A visit to a modern bathhouse or steam room is not just a desire for cleanliness or a tribute to fashion. A bathhouse with healing steam and heat from the stove promotes health, beauty of body and spirit, good mood, and restoration of vitality. However, this is possible with a sufficient amount of fresh air and the absence of microorganisms that can cause disease. A well-equipped hood in the bath as an element of the ventilation system of the room.
Is a ventilation system needed in a bathhouse?
Breathing is a reflex process that our lungs perform to take the required amount of oxygen from the environment. Normal air consumption is not noticed until a person enters a room where the air is stale or insufficient. Baths and steam rooms are precisely such risky places; they should always be hot, fresh, and clean. The question of whether ventilation is needed in the bathhouse and steam room is not even discussed. According to sanitary standards, owners must provide an air exchange system in the project and apply step-by-step guidance during the construction phase.
During the ventilation process, conditions are created under which the proliferation of bacteria and fungi becomes impossible, which means that mold and mucus will not grow in the corners and crevices of the structure.
FAQ
Is it possible to organize air intake for ventilation from under the floor into the steam rooms?
You shouldn't do this for 2 reasons. Exhaust air with unpleasant odors flows underground, and its penetration back into the steam room is not desirable. In winter, it is recommended to close the underground, so the flow of fresh air is impossible.
Why not use the hole in the ceiling leading to the attic as ventilation?
This is fundamentally wrong. Moist, warm air flows from the steam room into the attic, causing the ceilings to quickly fail.
Isn’t it enough to periodically open the door to the steam room as ventilation?
This is ineffective. Humid air enters the adjacent room and is concentrated there, so the steam room is not actually ventilated. If you open the door from the rest room to the street, you will get a draft, which sharply reduces the temperature in both rooms and disrupts the soaring process.
I made a hole in the steam room with a diameter of 100 mm, there are no windows. Between passes I open the hole. Isn't this enough for ventilation?
Not enough. Calculate the volume of air that escapes through such an opening. Such ventilation is ineffective. Still, it is worth organizing a serious ventilation system.
Is it possible to use a ventilation duct in a steam room, inside of which there are electric motors for air suction?
To organize a ventilation system in a steam room, it is preferable to choose systems without the use of electric motors. Only a specialist can correctly calculate the power of the electric motors used. Such a system will not work very efficiently. In addition, if you do not turn on the electric motors while heating the bathhouse, then there is a chance of them overheating and failing.
The principle of operation of the ventilation system in the bathhouse
ventilation is conventionally divided into constant (includes wall, roof and foundation) and ventilation, which operates periodically, when the bathhouse is in operation, the stove is heated. Both are included in a single ventilation system, which is designed together with the construction of the bathhouse.
The principle of operation is to displace exhaust air with clean, fresh air. For this purpose, through holes are installed, at least two, which operate depending on the direction of flow and only when there is a difference in temperature indoors and outdoors.
A few more rules, if you follow them when arranging ventilation in a bathhouse with your own hands , the principle of operation will not be violated:
- When the bathhouse warms up, close the vents in the foundation and the dampers in the steam room.
- During procedures, windows are opened as needed.
- After steaming, the sauna is completely ventilated.
The supply and exhaust supply and exhaust air in the volume that the dampers on them allow. Calculating the size of the window is simple: for every cubic meter of room you need 24 cm2 of holes. And one more thing: the windows cannot be placed opposite each other.
Selecting a type and pattern depending on the wall material
The ventilation system directly depends on the characteristics of the structure itself and the material of its walls. The bathhouse can be a separate room or adjacent to the house. The first option is much better. In such a bathhouse you can install the most economical ventilation option.
The bathhouse adjacent to the house must be dried in the most serious manner. This will protect all walls from rotting. For such a bathhouse, exclusively forced ventilation is used, taking into account the safety of the walls and supporting structures of a residential building.
The bathhouse’s ventilation ducts can be connected to the common ones or separately exit to the street through the roof or through the wall.
