- February 23, 2020
- Construction
- Daisy Angel
Concrete is one of the most popular materials in construction. The most suitable conditions for its hardening are considered to be an ambient temperature of + 20 ˚С. But sometimes you have to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures. In this case, it is better to use the services of specialists.
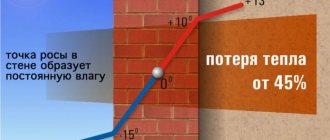
Water can become an obstacle to quality work. It is needed in concrete not only for fluidity. Water performs an important function in the hardening process. At low ambient temperatures, it changes from a liquid state to a solid state (turns into ice). This stops the hardening process and promotes the destruction of bonds formed before freezing.
Concrete can harden even at a temperature of -4 °C. However, if it drops below + 5 ˚С, then the hardening process slows down, and the strength gain is suspended and resumed only when it becomes warmer outside. The longer the stagnation in the hardening process, the less strength the material will gain. This means that at low temperatures it is necessary to provide conditions under which the concrete will not freeze and will continue to gain strength.
Use of additives
If you are interested in knowing how to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures, then you should familiarize yourself with the technology of using additives. Antifreeze substances are not very expensive and are widely available. If you purchase ready-made concrete, then all additives should already be in it. In this case, the temperature values in a specific area are taken into account.
Additives contain chemical impurities - salts of monocarboxylic acids, sodium formate and nitrite. They speed up the hardening process, prevent water from freezing, and also increase the final strength of the material. The main disadvantage of using various additives is that such substances cope with their work only at -5 ˚С. If you are interested in at what negative temperature concrete can be poured, then you should know that in severe frosts, although some additives will work, hardening will not begin as quickly as required by technology. Ultimately, the lack of strength can be 30%. Some additives are aggressive towards metal reinforcement. They destroy it, causing the structure to lose strength.
Features of concreting in the winter season
Low temperatures generally have a negative impact on the quality of concrete placement. This material is formed due to the hydration of various minerals. It is known that for a successful hydration process a temperature above zero is required, otherwise the reaction stops. But this is not the only problem: due to cold, the material expands due to an increase in internal pressure, the reinforcement does not adhere well to the concrete, and the resulting material is not strong enough.
The main task in winter is to ensure the strength and reliability of concrete. The minimum permissible strength is 30-50% of the design, it is achieved already on the 4th – 6th day.
Benefits of Using Supplements
Many people want to know how to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures. In order not to make a mistake, you first need to familiarize yourself with all the advantages and disadvantages of a particular method. The most common technology is the addition of additives. They have one significant advantage - this approach allows concreting to be carried out at any time of the year.
Using additives, it is possible to transport concrete mortar at low temperatures. To ensure high-quality setting of the material, it is not necessary to use additional heating systems. When antifreeze additives are added, a concrete monolith receives additional strength, and the solution consumption is reduced (if compared with a material prepared according to a conventional recipe).
The main disadvantages of antifreeze additives
In order to pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures without compromising the quality of the material, it is necessary to become familiar with the disadvantages of anti-frost additives. Firstly, they can lead to the appearance of salt crystals on the surface, which are almost impossible to remove. Secondly, sometimes they reduce the strength of concrete stone. This happens if the proportions are calculated incorrectly, and the cooking or setting technology is broken. Thirdly, individual components may be unsuitable for use in residential areas as they are toxic.
Heating technology
Many novice craftsmen do not know at what temperature concrete should be heated. It is important to take into account one rule: if the thermometer drops below + 5 ˚С, then the hardening process slows down. To avoid this, heating must begin when the ambient temperature drops below this mark. You can do this as follows:
- pass current through the concrete using an electrode;
- pass current through a wire pre-laid inside the material.
The first method is cheaper, since metal rods can act as electrodes. If you follow the rules, you will need special equipment for these purposes. However, some craftsmen connect a welding machine to the reinforcing electrodes, passing current through the solution and heating it. Reinforced concrete is heated at a voltage of up to 127 V. Without metal reinforcement, voltages of up to 380 V should be used.
The second method involves additional costs for the heating cable. It is laid with a reinforcement frame. Current is connected to it through substations. This method is more expensive, but is more effective compared to heating using electrodes.
