Home / Installation, repair, maintenance / Decorating the walls near the stove - what heat-resistant panels are used?
To prevent such a nuisance as a fire from happening, heat-resistant materials are used to decorate the walls near the stove. Any such heat source not only heats the air in the room, but also heats up itself very strongly and therefore, the surrounding partitions can easily catch fire. In our case, these are walls and floors.
Finish options
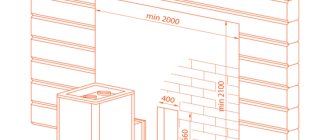
It is necessary to create heat-insulating structures or apply coatings of this type when the distance from the walls of stoves or fireplaces to the protected surface is less than the established standards. They are as follows: from the walls to the surface of the stove made of brick there should be at least 32 centimeters, to the heating device made of metal - at least a meter, and to lined metal fireboxes - at least 70 centimeters. In other cases, fireproof material is needed to decorate the walls in the place where the stove is located and underneath it. You can complete the design with the following types of coatings:
- Reflecting heat into the room. As a rule, this role is played by a stainless steel sheet or a special heat-insulating screen made of the same factory-made stainless steel.
- Protecting the surface due to its characteristics - physical and chemical. There is more choice here - fire-resistant gypsum plasterboard, mineralite, glass-magnesium sheet, various ceramics and porcelain stoneware slabs.
Both finishing options are quite effective, but mixed-type structures are often used, including both a reflective coating and an internal fire-resistant layer. These are the solutions that are used most often and provide the highest degree of insulation.
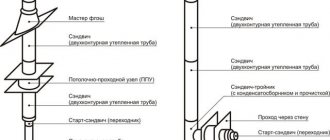
Technology for installing fire-resistant materialheat-resistant materials for finishing walls near the stove
Multilayer protective technology, using the example of wall cladding near a heater in a bathhouse, consists of a sequence of actions:
- A layer of vapor barrier and waterproofing is attached to a wall made of combustible material. As a vapor barrier, you can use a three-layer film consisting of foil, polyethylene, and kraft paper for strength. It is attached using a metal profile (wooden blocks can be used instead of a metal profile).
- Next, insulation is installed, for example, foiled mineral wool. It is placed inside the sheathing so that the foil layer is on top. The joints of mineral wool slabs must be sealed with aluminum tape.
- Using self-tapping screws, fire-resistant boards, for example, made of fiber cement, are attached to the sheathing. An alternative to fastening a multilayer structure is to install the plates with self-tapping screws through a sleeve. This creates a space between the slab and the wall.
- After fixing the slabs, they can be faced with ceramic tiles for aesthetics. To do this, a metal mesh is screwed onto the self-tapping screws onto the slabs, onto which heat-resistant adhesive is subsequently applied and the tiles are glued.
If the installation is carried out in compliance with the technology and ventilation gaps, the wall near the stove will not heat up and will not create a fire hazard.
A budget-friendly way to protect between a stove and a wooden wall is to use profile metal used for the roof. To do this, you will need two sheets of such metal and hollow tubes. Hollow metal tubes are attached to the wall, and a metal profile is mounted to them. The distance to the floor and ceiling should be at least 10 cm. The tubes are attached to the sheet in the same place as the first ones and covered again with the sheet. Hot air moves in the gaps between the wall and the floor, while the wall remains unheated.
Fireproof plasterboard
One of the simplest to implement, but far from the worst option in terms of its qualities. The sheets are easy to attach to any surface, they are not too expensive and after installation the structure can be painted in the desired color or its front side can be decorated with another type of decorative coating. If appearance and design is not of paramount importance, then this is the best option.
Advantages
When making a comparison between non-combustible materials and traditional products, a number of differences can be seen.
Among the advantages the following points can be noted:
- they are safe in their composition;
- do not burn, which means they do not emit smoke or harmful substances;
- have increased strength;
- significant resistance to mechanical damage;
- moisture-resistant material;
- not susceptible to mold and fungi;
- panels make it possible to level the surface, hiding its defects;
- the coating is not exposed to aggressive environments;
- high aesthetic qualities;
- durability.
Stainless steel protective screens
Such heat-resistant panels for finishing walls near the stove are used very widely. Due to the fact that the screen consists of several layers, it protects walls very effectively. The design of such panels is a stainless steel shell, inside of which there is a fire-resistant material. The combination of a heat-reflecting outer layer and a protective inner layer allows you to reduce the distance to the protected surface from the heat source to 5 centimeters.
Manufacturers and prices
- Basalt fiber panels cost of 1 sq. meter - from 390 to 690 rubles, depending on the decor of the front side, produced by ESCAPLAT;
On a photo panel made of basalt fiber - Rolled Fireproof Nonwoven Fabric – cost of 1 linear meter from 112 rubles, produced by OgneuporEnergoHolding, LLC, Moscow;
Photo Roll Fireproof Nonwoven Fabric - Non-flammable composition for plastering walls with a volume of 20 liters at a price of 410 rubles per bucket, produced by a company from Perm.