Depending on the wall material, experts advise choosing the following types and ventilation schemes:
In brick and frame baths, it is recommended to install ventilation ducts in the walls, leading them to the roof or higher. For inflow, an air duct is laid, a ventilation valve or vents are used in the foundation. It is imperative to supplement the vents with exhaust fans for better removal of exhaust air.
Due to the characteristics of this material, bathhouses made of aerated blocks are equipped with galvanized air ducts made from ready-made pipes. Sometimes a channel is made from galvanized sheets, giving them the appropriate shape and reliably sealing the joints. The ducts must run over the wall.
Natural forced ventilation is allowed in log baths. When the wood breathes, there are the necessary gaps between the logs, windows are provided in all rooms of the bathhouse, gaps from the floor to the bottom edge of the door are 2-3 cm, the construction of additional ventilation channels may not be necessary. But in order not to “drown the street”, it is advisable to provide valves or dampers in the vents.
Advice! When organizing ventilation in the steam room, avoid using plastic elements: corrugations, boxes, plugs. They cannot withstand high temperatures and will melt, releasing harmful substances and acquiring an unaesthetic appearance. Only wood can be used as plugs for vents or hatches, since metal can burn from heat or rust when exposed to moisture.
Salvo - an economical solution for ventilation
If you are not sure that you can correctly calculate the size of the entrances and exits of ventilation ducts or their location, you can use the long-tried “old-fashioned” method - burst ventilation in a Russian steam bath.
Its essence is to quickly ventilate with wide open windows and doors. They are opened for 1-2 minutes. For maximum effect, it is best to use opposite windows and doors.
The method does not require additional financial costs, since you use the elements that are in the bathhouse design.
IMPORTANT! Do not overdo it with ventilation, because you can make the bath too cold. The method is most suitable for Russian baths, which are heated in black.
Proper ventilation in the sauna steam room
To provide for all the subtleties of installing ventilation in a bath means to protect yourself from dampness, rapid cooling of walls and furniture, cold floors and the accumulation of carbon monoxide. In addition to freshness, ventilation should not create drafts, cool the floor, or provoke sudden temperature changes.
The essence of ventilation is air flow at two ends: inflow and outflow. You need at least 2 holes, installed according to the rule - outflow above, inlet below. It is best if a ventilation device is included in the bathhouse design before construction. The shafts and the diameter for the holes are indicated. There are 3 basic solutions for choosing openings that provide not only air exchange, but also safety:
| Type of bath | Inflow, mm | Hood, mm |
| Russian | 100 | 100 |
| Finnish | 130 | 100 |
| Swedish | 100 | 80 |
It is prohibited to make the exhaust opening smaller than the supply opening. Also, according to the rules, ventilation openings must have valves that ensure tightness during the moment of kindling and warming up the steam room. In winter, the valves are closed halfway, because the greater the temperature difference, the stronger the air circulates.
Is it necessary to hire specialists for calculations and design?
If you want a proper, “easy” and trouble-free sauna, ventilation in the steam room plays an important role: from the longevity of the sauna to your own safety.
If the bathhouse is combined with a house, has a rest room or dressing room into which the stove is installed, or there are other reasons for using forced exhaust, then the answer to the question “is it necessary to hire specialists for calculations and design” will be clear: it is necessary .
Otherwise, you can make a mistake in a minor detail, and the purchased calculation equipment will not be suitable for this reason. And this in turn will cause additional expenses.
In addition, in order not to disturb the structure of the building, it is better to design the ventilation of the steam room in advance, before the bathhouse is erected , especially in situations where the entrance of air flows should be located on the foundation. Installing a ventilation system in an already constructed building is a troublesome and time-consuming process. It will be necessary to disassemble almost all finishing materials, make room for corrugations, etc.
When building a brick bathhouse, you cannot do without preliminary preparation, because not only wooden finishing materials are required, but also wall material - brick, which (some types, for example, silicate) is prone to absorbing large amounts of water.
Find out more about insulating brick baths on this page.
Types of ventilation
There are several ways to remove exhaust air and replace it with fresh air. It all depends on the configuration, area, and functionality of the room. The most suitable way to properly ventilate a bathhouse is selected taking into account:
- number and location of rooms;
- type of walls;
- type of heating: wood and electric appliances are part of the ventilation system of the bathhouse.
