The temperature regime during concreting is one of the main criteria for the quality of work in accordance with SNiP and GOST standards. Considering the variability of climatic conditions and the need to carry out work in the off-season, as well as in the cold season, temperature control becomes especially important. We will look at what temperature is best for concreting, and also touch on ways to artificially ensure optimal conditions.
The concreting temperature is an important parameter for the normal course of the mixture hardening reaction.
How concrete gains strength
Concrete is an artificial stone. It consists of crushed stone, sand, cement, water and special additives. Crushed stone and sand provide strength, while cement and water form the “glue” that forms the monolith. Special additives make it possible to give concrete the necessary characteristics: rapid strength gain, the ability to lay in winter, frost resistance, and so on.
Concrete gains strength gradually; this process consists of two stages.
Grasping
– this is a loss of mobility of the solution. Its speed depends on the air temperature. For example, if it is +5 °C outside, the concrete will set in 15–20 hours, but the reference, or design, temperature is considered to be +20 °C. With it, setting occurs 1–3 hours after mixing the concrete mixture, that is, mixing all components with water. Before setting begins, you need to have time to place the mixture in the formwork, compact and level it.
Strengthening, or hardening
is the process of achieving a given strength by a concrete mixture. The optimal conditions for its collection are a temperature of +20 °C and a humidity level of 80%. The estimated period of “hardening” to brand strength at normal temperature and without additional measures is 28 days. Then the strength gain of concrete slows down, but does not stop growing throughout its entire service life.
Brand strength is an important characteristic of concrete. It is designated by the letter “M” and numbers from 50 to 1000 - the higher the index, the stronger the concrete. Physical and mechanical characteristics are determined by the selection of the composition of the concrete mixture, its water-cement ratio, as well as the quality of the components used: fillers, cement, water and additives.
Special antifreeze additives for the solution
To increase frost resistance, special chemical components are used. They make it possible to carry out work down to a temperature of -25°C.
Additives – increase hydration in frost conditions. They accelerate setting and hardening in combination with additional heating of concrete.
Antifreezes are compounds that increase the adhesion properties of a solution under any operating conditions. Additives are divided according to the main active ingredient included in the composition:
- Sodium formate. Increases the accumulation of salts in the monolith, used only in conjunction with plasticizers.
- Sodium chloride. Provokes corrosion of reinforcement and prevents rapid thickening of the solution. Suitable for Portland cement based mixtures.
- Sodium nitrite. Not used for alumina mixtures. Working with the solution becomes possible down to -15°C.
- Calcium carbonate (potash). Increases the operating temperature range to -30°.
Plasticizers - increase the density of the mixture, reducing the cost of cement and water. The working time for concrete with these additives is much longer, which allows you to take your time when laying.
Hardening accelerator - reduces working time, increases the strength of finished monoliths, but reduces the plasticity of concrete.
Complex additives - combine several ways to improve frost-resistant qualities.
The nuances of using additives:
- The operating conditions of the concrete structure are taken into account. For example, if the monolith will be exposed to intense gas, the concrete solution should not contain additives obtained from the reaction of calcium and hydrochloric acid.
- It is not recommended to mix additives on your own to improve various properties of the solution. The chemical elements included in the composition can negatively interact with each other. It is better to use ready-made complex additives.
- The presence of outlet and insert elements implies the use of antifreeze. It is added to the solution at the mixing stage.
Why increase the water resistance of concrete?
The higher the water resistance of concrete, the less susceptible it is to water pressure, as well as the effects of chemically aggressive substances in the soil and groundwater: acids, alkalis, salts, and so on. The water permeability of concrete is negatively affected by excess mixing water, undercompaction of the concrete mixture and lack of maintenance of freshly laid concrete.
Water that has not entered into the hydration of cement (the so-called transformation of a plastic mass into a monolith) forms pores in the concrete after evaporation. Some of them are not closed and form end-to-end channels. Moisture penetrates through them into the foundation, which expands when freezing, which contributes to the further destruction of concrete.
