm, if the air duct is located closer than 1.5 meters from the edge of the roof.
- At the same level as the ridge or slightly higher, when the distance from the parapet to the ventilation shaft varies from 1.5 to 3 meters.
- If the pipe is more than 3 meters away, the height is selected so that the top of the deflector is not below the deviation line drawn from the ridge down to the edge of the roof at an angle of 10°.
It is optimal when the deflector is installed at the stage of roof installation.
Additional points to consider during installation:
- The deflector cannot be mounted in an area covered by the aerodynamic shadow of other buildings.
- The device must be mounted where there is free airflow. It is best when the cap is the highest point of the roof.
When organizing a ventilation system, you should also not forget how to install the ventilation grill correctly - up or down
Most craftsmen focus on the fact that if there is forced ventilation, air will somehow get into the shaft, so when installing it is better to focus on how the wall will look after installation and whether the grate gaps will be noticeable
Can it be installed on a chimney?
By installing a deflector, unlucky homeowners are trying to solve the problem of lack of draft. This happens when the chimney pipe is made incorrectly - the head falls into the zone of wind support of the roof, is raised to a low height, or a neighbor has built a tall building nearby.
The best solution for insufficient draft is to raise the chimney to the required height. Why is it undesirable to jam various attachments onto the head:
- It is prohibited to place umbrellas and other exhaust devices on pipes that discharge combustion products from gas boilers. These are safety requirements.
- When burning, stoves and solid fuel boilers emit soot that settles on the internal surfaces of chimneys and caps. The deflector will have to be cleaned, especially the rotating one.
- At the bottom of a properly constructed smoke channel there is a pocket for collecting condensation and excess moisture. There is no point in covering the pipe from precipitation; it is enough to attach a nozzle at the end that protects the insulation of the sandwich.
The heads of stove flues can be equipped with umbrellas, but a turbo deflector is definitely not needed there. The topic of installing hoods on smoke exhaust ducts is covered in detail in a separate material.
Turbo deflector performance
There are quite a large number of estimates of the efficiency and performance of a turbocharged deflector, from advertising statements about increasing pipe thrust by 4-6 times, to minimalist estimates of 20-30%.
In reality, the increase in thrust using a turbo deflector in ideal conditions and with average winds is 150-250%.
As can be seen from the graph, the theoretical performance of the device increases almost linearly with increasing wind speed over the pipe. In practice, such growth is only possible if it is possible to place the turbo deflector in the most favorable location on the roof.
What is a diffuser
A diffuser is a part of a ventilation system designed to introduce/exit air into a room and mix it effectively. It also performs decorative functions - it closes the entrance/exit to the ventilation duct. Outwardly it looks like a regular ventilation grille, but has a slightly more complex structure and may have additional devices - an impeller and a static pressure chamber.
Diffusers are designed for rapid air mixing
The difference between a diffuser and a ventilation grille
What is the difference between a diffuser and a ventilation grille? Yes, actually, nothing. The ventilation grille is simply the simplest of diffusers. Why is the price so different? There are reasons for this.
When developing diffusers, manufacturers calculate the movement of air, position the blades and partitions in such a way that the air in the room is mixed in the best possible way. Therefore, the air is mixed, evenly distributed throughout the room.
Several supply ceiling deflectors with air distribution patterns
Manufacturers of cheap ventilation grilles are unlikely to conduct any research, copying external features and not caring about efficiency. The air enters a certain point, and obvious zones with different temperatures are observed. So much for the price difference.
When to install a diffuser
Where and when can ventilation grilles be used, and where are diffusers needed? In ordinary old apartment buildings there are only exhaust ventilation ducts that operate due to pressure differences. The exits of the ventilation shafts are located in the walls. In this case, you can install ventilation grilles, since installing a more complex device has practically no effect on the situation.
But, if you have made a suspended ceiling behind which you have hidden an air duct connected to this duct, it is advisable to install diffusers. They work more efficiently. Since the presence of a suspended/tensioned structure impedes the movement of air, more efficient devices are needed for the normal operation of the ventilation system.
A deflector is installed in any type of suspended or suspended ceiling
If the ventilation system was specially designed, you will most likely be given precise recommendations as to what, where, and what type should be installed. In such a situation, any replacement may have a negative impact on system performance.
There can be no problems with traction
Ready-to-install rotary deflector
The purpose of any ventilation system is to remove polluted air and excess moisture from the premises, that is, to ensure normal air exchange. This will take place if the ventilation duct functions efficiently and correctly - the draft in it is excellent. If there are problems in this regard, they are often provoked by rain, snow, or wind masses entering the canal shaft.
Diffuser Body
The body diffuser is part of the car’s additional body kit, which performs the function of redistributing the oncoming air flow between the bottom and the road surface. Usually it is a tuning element or a structural part of a sports car. But it can be installed on a production car.
Why do you need a body diffuser?