When building baths, natural and forced ventilation are used.
Natural
The operating principle is based on temperature differences and atmospheric pressure changes inside and outside the building. The advantage of natural ventilation is autonomous operation without power supply and the use of other factors that encourage air flows to move. It is easy to install, does not break, and does not require large expenses. To regulate ventilation and limit the access of frosty air, valves or vent covers are purchased.
Forced
Here air flows are created or strengthened forcibly. Fans are used for this. The system allows you to supply or displace air stably and continuously, its operation does not depend on weather conditions. Human intervention is minimized, and the ability to control and make fan operation settings via a smartphone makes this method of maintaining comfort even more convenient.
Combined
Buildings made of stone, frame-panel, lined and insulated in different ways require different approaches to the arrangement of ventilation systems. In addition, the designs of modern baths are not limited to only the dressing room and washing room: steam room , locker room, bathroom, rest room - in each of these rooms one or more types of ventilation are installed and used depending on the situation, before, during the procedure or after her.
Features of operation
At its core, ventilation in the bathhouse, shown in the photo, consists of several special holes designed for the intake and removal of air flow. These openings are called supply and exhaust.
Moreover, the bath ventilation system can consist of either two (one supply and one exhaust) or several openings. Their number directly depends on the dimensions and location of the rooms in the room.
The principle of operation of ventilation is that:
- fresh air flows from the street into the room through the supply holes made in the wall;
- the incoming flows are combined with warm air, which is formed from the heat source;
- warm air is distributed throughout the room;
- With the help of exhaust holes there is a natural exit of “exhaust” air.
For a high-quality ventilation device in a bathhouse, a number of requirements must be met:
- The area of one hole is calculated depending on the area of the room multiplied by 20 cm².
- Ventilation openings must be of such a size that fresh air does not leave the room in too short a period of time. Naturally, there should be no drafts.
- On the other hand, air flows should not stagnate for a long time.
- One of the walls of the steam room should be in contact with the street. This is the only way to achieve sufficient air exchange for the room.
- Effective ventilation in a bathhouse in quantitative terms represents 3 fresh air intakes within 1 hour of a health procedure.
- Additional ventilation is provided by a 2-3 cm gap that is left under the door.
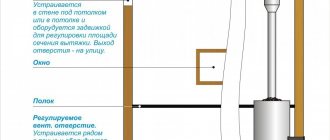
Where to place the cold air vent
The lower vent is responsible for the influx and supply of cold air. A pipe is laid under it during construction or a shaft is left. Bottom hole installation options:
- In the wall, opposite the stove.
- Under the sun loungers, you can’t see it there, and there are no drafts. However, to adjust the position of the damper, you have to bend down under the shelf, which is inconvenient. The situation is corrected by opening the upper outflow, and after the procedures both outflows are opened - both the upper and the lower.
- Behind the stove, if the stove is not installed in a wall and there is access to it. The cold stream immediately warms up, causing the coals to burn hotter.
Outflows are made either in the wall or in the ceiling, providing a place for them in the project.
How to ensure air flow in a room with a sauna stove
A simplified option is to install an opening window in the steam room. Excess steam will escape through it and fresh air will enter. Plus, it saves on lighting. The box and frame must be made of wood. It is not recommended to install plastic ones - plastic cannot withstand high temperatures and releases toxins when heated.
Another way is to install a supply and exhaust system. Under the floor from the street side, an air duct under the stove enters the room. In this case, the stove becomes a pump - it drives cold air through itself, heats and dries it. The exhaust air exits into an exhaust hole in the wall opposite.
Ventilation of various auxiliary rooms
Ventilation in the bathhouse is on the list of mandatory construction measures. Understanding the importance of sufficient air exchange has led to the development and application of various step-by-step schemes for each individual room.
Steam room
If some of the air in a confined space is not removed, then new, fresh air will not be able to enter the steam room. The diagram and device of the steam room ventilation is as follows:
- An influx of fresh air is provided. To do this, a hole is made in the wall below near the floor next to the stove.