To reduce the amount of mixing water while maintaining the mobility of the concrete mixture, plasticizers are used. They reduce the water-cement ratio, reduce the pore volume in concrete and increase its density. It should be taken into account that it is necessary to select the composition of a specific concrete mixture in laboratories, taking into account the features and characteristics of the materials used: cement, coarse and fine aggregates and various additives.
During installation, special attention is paid to compacting the concrete. The concrete mixture must completely fill the required space without creating voids. This is especially important with dense reinforcement of the structure. For these purposes, special devices are used - deep and surface vibrators.
How to care for concrete after pouring
In concrete with a low water-cement ratio, it is necessary to retain water, which is needed for the hydration process. If this is neglected, the quality of the final product will noticeably decrease. The standard concrete care regimen involves moistening the freshly laid foundation every 3-4 hours for the first 3-5 days after pouring, depending on the ambient temperature. Also, the concreting area is covered with damp burlap or film, and special film-forming compounds are used.
What are penetrating additives
To increase the water resistance grade of concrete, mineral materials of penetrating or penetrating action are often used. They are added to the mixture during preparation or applied to a prepared surface, that is, cleaned of dirt and cement laitance, as well as a water-saturated surface using a plaster sprayer or brush.
Active chemical additives in the material react with the components of the concrete mixture. As a result, insoluble compounds or crystals are formed. They create a continuous barrier that prevents the flow of water. Depending on the type of concrete being processed, the degree of its waterproofness can be increased by two or three levels.
The influence of negative temperature on concrete hardening
At temperatures above +5°C, cement hydration occurs normally. If the temperature suddenly drops below 0°C, the water in the mixture will freeze and the process will freeze. In this case, the crystals that began to form in the warm mixture will remain in the solution. Winter concrete hardens much longer. If additives are not added to it and it is not heated, the monolith will be heterogeneous, with cracks.
If, after freezing, the solution is heated and the water is melted, then new bonds will form incorrectly and the monolith will not receive the necessary strength.
What to look for when concreting a foundation
In order to competently carry out construction work and reduce further costs of repair and operation of the foundation to a minimum, you must adhere to a few simple rules:
- The foundation design should not allow cracks to form under any load.
- The entire volume of concrete must be poured without technological and “cold” joints, that is, in one technological cycle.
- If the work involves the formation of technological seams, they must be sealed using swelling cords, sealants or waterstops.
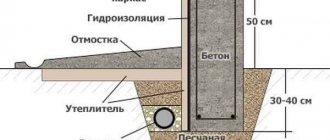
- Working reinforcement must be installed in strict accordance with the design; the thickness of the protective layer of concrete must be at least 15 mm.
- It is necessary to compact the laid concrete with vibrators or use self-compacting concrete.
- Newly laid concrete needs to be maintained.
Concreting in winter
It may be necessary to use concrete in cold weather in a variety of cases - when it is unprofitable to stop construction for an entire season, in case of emergency work, etc. Taking into account the detrimental effect of sub-zero temperatures on the material and its technical characteristics, concrete must be heated. When the temperature inside the solution is higher than the temperature outside, deformations may occur.
The concrete is heated until a critical strength indicator is reached. If such data is not in the design documentation, then the value is taken as 70% of the design strength. When there are requirements with waterproof/frost resistance values, then the critical strength is 85% of the design.
The main methods of heating concrete for pouring at minus temperatures:
- Warming up the components themselves to prepare the mixture.
- Using the thermos effect.
- Implementation of electric heating.
- Application of steam heating.
Thus, there is no question at all at what minimum temperature concrete can be poured. The task is to optimally prepare the mixture and the object in accordance with the working conditions to preserve the technical properties of the material and the basic requirements for strength, reliability, and durability.
The simplest and cheapest option is to heat up all the components used to prepare concrete. They are heated so that at the time of pouring the concrete has a minimum temperature of +35-40 degrees.
All materials except cement are heated: crushed stone/sand up to +60, water up to +90, cement is simply left in a warm room for a while (so that it is at room temperature). Then mix all the components and fill.