The main purpose of the diffuser is to improve the aerodynamic characteristics of the car. It converts the kinetic energy of the oncoming air flow and creates a vacuum area under the bottom, which tends to press the car to the road. An increase in downforce improves the quality of tire adhesion to the road surface. Due to this, the car receives improved maneuverability, efficient acceleration, and safe braking. An additional function of the diffuser can be the distribution of air flow for additional cooling of the brake mechanisms.
Design and location of the body diffuser
Diffuser for the rear of the car
Most often, the diffuser is mounted under the bottom in the rear of the car. It can also be installed directly under the bumper.
The diffuser consists of several structural elements. Longitudinal ribs forming air channels that break up the flow and increase its speed. They also restrict airflow from the sides. Sometimes such ribs can also direct air to the discs and brake pads.
Modern diffusers are made of high-strength and lightweight carbon fiber plastic (carbon fiber). The diffuser, regardless of its design, contains voids that increase in volume along its entire length - for ease of construction.
How it works
The action of the body diffuser is based on Bernoulli's law. The volume of air passing through the narrow channels of the device is divided into several separate streams. In this case, the speed of the medium increases, which leads to a decrease in pressure. At the outlet of the diffuser, the pressure is compared with atmospheric pressure, and under the bottom it will be lower. Due to the resulting rarefaction of air, downforce increases. This effect increases overall downforce and reduces rear lift.
Of great importance is maintaining the correct angle of inclination of the diffuser walls, which should not change abruptly. The air flow should not be separated from the top and side planes. Vertical baffles help improve its efficiency and ensure that air escapes from underneath and does not affect the top of the vehicle.
Types of bumper diffusers
Depending on the design and location, there are several types of diffusers:
- a rear diffuser that ends under the car's bumper;
- a front diffuser or splitter that creates a low-pressure zone in the nose;
- rear two-level or secondary diffuser, which has an increased volume and allows you to draw more air from under the bottom.
Source
How does an air turbine pipe attachment work?
The operating principle of the turbo deflector is based on the effect of asymmetric air flow around the dome-shaped body of the device. Regardless of the direction and strength of the wind, the air flow, moving perpendicular to the axis of rotation, flows around the left half at a lower speed than the right. When interacting with the open edges of the blades, the air flow is slowed down and at the same time imparts rotation to the body.
On the right half of the turbo deflector wheel, the blades face in the opposite direction, so the incoming air flow flows around the surface without resistance and loss of speed. As a result of the Bernoulli effect and centrifugal force, flue gases or polluted air are thrown out of the housing at a speed only 30% slower than the wind. True, the gases ejected from the turbo deflector are dispersed unevenly in the surrounding space.
Features of installing a turbo deflector for ventilation
In the operation of any ventilation system, it is important to ensure not only the flow of fresh air, but also the removal of exhaust air. In some cases, the ventilation shaft does not cope with its task and needs to be “helped”
Electric hoods are not the only solution in this situation. Another option is to install a turbo deflector.
Design and principle of operation of a turbo deflector
Structurally, the product consists of 2 parts:
- The turbine head is a round moving part consisting of a large number of thin bent plates, “assembled” with small gaps between each other. The plate material is metal (usually galvanized steel or aluminum), up to 1 mm thick. The head is fixed on top of the supporting part, on bearings.
- Supporting part - needed for fastening to the ventilation shaft exit. May have a rectangular, square or round cross-section. The nozzle (transition) for installation can have different sizes - from small (about 10 cm) to large (more than 50 cm).
The turbo deflector, installed on top of the ventilation shaft, is located in an open place and is blown by the wind.
The air flow hitting the blades (plates) sets them in motion - the head begins to rotate.
Even a light wind of 0.5 m/s is enough to rotate. The turbine rotates only in one direction.
Due to the rotation of the plates in the ventilation duct, draft increases and the operation of natural ventilation improves: air is removed from the premises more efficiently.
Review of popular models
In practice, the following types have proven themselves well: Grigorovich, Volpera, TsAGI, double and H-shaped deflector, rotary weather vane of the “Net” or “Hood” type.
The choice of “wind nozzle” is based on efficiency, cost of the deflector and climatic conditions of the area. Some models are available for self-assembly and installation
View #1 - classic Grigorovich cap
The most common option used in ventilation and smoke removal systems. Due to its simplicity and accessibility, the Grigorovich deflector holds a leading position among analogues.
The device is represented by a pair of umbrellas connected into a single “plate”.
The cap is installed on round pipelines or mounted through an adapter plate on rectangular and square shafts.
Basic equipment: 1 – diffuser in the form of a narrowed cone, 2 – protective umbrella, 3 – return hood. Mounting spacers connect the nozzle elements
Thanks to the design, double air ejection is carried out - in the direction of the expanded part of the diffuser and in the direction of the return hood.
The flow velocity under the lower cone increases due to the narrowing of the channel cross-section, as a result, the pressure difference increases.