The main disadvantage of the above method can be called financial costs. In addition, when heating, you need to constantly monitor the temperature. If it rises excessively, this will cause the material to dry out and may compromise the strength of the structure. If frosts are severe, the formwork should be additionally insulated. Now you know at what temperature you need to heat concrete.
What to look for when concreting a foundation
In order to competently carry out construction work and reduce further costs of repair and operation of the foundation to a minimum, you must adhere to a few simple rules:
- The foundation design should not allow cracks to form under any load.
- The entire volume of concrete must be poured without technological and “cold” joints, that is, in one technological cycle.
- If the work involves the formation of technological seams, they must be sealed using swelling cords, sealants or waterstops.
- Working reinforcement must be installed in strict accordance with the design; the thickness of the protective layer of concrete must be at least 15 mm.
- It is necessary to compact the laid concrete with vibrators or use self-compacting concrete.
- Newly laid concrete needs to be maintained.
Warming during hardening
It is allowed to use conventional insulation methods. This is true if the ambient temperature is not lower than 5 degrees Celsius. Most often, the formwork (if any) is insulated, as well as visible parts of the concrete. For this purpose, you can use all kinds of materials, such as sawdust or polystyrene foam.
One of the most popular ways is to create a tent around the object. Heating guns can be installed inside such a structure. This method has the disadvantage that the concrete must be at a predetermined temperature when supplied. In addition, conventional insulation without additional heating will be ineffective if there is severe frost outside.
Types of antifreeze additives
To pour concrete at sub-zero temperatures, which additive should I choose? The following types of these products are available on the market:
- Antifreeze.
- Sulfates.
- Antifreeze additives.
Antifreezes are substances that reduce the crystallization temperature of a liquid and speed up the setting time of the material. Sulfates are additives that accelerate hardening as much as possible and generate heat, so that the components of the solution mix faster and become a homogeneous mass. This lowers the freezing point. On sale you can find antifreeze additives called accelerators. These components are able to increase the rate of dissolution of silicate components, which react with the products of solution hydration. This ensures the formation of basic and double salts, which reduce the freezing point of the mixture.
Antifreeze additive CemFrio
Among the inexpensive offers on the market, CemFrio should be highlighted. It is designed to increase the strength of material poured at sub-zero temperatures. This complex additive is used not only for concrete, but also for other mortar mixtures. It accelerates hardening and provides a plasticizing effect. Concreting with its use can be carried out at temperatures up to - 20 ˚С.
Prefabricated monolithic or monolithic concrete, as well as reinforced concrete structures can be erected with its help. The additive prevents the possibility of their destruction when exposed to negative temperatures. This substance should be dosed with a larger margin, focusing on the approximate readings of the thermometer during the day (not only during the day, but also at night) throughout the entire stage of hardening of the solution. In this case, the strength gain of concrete at sub-zero temperatures will be ensured in the range from + 10 to - 20 ˚С. At the same time, the need to add water to mortar mixtures is reduced by 5%, and the strength characteristics increase by 10%.
How to heat concrete yourself
Now you know that you can pour concrete in cold weather in different ways. If you do not want to use the appropriate additives, use the solution heating method. For this purpose, they most often work with electrodes. This is due to the simplicity and low cost of the method, because there is no need to use heating wires and transformers. This method is based on the physical properties of electric current, which passes through a conductor and releases a certain amount of heat.
The conductive material is concrete. When current passes through a water-containing solution, it heats it. If the concrete structure contains a reinforcement frame, it is not recommended to apply a voltage of more than 127 V to the electrodes. If such a structure does not exist, you can use both 220 V and 380 V. It is not recommended to apply a higher voltage.
If we pour concrete in cold weather, we can use different materials for heating, for example, rod electrodes. To create them, you should take metal reinforcement with a diameter of 8 to 12 mm. Such rods are inserted into concrete at a certain distance from each other and connected to different phases.
If the design is complex, heating electrodes will be indispensable. Fiberglass reinforcement is not suitable for such purposes, since it is a dielectric. Electrodes in the form of plates can be used. In this case, the heating circuit is very simple. The plates must be placed on opposite sides of the poured solution and connected to different phases. The passing current will heat the concrete.