Thermos method
This option is relevant in the case of pouring massive structures. Additional heating is not provided, but the mixture being laid must exhibit a temperature of at least +10 degrees (preferably more). This method consists in allowing the poured mixture to acquire critical strength during the cooling process.
The principle of this method is that the concrete reacts and begins the hardening process, which is exothermic (that is, accompanied by the release of heat). Thus, the concrete will self-heat. If heat loss is excluded, concrete can warm up to +70 and above.
The formwork is reliably protected with heat-insulating materials, eliminating heat loss from concrete that is in the process of hardening. Water does not freeze, the concrete monolith gradually gains strength without destroying the internal structure. This option is used for pouring foundations in winter; it is considered the simplest and most economical, since it does not require the use of any equipment.
Electric heating of concrete mixture
When thinking about the temperatures at which concrete can be poured, many consider electric heating as a way out of the situation. Warming up can be carried out using several methods: using electrodes, the induction method and various electric heating devices.
Heating by electrodes is carried out as follows:
- Electrodes are introduced into the freshly poured mixture.
- Then current is applied to the electrodes.
- As current passes through the electrodes, they heat up and transfer heat to the concrete.
The current must be alternating, since a constant one will cause the electrolysis process, which is accompanied by the release of gas. The gas shields the surface of all electrodes, the current resistance increases significantly, as a result of which heating is noticeably reduced. If reinforcement is laid in concrete, it can be used as an electrode.
What time of year is best to pour the foundation?
Difficult weather conditions negatively affect the strength gain of concrete.
Abundance of precipitation
at the stage of setting the concrete mixture can lead to its saturation with excess moisture. This leads to an increase in the water-cement ratio and a decrease in the strength of concrete.
Frost
turn mixing water into ice, which disrupts the hydration process of cement. When water freezes, it expands and internal stresses arise in the freshly laid concrete, which leads to damage to the foundation.
High air temperature, low humidity and wind
increase the rate of water evaporation from freshly laid concrete. This leads to disruption of the process of cement hydration and destruction of concrete in the surface layer, the appearance of shrinkage cracks.
Based on this, and also taking into account that the process of concrete gaining strength lasts 28 days, the optimal time for pouring the foundation is the period from late spring to early summer.
In addition to the advantage of comfortable conditions for carrying out work, there will be enough time ahead to eliminate possible defects, arrange waterproofing and additional protection. As a result, a foundation built in the spring will not be afraid of autumn temperature changes and winter frosts.
Winter concreting
Concrete is also laid in winter.
Concreting at low temperatures is a special practice that requires the use of special technologies and additives. As we have already said, the temperature should not fall below +4 degrees, but often the production process excludes the possibility of a winter break in work.
In this case, concrete heating is used.
This can be done in several ways:
- The thermos method . Here, the heat generated by the hydration reaction of cement is used, to retain which the mixture is poured into insulated formwork, which is additionally covered with greenhouses and other protective means. Suitable for massive large objects;
- By heating with steam or hot air . A wooden or canvas greenhouse is built around the object, into which steam, warm air is supplied, or a heater is installed;
- By heating the mixture with electrodes or special heating cables (PNSV) . According to a pre-calculated scheme, special heating elements are introduced into the concrete mass, which make it possible to convert electrical energy into heat;
- By heating using electric mats or infrared emitters . Heating mats or IR emitters are placed on the surface of the screed, which prevent the mixture from freezing.
Thermoelectromats allow you to work in winter.
It is most important not to let the concrete freeze during the first three days, during which it gains up to 70% strength. Afterwards, frost is no longer dangerous; it only slows down the process of gaining strength, which will continue after thawing.
Warming up is carried out to temperatures from +10 to +30 degrees. It is not advisable to go beyond these limits.
The heating cable is laid directly into the formwork.
Important! If the mixture has not gained 50% strength, then after thawing it will loosen and will not gain brand strength.
In addition to heating, you can use chemical additives that prevent water from freezing and accelerate the hardening process.
It could be:
- sodium chloride;
- calcium chloride;
- sweat;
- and sodium nitrate.