- The exhaust hole for natural ventilation is installed on the opposite wall from the stove under the ceiling, and is closed at the time when people are busy with procedures.
- The air entering the steam room immediately heats up and rises upward using convection.
- Up above, under the ceiling, in the Russian bathhouse it begins to become saturated with moisture. Humid air is heavier, so the steam gradually cools in the corner farthest from the stove and falls down.
View this post on Instagram
Post from I’m building a bathhouse as best I can (@banpartal)
It is at the regiment level, at the time of taking bath procedures, that this air must be taken in and removed so that it does not evaporate again. To do this, an exhaust ventilation hole is made on the opposite wall from the stove under the shelves, into which a fan is installed. Damp cooled air comes out, and at the top, where people are steaming, there is good steam and heat.
After the procedures, you need to quickly empty the steam room of warm and humid air. Ventilation in the steam room occurs using a diffuser installed using a tee.
Is it possible not to install such ventilation in the steam room of a bathhouse ? Perhaps a window will suffice? Experts are categorical - the window serves for rapid ventilation of the steam room and rapid removal of air. It is not suitable for maintaining comfort during procedures.
Attic
The attic space should not simply be ventilated using a window. Steam reaching the rafters leads to the beginning of destructive processes. Solution: inflow under the roof canopy, outflow at the ridge. The two-way natural movement of flows occurs from bottom to top.
The space between the roofing material and the membrane is ventilated forcibly or naturally, but only with aerators and soffits. Aerators are placed on the roof area or on the ridge and extract air. Soffits allow air flow.
Washing
Most often, air exchange is forced. The outflow is directed towards the vestibule. In the corner, under the floor, there is a ventilation riser. It can be made from an asbestos-cement pipe, which draws air out due to the difference in pressure in the room and the end of the pipe leading to the roof.
Ground floor
Arranging a bathhouse in the basement places increased demands on the waterproofing of floor panels and walls. The ventilation system is only forced in all rooms.
Shower room
Refreshment in the shower and toilet occurs through the projection of air from fans in the ceiling or at the top of the wall . Installing exhaust ventilation in the hole closest to the shower will speed up drying.
Waiting room
The proximity to the steam room causes condensation on the walls and temperature changes. A window is installed in the dressing room and forced ventilation is provided.
Arrangement of supply and exhaust openings
When designing a bathhouse, you must immediately provide for the location of vents in the walls or foundation. It will be easier to make them during the construction process, rather than punch them after completion. In the case of forced ventilation, their dimensions are not particularly important, since a fan of calculated power will provide the necessary air exchange.
It is easier to lay a piece of pipe when pouring it into the foundation than to drill a vent in hardened concrete Source readmehouse.ru
Another thing is how to properly make ventilation in the steam room of a bathhouse if the use of mechanisms is not provided. For good natural air exchange, the cross-section of the supply opening must be sufficient. It is calculated according to a standard that regulates the dependence of this section on the volume of the room. For each cubic meter of ventilated space it is necessary to install a vent with a cross-sectional area of 24 cm2.
If we take our example with a steam room 2x3x2.2 m, then its volume will be equal to 13.2 m3. Multiplying it by 24 we get 317 cm2. To determine the diameter of a round hole with such an area, use the converted formula for the area of a circle: divide it by Pi and take the square root from the resulting value. The radius of our hole is equal to 10 cm, so its diameter should be 20 cm.
The radius is found using the inverse formula for the area of a circle Source ds04.infourok.ru
It is even easier to find the length of the side of a square hole - it will be approximately 18 cm. The sides of the rectangle are also selected in accordance with the cross-sectional area - for example, 10x32 cm.
To arrange round vents, steel or plastic pipes of the appropriate diameter or slightly larger are used, and the channels in the rectangular wall are made in the form of wooden boxes made of boards.
The exhaust hole, as already mentioned, should be made larger than the supply hole. The gaps between the wall and the walls of the channel are filled with tow, other insulation, or foamed.
Another important point in such a matter as making an outlet in a bathhouse is protection from the outside from the penetration of insects, rodents, and debris into the channel. To do this, cover the hole from the outside with a mesh or lattice.