Sometimes craftsmen use narrow stripes. The principle of their operation is the same as that of the plates. Electrodes can also be string electrodes. They are used when pouring columns, pillars and beams. The principle of operation is similar. The strings should be connected to different phases. Warming up with electrodes must be carried out with alternating current, since direct current passing through water promotes electrolysis. In this case, the water will chemically decompose without fulfilling its role in the hardening process. Now you know whether concrete is poured at sub-zero temperatures.
How to pour a foundation in winter: detailed instructions with photos and recommendations from experts
Traditionally, building a house has always been a “summer” activity, and among private developers, few even thought of starting active work in the winter. However, it just so happens that Russian winters are quite long, and in some regions the cold season generally reaches a period of 6 ÷ 8 months. And if you exclude them from the process of constructing a building, then the construction of a house can take several years. To speed up this process, special technologies have been developed and special materials have been produced that make it possible to start concrete work or not stop it even in the winter cold.
How to pour a foundation in winter
However, in order for the foundation of the building to be reliable and monolithic, you need to very accurately understand how to pour the foundation correctly in winter. Knowing all the nuances of this rather complex process and following all the technological recommendations, you can start working at low temperatures so as not to waste winter time in vain. Often, starting construction during this period, the owners expect to move into a finished new house by the fall.
In addition to the need to speed up the construction of a house, the need to fill the foundation in winter may also be due to specific reasons. For example, such measures are also resorted to due to the fact that the soil in a given area is characterized by increased flowability, so it will be much more convenient to work with it when it is in a frozen state.
When laying the foundation, you need to remember that it is not recommended to install a columnar structure in winter, since small volumes of concrete, when hardened, are incapable of retaining heat in any way and quickly cool down, disrupting the hardening and maturation processes of the solution. That is why, if the foundation is poured at sub-zero temperatures, you need to choose a monolithic or strip option.
It is necessary to begin work on laying out the foundation for the construction of a house with preparatory work, which in winter is usually characterized by increased labor intensity.
Preparatory work
- The place where it is planned to build the building must be cleared not only of snow, but also of the surface layer of soil.
- Next, a general marking of the cleared area is carried out - this is done by installing pegs on which a marking cord is pulled - it will visually indicate the external dimensions of the future foundation.
Carrying out marking and tracing work at the construction site
The next step is marking the width of the required trench - also with installing pegs and pulling the rope. To make it convenient to dig a foundation pit, its inner boundary is outlined along a stretched rope, and an even strip is hollowed out in the ground along it using a hammer drill or a pneumatic jackhammer - this will mark the edge of the foundation.
- Next, a trench is dug, which must have a depth of at least 500 ÷ 750 mm. The depth is usually calculated depending on the type of soil.
If the soil cannot be shoveled, then you should gradually crush it with a hammer drill or pickaxe. In this case, the earth is removed from the pit in layers.
- When the trenches are completely dug, they are prepared for pouring concrete. To do this, sand is poured into the bottom - it must be dry, so you need to choose material that was stored indoors or at least under a roof. The sand cushion will be an excellent waterproofing layer for a strong foundation if it is well compacted. After compaction, the layer thickness should be 80 ÷ 100 mm.
A layer of crushed stone of the same thickness is poured onto the sand cushion and also thoroughly compacted.
- Next, from the bottom of the trench and to the height of the future foundation, formwork is built from boards. If smooth, high-quality boards are used for it, which are tightly fitted to each other during assembly, then additional insulating materials do not seem to be required.
Formwork for a “winter” foundation with a reinforcing belt
If cracks have formed between the boards, and there is a risk of mortar leaking through them, then it is best to waterproof the formwork with a plastic film with a thickness of at least 200 microns before installing the reinforcement structure.
It would be more expedient to provide a layer of film waterproofing on the inner walls of the formwork
Good advice is to use such an insulating layer in all cases. It will maintain the correct water balance in the concrete solution (water will not flow out or be absorbed into the formwork material), and the maturation of concrete will proceed more evenly and efficiently.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the detailed technology for constructing formwork for the foundation with your own hands. This article describes the main tasks of formwork and the technology of its step-by-step construction.
In addition, we advise you to pay attention to the material - about waterproofing the foundation, because... It is waterproofing that will preserve the integrity of the foundation for many years.
Another option for waterproofing formwork is to use ordinary inexpensive roofing felt.