It is also advisable to use highly active grades of cement.
The construction of a greenhouse is an old but proven method.
It should be taken into account that cutting reinforced concrete with diamond wheels and diamond drilling of holes in concrete should be carried out after gaining strength, and not on frozen material. Also keep in mind that the price of work increases by 30 - 40%.
Important! For successful winter concreting, it is better to use a set of measures, including heating, the use of chemical additives and highly active cement.
How to pour a foundation in winter
If it is still necessary to concrete the foundation in winter, several technological methods are used.
Antifreeze additives and hardening accelerators
– they allow work to be carried out at sub-zero temperatures without loss of speed and quality.
Heating concrete with an electric cable
– it is attached to the reinforcement frame and connected to the network, and then remains in the body of the concrete.
Warming up concrete with heat mats
– unlike cables, mats are installed on the surface of a heated structure and can be used repeatedly.
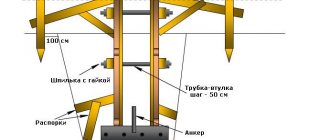
Arrangement of the greenhouse
− this is a structure similar to a greenhouse, which is assembled above the work site. Heat guns are installed inside to maintain positive temperatures, so in the “warmhouse” you can safely carry out foundation construction work: knitting the reinforcement frame, concreting, installing waterproofing and installing waterstops.
Bottom line
The optimal time for pouring the foundation in most regions of Russia, except the northern ones, is the second half of spring or early summer. During this period, the optimal weather for concreting work is established. Here are the main points to pay attention to when conducting them:
- Entrust the work of decoupling the reinforcement frame and concreting to a specialized organization. This way you will avoid mistakes, the correction of which can be very expensive.
- Use only ready-mixed concrete of appropriate strength and water resistance grades. Methods of preparing concrete on site in a metal bath and using shovels are strictly unacceptable.
- Carry out concrete work without forming cold joints.
- Increase the water resistance of concrete using special additives. For example, penetrating.
- Freshly laid concrete needs to be maintained. Cover it with damp burlap and water it every two or three hours, even at night, for 3 to 5 days. If the weather is hot, it is better to water within 7 days.
- Carry out foundation work in winter using special methods.
- If possible, check the thickness of the concrete cover using a rebar locator. It must be at least 15 mm.
- Additionally, protect foundation structures from the negative effects of soil and groundwater.
Technology and features of pouring in autumn
At what average summer temperature should construction begin? The warm season - from +15 to +30 degrees is suitable for construction work. Pouring concrete in summer is acceptable. The only condition is to protect the freshly laid monolith from rain.
Choosing the right time
In the fall, the weather is unpredictable, so it is important to know at what temperature you can pour concrete in the fall.
The optimal air temperature is from +20 to +5°, so it is recommended to start laying the foundation in September-October before frost. In the process of arranging the foundation, it is important to consider to what point on the thermometer the work needs to be completed before the cold snap. It should be +10 degrees Celsius. The concrete mass gains strength within 1 month. Before frost, it is recommended to make a shelter, and in the first two days, protect the mixture with film from rain.
Advice! Before pouring your foundation in the fall, check the weather forecast.
Factors influencing dough setting in autumn
Pouring a monolith will be of high quality if you take into account several points:
- air temperature. At what temperatures can concrete be poured in the fall to start building a house? The normal value is plus 16°. During this period, the solution hardens slowly, which ensures the quality of construction. Frosts occur at the end of October, so it is better to start construction in mid-September;
- humidity characteristics. Damp weather and wet soil promote the curing process. Freshly laid mortar does not need to be regularly sprayed with water, and slow drying ensures increased strength;
- presence of precipitation. If you have figured out the optimal temperatures at which you can pour the foundation, then you need to take into account the presence of rain. Overmoistening of the monolith leads to the leaching of cement laitance;
- ground water level. In swampy areas there is less water in the fall, which makes it possible to make a pile foundation. You can check whether the water has risen by digging a trench. If water has risen in it, the foundation cannot be poured.
Important! If at least one factor does not comply, the structure will lose strength.