Ventilation grille with insect mesh Source www.video-sovety.ru
And inside, to regulate the intensity of the air flow, valves are installed, partially or completely blocking the holes when necessary. For example, in winter, the draft, due to the huge difference between the low temperature of the street air and the high temperature in the bathhouse, increases so much that the cold currents do not have time to heat up from the stove and quickly cool the room. It is reduced using a valve, leaving only a small gap or completely blocking the vent for the duration of the procedures.
The need for ventilation in modern baths
The ventilation of the bathhouse carries out the influx of cold air into the steam room, heating and removing the air that is already humid and cooled after heating. What does a good exhaust system provide:
- quickly removes moist air from the room;
- promotes rapid drying of wooden structures, extends their service life;
- removes carbon dioxide, keeping its concentration at an acceptable level;
- regulates temperature efficiently;
- supports the combustion process in baths with gas and solid fuel stoves, providing air flow.
In a bathhouse with proper ventilation you will never encounter a musty, stagnant, unpleasant odor.
View this post on Instagram
Publication from ATELIER SAUNA - the best for a bath! (@ateliesaun)
Facade ventilation with additional insulation
If it is impossible to build a bathhouse from thick timber (the best option) and the low insulation capabilities of the walls, the structure must be insulated from the outside followed by finishing the facade. When using materials with low permeability for these purposes (thermal panels, siding, lining, sheet fiber cement or their analogues), the facade must be ventilated. Ignoring this requirement leads to accelerated accumulation of condensate inside the walls of the bathhouse and reduces their service life significantly.
In practice, this means placing a mandatory vent between the insulating layer and the outer closed side of the bathhouse wall. The dimensions of this gap are standardized and amount to 50-60% of the thickness of the insulation for wall heights within 4 m. For walls with a lower height, the gap can be reduced to 30% of the thickness of the insulating layer.
In the facades of two-story bathhouses and buildings higher than 4 m, additional intermediate vents are installed to allow free air access. In any case, the upper and lower parts of the cake remain open and are protected from precipitation by perforated plinth elements or soffits, laid with appropriate ventilation indentations.
The required ventilation gap is ensured by the sheathing and counter-lattice. When packing or installing them, the possibility of blocking the vent horizontally is eliminated. Additional protection of fibrous insulation from steam coming from inside the bathhouse is provided by membrane films, carefully laid on the counter-lattice with an overlap of at least 5 cm and secured with staples.
Expanded polystyrene boards generally do not need such protection and it is better not to insulate a wooden structure with them; practice shows that systems with membranes have better thermal conductivity. The exact sequence of layers of the cake also depends on the quality of the internal insulation of the steam bath.
In addition to ensuring sufficient ventilation, when installing such facades, attention is paid to sealing and laying the correct angles of ebbs of window and door openings, eliminating the general curvature of the walls and deviations from flatness. Any defects are eliminated at the stage of fastening and aligning the guide profile of the sheathing; it is difficult to eliminate errors after
The same applies to checking the ventilation efficiency of the insulated bathhouse facade; critical errors are identified after, in the first years of operation.
Now you know the answer to the question. How to do ventilation in a bathhouse correctly with your own hands? So, you need to do:
- Steam room ventilation
- Ventilation of the shower room and toilet
- Ventilation of the rest room
- Facade ventilation with additional insulation
Floor ventilation device
To ensure that the bathhouse boards do not rot and serve for a long time, it is necessary to install vents under the floorboards. Ventilation of the floor in the bathhouse with vents occurs even during procedures. The boards dry when ventilated from the outside, and when the hood is running, from the inside. Proper drainage of water from the steam room, away from the floor covering , will prevent deterioration and help the wood dry quickly with the help of ventilation.
Another method of forced air exhaust is through the underground of combined adjacent rooms. Suitable for washing rooms and steam rooms, in which the boardwalk lies on a concrete base, where natural ventilation cannot provide exhaust air.
A hole is provided in the foundation for the exhaust duct. It is made under the floor and equipped with a fan. The inlet opening is located close to the stove. The incoming air immediately begins to heat up and rise. If you make openings in adjacent rooms, heat will flow into the adjacent rooms.