- You can often use permanent formwork made of polystyrene foam separately for foundations, which will at the same time act as insulation for the mortar being poured and will not allow it to quickly harden. The hardening process will take place gradually, which is very important for the strength of concrete.
A modern convenient solution - permanent formwork made of hollow polystyrene foam blocks
- Next, a structure of reinforcing bars is mounted into the prepared formwork, which are connected to each other by welding or twisting wire. For this design, metal rods with a diameter of 8 to 15 mm are suitable - this parameter will depend on the width of the foundation and the planned design load on it.
After all the preparatory processes have been carried out, you can begin to calculate the consistency and component composition of the solution. These parameters are selected depending on the approximate temperature at which concrete work will be carried out.
Pouring concrete
When preparing a solution, it is necessary to take into account such factors as the brand of the solution, the outside temperature, the quality of the material, and special additives that can delay the crystallization of water at low temperatures. Without taking into account all these nuances, the solution after hardening will not be as strong and durable as planned, since it will quickly begin to crumble. In this case, the work will have to be completely redone, because such a foundation simply will not withstand the load from the walls.
- To mitigate the effects of low temperatures, after installing the formwork, before pouring concrete into it, a temporary tent is erected over the structure. Its frame can be put together from boards and timber - the base must be rigidly installed and have a height higher than human height, since the builder will have to work under it. Metal parts – profiles and reinforcement – can also be used for a temporary frame.
A tent over the poured foundation will allow you to maintain at least the minimum required temperature.
From the outside, the structure is covered with reinforced polyethylene film, which has sufficient strength to withstand wind loads and the weight of snow cover. The roof of the awning must have a steep enough slope so that precipitation does not linger on it, otherwise even the reinforced film can tear, and the presence of an awning will simply lose its meaning.
The sheets of film covering the foundation must be securely fastened together, or even better, purchase or rent a ready-made specialized awning, which you simply need to install over the structure.
Awnings for the construction of a temporary tent in folded form
Such a temporary tent will allow you to maintain the required temperature for the solution to gradually harden without the risk of freezing, that is, the tent will become a kind of greenhouse that will trap heated air. In severe frosts, under such shelter you can turn on heating devices, for example, heat guns.
Maintaining the temperature can be achieved by installing an electric or gas “heat gun”
To pour concrete, it is necessary to create a temperature in the tent of at least 5°C; for concreting without the use of antifreeze additives, it is critical. Lower temperatures will lead to crystallization and destructive processes.
But even at a critical temperature, the setting of concrete and its hardening will take much longer, therefore, if it is possible to postpone the pouring of the foundation to warmer days, then it is recommended to do so. By the way, if you analyze the table with the maturation times of concrete under different temperature conditions, you can see that the time gain in some cases will be very insignificant.
- When pouring the foundation in winter, it is recommended to use finely ground cement to prepare the mortar, which generates more heat when reacting with water and additives than regular cement. To mix concrete, it is best to use water heated to 40 ÷ 80 degrees.
| Brand of cement used | Temperature of water when preparing the solution | Temperature of concrete when leaving the concrete mixer |
| Portland cement; slag-Portland cement; Portland cement grade below 600 | 80 | 35 |
| Rapid-hardening Portland cement and Portland cement grades below 500 | 60 | 30 |
| Aluminous cement | 40 | 25 |
When mixing a solution with hot water, it is first mixed with additives, and then introduced into the cement in parts and mixed thoroughly. since increasing the time for preparing the solution helps to maintain the desired temperature in the solution for a longer period. A homogeneous mass of solution better fills the entire space of the formwork, as its fluidity increases.
Medium or small crushed stone is often added to a thin, well-mixed concrete solution, which will add the rigidity necessary specifically for the foundation.
Crushed stone of small or medium fraction is often added to the foundation solution.
In addition to crushed stone and additives for frost resistance of concrete, plasticizers are often added to it; they contribute to the strength and moisture resistance of concrete, as well as its adhesion to reinforcing structures. Thanks to plasticizers, it is possible to reduce the consumption of cement mortar by 25%.
- Another way to keep the foundation warm is to connect it to a 12-volt electrical cable. It will heat up the reinforcement bars, which in turn will give off heat to the solution, preventing it from freezing. The significant disadvantages of this heating method are the complexity and cumbersomeness of the preparatory work, the need for special equipment, the wasteful use of electricity, and therefore very significant financial costs.