Minerite slabs
One of the most effective ways of protection. Ninety percent of the slab composition is ordinary gray or white cement, which serves as an excellent heat insulator. The remaining ten percent of the composition is reinforcing fiber and mineral fibrous material. Outwardly, they are not always beautiful and therefore they are often additionally decorated with artificial stone, tiles or painted.
Important: mineralite can easily withstand heating up to 150 degrees, but to more effectively protect the walls, it is better to leave an air gap between the mineralite sheet and the insulated surface. If this is undesirable or impossible, then the mineralite sheet is mounted on a heat-resistant substrate, which increases the effectiveness of protecting the structure.
In addition, the sheets can be deformed from heating and when installing two sheets at once, it is necessary to leave small gaps for temperature deformation.
Regulations
The following norms and standards are directly related to the production, certification testing of serial products, fire-resistant heat-insulating materials, and the possibility of their use to reduce the fire danger of protected objects:
On this topic ▼
Fire retardant plaster
Types for structures and applications
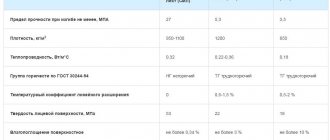
- GOST 4640-2011 on the production of mineral wool - the source material for the production of fire-resistant insulation, capable of operation in the temperature range - 180 to 700℃.
- GOST 21880-2011 on the technology of manufacturing pierced fire-resistant mats from mineral wool.
- GOST 32313-2011 – the same about frame slabs, mats, foil cylinders made of mineral wool that can withstand temperatures up to 1000℃.
- GOST 32314-2012 – on the types of fire-resistant insulation materials produced from different types of mineral wool used in the construction of construction projects.
- GOST 30244-94 – about flammability tests. The standard is not applicable to those classes of non-combustible insulation materials that are produced in the form of granules or ready-made liquid solutions.
- NPB 244-97 – on the fire hazard parameters of thermal insulation materials.
And also SP 112.13330.2011 - on fire protection of construction sites, SP 4.13130.2013 - on limiting the development of fire inside protected objects, SP 2.13130.2012 - on ensuring their resistance to fire, regarding the use of fire-resistant insulation in the design, construction of fire barriers, and manufacturing fire-resistant filling of openings in them; a general reduction in the fire hazard of buildings and structures as a result of the use of non-combustible types of insulation.
Other options
You can take a different route and build a protective screen around a heat source made of stone or brick. However, such structures are quite cumbersome and require some mason skills for construction and quite a lot of time for installation. Therefore, much more often, any sheet non-combustible material from those discussed above is used to decorate the walls behind the stove.
A sufficient degree of insulation and a very beautiful appearance can be ensured by decorating the surface with terracotta or ceramic tiles. However, in this case, the firebox will have to be placed at a distance of at least 30 centimeters from the walls. This is not particularly much, but in some situations it can become a problem. If aesthetics are still important, in such a situation you can create mixed protection: assemble the surface from non-combustible plasterboard or mineralite and finish it with terracotta tiles.
Application area
The greatest scope of application is all kinds of public spaces, these can be both work spaces and entertainment venues. Numerous criteria and complaints from fire inspectors against the owners of such facilities encourage owners to resolve issues related to fire safety on a one-time basis.
Modern non-flammable materials for wall decoration are known for their high aesthetic qualities and visually differ slightly from natural products. Thus, their use is advantageous in all respects. In private houses and apartments, such materials are less popular and are used in kitchen areas.
The usefulness of such materials is manifested when used in the decoration of open balconies.
Waterproofing wood. What are the features?
How to protect a wooden house from moisture? After all, he needs protection much more than others. Wood, even dried and processed, is a natural material subject to rotting and deformation.
To prevent the wood from deteriorating, it should be treated with a number of protective agents: an antiseptic - a solution against pests, a fire retardant - a fire-resistant compound, a protective varnish and, of course, a waterproofing solution. There are dual-action drugs: for example, an antiseptic that protects against water ingress. You can also find products that only protect against moisture.
There are two types of wood protectants: penetrating and film-forming. The first are more durable, as they create a fairly thick waterproof layer inside the wall. Film-forming materials are more susceptible to mechanical damage. Over time, the crust peels off. It is worth updating the coating regularly.
In a wooden house, both external and internal waterproofing of walls is required. To treat the inside of a room, it is recommended to use products that are less aggressive in composition.
Types of waterproofing
Let's consider the types of waterproofing that are currently used in construction.