Type #2 - TsAGI universal nozzle
This design was developed during the USSR by a specialized research institute (scientific institute). The deflector consists of the following parts (shown in the drawing):
- lower glass with a diffuser (extension) at the end;
- outer body – shell made of cylindrical roofing steel;
- cover in the form of an umbrella;
- cover fastening posts made of metal strips.
The operation of the product is simple: wind blowing the body from any side creates a vacuum zone above the diffuser open at the top. The exhaust gases coming from the mine are carried away by this rarefaction, come out and are picked up by the wind - the ejection principle works.
The table below shows the characteristics of typical TsAGI deflectors - dimensions, performance depending on the wind flow speed.
Comment. Capacity does not include the resistance of the duct system crossing the roof. The actual exhaust volume depends on the height of the pipe and the temperature difference between the indoor/outdoor air.
Of all the static traction amplifiers, the TsAGI cap is recognized as the most effective, despite the venerable age of development. Design advantages:
- ease of manufacture and installation;
- maximum protection against rain and snow, and traction overturning;
- reliability, no rotating parts;
- the direction of wind flows does not matter;
- lowest drag coefficient (0.6).
The disadvantage of the deflector is its dependence on wind speed. If the flows move slower than 2 m/s, the efficiency of the device tends to zero. However, calm weather has a negative impact on the operation of any attachment designed to enhance natural draft in the ventilation duct.
The hood works thanks to wind support - a vacuum appears above the cut of the air duct
Please note: in modern versions of TsAGI factory-made, insulation of the lower glass is provided if the cap is attached to the roof sandwich pipe. Under the “fungus” we see a skirt, although the flow area of the channel does not decrease.
View #3 - Astato static-dynamic hood
The static-mechanical deflector is a development of the French company Astato . The device increases the draft of the exhaust flow of the natural ventilation system due to the wind and the fan.
The nozzle is mounted on houses of any number of floors, reconstructed and new buildings.
In passive mode, the vacuum level created by Astato is equal to the sum of wind and gravity pressure. This value corresponds to the operation of a static deflector
After turning on the electric motor, the aerodynamics of the ventilation duct are maintained, the degree of vacuum is the total value of the fan pressure and pressure.
Deflector characteristics:
- Installation methods . Nipple connection for round ventilation ducts, through an adapter - for a group of air ducts or rectangular shafts.
- Control modes . Manual regulation and automatic regulation are permissible - via a pressure sensor or time relay.
- The material of manufacture is aluminum.
- The lineup . The Astato deflector is available in six positions, with a nominal diameter of 16-50 cm.
Modifications of the DYN-Astato are equipped with a two-speed fan, the cost of products is 1300-4000 USD. depending on the dimensions of the deflector.
View #4 - DS series deflector
The open-type static nozzle DS looks like the Astato deflector. But, unlike the French cap, the DS series models do not have moving parts. The cap contains three conical disks.
The umbrellas of this type of deflector are truncated and located opposite each other, forming a channel similar to a Venturi nozzle. The diameter of the central hole of the lower disk corresponds to the cross-section of the pipe. Brackets hold the mesh
The highest speed of wind swirl is observed in the truncated channel of the hood - above the ventilation pipe. The pressure difference inside the deflector and remotely from it causes additional vacuum, which increases thrust.
Features of the DS series model:
- the deflector is compatible with forced means of inducing air exchange - fans;
- a wind flow speed of 5-10 m/s increases thrust by 10-40 Pa - the data is valid at a relative humidity of 50°, air temperature +25 °C and a wind flow deviation of up to 30° from the horizontal plane.
Deflectors are available in 13 standard sizes. Designation of ventilation hoods: DS-*** , where *** is the internal diameter in mm . The DS-100 model has the minimum dimensions, the DS-900 has the maximum dimensions.
Type #5 - rotary turbine or turbo deflector
The dynamic deflector consists of a fixed base and a rotating turbine head.
The elements of the spherical cap are made of light, thin metal, which allows the drum with blades to start working in light winds - from 0.5 m/s.
The head rotates in one direction of the wind vector. There is a “partial vacuum” under the hood - the air at the top of the ventilation duct is rarefied, the likelihood of the ventilation overturning is minimized (+)
Advantages of a turbo deflector:
- efficiency is 2-4 times higher than that of static models;
- protecting the premises from overheating in summer and reducing air conditioning costs in hot weather;
- aesthetic appearance - the deflector head is made in the form of an elegant spherical cap;
- preventing the appearance of condensation inside the roof by lowering the temperature in hot weather;
- economical operation - the active deflector operates without electricity.
The turbo deflector removes excess heat, moisture, dust, vapors and harmful gases from the shaft from the building and under-roof space, thereby increasing the service life of the structural elements of the house.
The disadvantage of an active deflector is zero performance in calm weather.
The marking of Aerotek products is presented as TV-160, etc. The digital index indicates the cross-sectional diameter of the fixed base of the cap
Dynamic nozzles are available in a wide range. The products of the following companies are in demand: Aerotek (Russia), Turbovent (Ukraine), Rotowent (Poland) and Turbomax (Belarus).