- You can hear many different opinions about the benefits of special anti-freeze additives in concrete mortar, they say, they make it possible to pour the foundation in conditions of negative temperatures without any other measures for temporary insulation of the structure. Is this so, and what are anti-frost additives in concrete?
Will antifreeze additives solve the full problem?
Alas, no... These are special chemical compounds that solve two main problems. Firstly, they increase the density of the aqueous base of the solution, which means they sharply lower its freezing point. Secondly, they contribute to a kind of catalysis of the concrete ripening process by more actively involving air oxygen molecules in the reaction precisely under conditions of low or even negative temperatures.
In construction practice, sodium nitrite or formate, potash, calcium hydrochloride, and lignosulfonate are usually used to prepare “winter” solutions. Such reagents can be purchased in specialized stores, but preparing high-quality concrete on your own, without special equipment, without special calculation methods and correct dosage, is extremely difficult, to say the least. An incorrect component ratio can completely ruin concrete, which, even under the most optimal hardening conditions, will turn out to be brittle, crumbling, loose, etc. In addition, it must be borne in mind that the use of special additives can have a “detrimental” effect on the condition of the reinforcement - not every metal is suitable for these purposes.
Another consideration that is not at all in favor of antifreeze additives. Yes, they allow certain technological processes to be carried out at subzero temperatures. However, this does not mean speeding up construction work. Take a look at the table - it shows the approximate time frame for concrete to gain grade strength at low temperatures using antifreeze additives:
| Type of antifreeze additive | average temperature during ripening | 1 Week | 2 weeks | 4 weeks | 3 months |
| Sodium nitrite | -5° C | 30% | 50% | 70% | 90% |
| -10° C | 20% | 35% | 55% | 70% | |
| -15° C | 10% | 25% | 35% | 50% | |
| Potash | -5° C | 50% | 65% | 85% | 100% |
| -10° C | 30% | 50% | 70% | 90% | |
| -15° C | 25% | 40% | 60% | 80% | |
| -20° C | 23% | 35% | 55% | 70% | |
| -25° C | 20% | 30% | 50% | 60% |
Conclusion: even with relatively mild frost - about -5°C, and with the use of anti-frost additives, it is possible to talk about the readiness of the foundation to continue any further construction work only after 3 months. So, does it make sense in the context of private construction to rely on such technology if there is practically no gain in time, and the quality of the solution can significantly decrease? What is profitable and justified during large-scale industrial construction with its laws of planning and logistics, in the conditions of a private small construction project can turn out to be a completely unjustified, unnecessary waste of effort and money.
Prices for various types of antifreeze additives in concrete
Antifreeze additive in concrete
Video: pouring a strip foundation in winter
Some important recommendations
So, let's go back a little to the advisability of pouring the foundation in winter. It is usually carried out in the following situations:
- Construction must be completed within a strictly defined time frame, without the possibility of postponement.
- The climatic conditions of the area where construction is taking place are unsuitable for carrying out this process during normal summer periods.
- Loose soil makes it extremely difficult to construct a foundation in the summer, and it can only be built in hard, frozen soil that can maintain the desired shape of the trench for a long time.
- Saving money, since in winter the prices for building materials are much lower.
- Construction companies reduce prices for their services in winter, due to the lack of a large number of requests for work.
Before starting work, it’s worth weighing everything very carefully - wouldn’t it be more profitable to postpone the start of pouring to spring?
But, despite the above arguments for saving on materials, building a foundation in winter will always cost more than at above-zero temperatures, since large amounts of electricity will be required for heating. Therefore, when planning these events, you first need to carefully calculate everything and choose the option that will not only help you save personal funds, but will also create comfortable working conditions.
If you still decide to fill the foundation in winter, then you need to know some of the nuances of this process that will help create a high-quality foundation for the future building:
- The materials used in the preparation of the solution must be of high quality. It is unacceptable for the components to be frozen, with inclusions of snow or ice. Therefore, it is worth purchasing components for the solution that were stored only in the right conditions and at positive temperatures.
Better yet, don’t bother with preparing “winter” concrete yourself, purchasing a ready-made solution balanced for specific conditions of use from local manufacturers.