Injection waterproofing
Complex, but effective. The wall is impregnated with a hydrophobic substance throughout its entire thickness, closing the slightest pores. To do this, passages are drilled along the entire wall, where the substance is injected through a pump. They perforate the walls from the inside - but as a result, the protection is double-sided, which is very convenient.
Where is it used? This type is popular when working with brick and concrete walls. It is the best option for a country house. Injection waterproofing is also used for the basement: to protect the walls on all sides, there is no need to dig up the house from the outside.
Pros:
- materials for injection waterproofing are environmentally friendly;
- monolithic protective layer without joints;
- uniform and reliable insulation throughout the entire thickness of the wall.
Minuses:
Materials. Injection waterproofing is made with acrylate and hydroactive gels, epoxy polymers, cement-sand compositions, and silicate-based products.
Penetrating waterproofing
The process is simple: covering the wall with mortar. And he himself will do everything “for you.” The distinctive feature of this method is indicated by the name itself: protective substances penetrate tens of centimeters into the wall, creating a thick and strong protective layer.
Where is it used? This is an option for concrete, reinforced concrete and brick. This method does not work with foam concrete. The main area of use is vertical waterproofing of walls.
Penetrating agents are not suitable for walls with significant voids or cracks.
Pros:
- non-toxic;
- durability;
- effective protection against aggressive environments.
Minuses:
- high price of materials;
- does not protect against pressure leaks.
Coating waterproofing
Involves covering surfaces with mastics. The mastic forms a strong waterproof film that tightly closes the smallest pores.
You don’t need any special skills to apply the mastic - you will need a regular roller for this. However, you should “spread” the material carefully and without gaps. Be sure to take breaks between approaches: do not take on a new layer until the previous one has dried.
Where is it used? This method is often used in the finishing of reinforced concrete, concrete, and metal structures. Widely used in waterproofing non-residential premises.
Pros:
Minuses:
- wears out quickly;
- spoils due to sudden changes in temperature.
Materials. “Coating” is done with various types of mastic: bitumen, polymer rubber.
Sprayed waterproofing
This is the application of liquid rubber by spraying. The desired surface is cleaned, primed and covered with material. The rubber layer provides 100% protection from moisture.
Where is it used? Rubber walls are not for residential premises. Sprayed moisture protection is most often used in basements and roofs.
Liquid rubber is the only “save” for basements in places with high groundwater levels.
Pros:
- strong rubber adhesion to almost any material;
- absolute waterproofness;
- speed of work.
Minuses:
- high price;
- the need for special tools for coating;
- the material does not allow air to pass through at all.
Today, spraying liquid rubber is completely fireproof.
Pasted waterproofing
Its essence is to cover the wall with bitumen material: panels, sheets or rolls. The task is to eliminate all the unevenness of the wall, prepare the surface and attach the insulator. The glue is often mastic.
Where is it used? The classic use of this method is to insulate foundations and basements. Often, bitumen sheets - for example, roofing felt - are used to cover the roof.
Pros:
- quick covering of even the largest surfaces;
- ease of use;
- strength - materials can withstand heavy loads;
- high degree of vapor barrier;
Minuses:
- not suitable for hard-to-reach places;
- waterproofing cannot be done in winter;
- Can not be repaired.
Materials: bitumen cardboard, varieties of hydrosol, bitumen-polymer products: isoelast, technoelast.
When using adhesive waterproofing, an overlap must be observed - at least 10-15 cm.
Film waterproofing
Everything is simple here: wrap it with film - no water will get in. Waterproofing the walls of residential premises is not done with film - it does not allow air to pass through at all. This material is used to protect roofs, foundations, and floors.
If you insulate the foundation with film, you definitely need a geotextile backing. As with the previous method, overlap is required. The seams should be carefully secured with tape.
Don't expect cheap film to last long. Of course, the material does not allow water to pass through. There is another disadvantage - it breaks easily. Cheap polyethylene can be laid in two or three layers - but sometimes this does not help. High-quality waterproofing film is expensive.
A progressive method of film waterproofing is the use of a membrane. This is a polymer material that does not allow moisture to pass through, but can also breathe. At the same time, the membrane provides an effective vapor barrier.
Pros:
- efficiency;
- durability;
- ease of installation;
Read also: Paintwork on metal
How can I make this work?
- Buy only high-quality materials: choose trusted manufacturers and remember that building materials, like food, have an expiration date. More expensive is not always better, but a good waterproofer will never be too cheap.
- Hackwork is unacceptable. Under no circumstances leave cracks, gaps, or weak points. If the waterproofing is done by a team, carefully monitor the quality of the work. Are there any flaws? Make it change!
- Choose the material that is best suited for your walls. What is the best way to cover a particular house is in the next paragraph.
- Don't ignore the instructions. It was said not to install this waterproofing in winter - wait until spring.
- It's not worth saving. Do moisture insulation wherever necessary. Don't expect a smaller layer of solution to be as effective.