- The solution is poured into the formwork at one time and, if possible, as quickly as possible, so that negative temperatures do not have time to affect the ingredients of the solution.
This is another argument that it is impossible to prepare and pour a large amount of mortar on your own at one time - it is better to take advantage of the offers of companies that will manufacture, deliver and pour concrete into the formwork. You will only need to quickly distribute the solution over it yourself.
It is almost impossible to independently prepare a solution for “winter” pouring of the foundation, since it is necessary to quickly and uniformly fill the entire volume of the formwork
- You cannot pour the solution in layers, as cracks may form between them, into which moisture will penetrate, and at low temperatures it will turn into ice, which can destroy the hardened concrete.
Concrete maturation processes
Concrete poured and distributed over the formwork goes through two stages until it is completely ready - setting and hardening.
- The first stage takes place within 20 ÷ 30 hours. At this time, the concrete becomes more dense, but not strong enough for further work.
- The second stage is the hardening and beginning of hardening of the concrete, since the latter lasts quite a long time. The hardening period depends on temperature, humidity, quantity and quality of additives, as well as the brand of concrete solution.
The most favorable temperature for pouring and hardening of concrete is considered to be from + 15 to + 25 degrees, and the closer it is to the highest point in a given “corridor,” the faster the hardening and hardening will take place. It is clear that creating such conditions in winter is simply unrealistic.
The grade of concrete determines its strength 27–30 days after it is poured, if the work was carried out under optimal temperature and humidity conditions. The higher the grade of the solution, the faster the foundation will be ready.
The rate of hardening and maturation of the solution directly depends on the temperature at which these processes take place. If the temperature changes, the processes slow down or speed up along with it. Strengthening of the finished foundation proceeds faster if the poured mass is maintained at an optimal temperature for this process using heating.
It is also necessary to take into account that if the temperature in concrete drops below + 4 ÷ 5 degrees, then the maturation processes slow down almost to a minimum, freeze, and can continue again only when external conditions are normalized. However, such jumps have an extremely negative impact on the structure of the created concrete structures.
At negative temperatures, the hardening of concrete stops completely, since it is mixed with water, and it crystallizes. When positive temperatures return, the concrete thaws and hardening may continue, but there will no longer be an optimal combination of materials and the required strength of the foundation.
Only after the concrete in the foundation structure has completely hardened will it not be afraid of any frost.
For greater clarity, here is another table that shows how temperature conditions affect the maturation of concrete structures. You can roughly estimate the timing of the work in order to make a preliminary conclusion whether it makes sense to get involved with laying the foundation in winter.
| concrete hardening time, days | -3° C | 0°C | +5° C | +10° C | +20° C | +30° C |
| 1 | 3% | 5% | 9% | 12% | 23% | 35% |
| 2 | 6% | 12% | 19% | 25% | 40% | 55%٭ |
| 3 | 8% | 18% | 27% | 37% | 50%٭ | 65% |
| 5 | 12% | 28% | 38% | 50%٭ | 65% | 80%٭٭ |
| 7 | 15% | 35% | 48%٭ | 58% | 75%٭٭ | 90% |
| 14 | 20% | 50%٭ | 62% | 72%٭٭ | 90% | 100% |
| 28 | 25% | 65% | 77%٭٭ | 85% | 100% | — |
A few explanations about the table:
- The percentages are calculated based on the reference brand strength for concrete mortar M200 - M300 made from Portland cement M-400 or M-500 without the use of additives.
- Values with one asterisk (٭) are the conditional terms for the possible removal of formwork of a poured foundation without the risk of deformation of the structure.
- Values with two asterisks (٭٭) are the possible time frame for resuming safe construction work on a poured foundation.
Cement prices
Cement
Video: example of pouring a foundation in winter
Having learned all the nuances of pouring concrete in winter, we can come to the conclusion that the best option would still be to carry out this technological process at favorable temperatures. If this needs to be done precisely at this time, then it is better to entrust this stage to professional builders who have experience in such work and the appropriate special equipment. Amateur work in such a matter can be extremely destructive - a huge amount of amateurishly done work can simply be ruined.
Infrared and induction methods
If you are thinking about how to pour concrete in sub-zero temperatures, you can also use the induction method. It is mainly used in crossbars, beams and purlins. This method is not very common due to the complexity of the device. It consists in the fact that the insulated wire creates induction and heats the fittings around which the element is wound.
Warming up using infrared rays is based on the ability of the latter to heat the surface of transparent objects with heat transfer throughout the volume. When using this method, the concrete should be wrapped in a transparent film, which will transmit the rays through itself, preventing the heat from quickly evaporating. The advantage of such heating is that transformers do not need to be used. The method also has a drawback. It is expressed in the inability of infrared radiation to uniformly heat large structures.
If you plan to pour concrete in sub-zero temperatures, you should know that the method described above is only suitable for thin structures. Regardless of what type of electric heating is used, you need to monitor the temperature. If it rises above +50˚C, it will create dangerous conditions. The heating rate (as well as cooling) should not exceed 10 ˚C per hour.
Increasing the grade of concrete for water resistance and frost resistance
Concrete mixture is a popular construction material for many reasons. First of all, due to reliability and strength, durability and ease of use, the ability to create a wide variety of projects based on the composition, as well as other qualities, including high levels of water resistance and frost resistance.
By improving these qualities, we increase the general characteristics of the material, making it absolutely problem-free in subsequent maintenance and increasing its service life.
It has long been known that special finishing or even waterproofing of concrete does not always cope with the task, and it quickly deteriorates due to exposure to the same atmospheric phenomena. We definitely don’t need this at our dacha, because if we are building a house, garage or even a small gazebo, we need the structure to last for a very long time.
Therefore, it is advisable to use special additives that have a positive effect on the quality and characteristics of concrete, especially when it comes to foundations and plinths, where protection is most needed. They can also include floors in the shower, on the area near the garage, where we often wash the car, in swimming pools, as well as in structures that are built on sites with a high groundwater level.
To obtain the desired characteristics, bituminous substances, surfactants, as well as components with the maximum inclusion of sodium aluminate are introduced into the composition. They work simply - they fill the pores in the finished concrete.
We have already said that often not one, but several additives are used at once, or several characteristics are improved with a certain composition. So, to improve water resistance qualities, you can use silicate glue, the same liquid glass, which increases the grade of concrete in terms of frost resistance and water resistance, and also increases the setting speed of the mixture and future strength.
What other substances can be used to heat concrete mortar?
We looked at how many degrees below zero it is possible to pour concrete. It should be said that antifreeze additives are most often used. Among others, it is allowed to use calcium carbonate, which is also called potash. This crystalline antifreeze component accelerates the hardening of concrete and is recommended for use exclusively together with sodium tetraborate (sulfide-yeast mash). Many people know it better under the name “borax”.
Calcium carbonate added in its pure form may reduce the strength of the structure. The amount of sodium tetraborate and mash should be no more than 30%. When choosing additives for concrete at sub-zero temperatures, you must take into account that potash is a dangerous substance. It can only be used in compliance with safety precautions. Sodium tetraborate can be used as a stand-alone additive. This additive is a mixture of sodium, ammonium and calcium salts. The sodium tetraborate impurity preserves the structure of the structure. Borax eliminates the occurrence of cracks and reduces the water permeability of concrete. Its strength increases by 30%.
Filling an armored belt at sub-zero temperatures
The reinforcing belt is designed to evenly distribute the load from the upper rows of masonry to the lower ones. It seems to connect the entire structure into a single whole. which significantly increases its overall strength and durability. The armored belt is made from steel rods laid around the perimeter, which must be welded together into a single structure.
When constructing a structure from gas silicate blocks, a reinforced belt is especially important. Such blocks quickly crack at the slightest movement of the soil or during shrinkage of the base. When installing a roof on such blocks, an armored belt is also necessary, since it is impossible to attach the timber to the blocks - they can crack. To avoid deformation of the walls and the building as a whole, a welded reinforced belt is simply necessary. It is welded into a solid structure, laid on top of the masonry and filled with concrete. It is sealed with mortar on both sides so as not to disturb the thermal insulation of the walls. Concreting of the belt is allowed in the cold season only using the above methods.
Working with concrete mixture at low temperatures is allowed in cases where there is no other option, because the optimal hardening temperature of the mass is from +5 degrees to 25.