Subtleties of arrangement
The design of the ventilation system depends on many factors. So the air exchange in a frame bath, in a bath made of blocks and in a wooden bath is different. Plus, the layout and size of air ducts and openings plays a big role. But first, let's look at the types of ventilation systems.
Types of systems
Natural air exchange - in this case we do not mean the absence of ventilation, but its operation without outside help. The air supply is regulated manually using valves. The option is good, but it is more suitable for isolated buildings, for example, when a bathhouse is made from a log house standing on the river bank;
Wide channels are needed for natural air exchange.
Forced system - here the supply and exhaust ventilation are equipped with electric blowers and hoods (fans). The efficiency of such a system is an order of magnitude higher. In a wooden bathhouse it can be installed at will, but in frame and block structures it is a mandatory attribute.
Forced exhaust circuit.
Steam room air exchange diagrams
Most often, the air flow is installed next to or near the stove. If the stove is located next to the front door, then instead of a separate ventilation duct, a gap of 20–30 mm in size is left under the door leaf, through which air leaks.
Sometimes a ventilation hole with a latch is made directly at the bottom of the door leaf. But in any case, in the absence of a separate ventilation duct, the dressing room must be well ventilated, since the air will come from there.
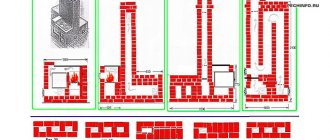
- The diagram below shows a ventilation option where the exhaust is approximately at the same level as the inlet. The heated fresh air flows around the entire room and, gradually cooling, escapes through the hood. The sauna with its dry steam fits this scheme perfectly, but in a Russian bath it works worse;
The bottom hood design is more suitable for a sauna.
- The following scheme is used in rooms where one of the walls borders the street. The problem is that when the air supply is far from the stove, cold air spreads across the floor and it will be cool. Therefore, here it is advisable to install a fan on the supply air and turn it on briefly;
It is advisable to install a fan on the inlet.
- The following scheme is more suitable for frame and block structures standing on a concrete foundation and having concrete floors. Here a wooden deck with holes is mounted on top of the concrete. If you put a powerful fan on the hood, the hot air, going around the room, will escape through the floor, thereby heating it;
Ventilation through the floor requires the installation of forced exhaust.
- Exhaust through a stove vent is most often used in a Russian bath. The stove here is installed directly in the steam room, and the inflow is mounted opposite, usually under the benches. At the same time, there should be a separate hood in the washroom and dressing room; it is undesirable to let everything through the steam room, as there is already a lot of humidity there.
The exhaust pattern through the stove vent is typical for a Russian bathhouse.
Methods of natural ventilation
The peculiarity of bath air exchange is that the flow of fresh air does not displace heat, but directs the flow heated by the stove in the desired direction, creating a special microclimate in the room. To know how to make inflow and exhaust , let’s remember the principle of operation of the system, which is based on simple laws of physics:
- in any room with any type of heating, the air moves - dense and heavy cold air goes down, warm air rises up;
- Without an influx of oxygen, this movement is ineffective: oxygen is used up, it becomes less abundant, and at the same time the concentration of carbon dioxide increases.
Breathing air that moves without renewal is not only difficult, but also life-threatening. When the temperature outside is lower than in the room, air enters through the hole in the lower part of the wall, and through the upper part it is removed from the building under the influence of draft , performing natural ventilation. One of the methods of natural ventilation in a bathhouse is ventilation by opening windows or doors. Fresh air comes in, which is good, but condensation quickly settles on the walls of the premises, and stable microclimate parameters cannot be achieved. Therefore, opening ventilation can be done before bath procedures, but not during or after them. And for more efficient air circulation, you should use other methods for ventilation in a bathhouse .
Ventilation through the chimney
A steam room equipped with a stove with a chimney will always have a comfortable temperature for receiving procedures, because the stove has a vent. draft occurs during combustion . The fume extraction process occurs only when air from outside flows into the room. A few simple ways to ensure inflow:
- A hole is made in the wall opposite the stove at a height of 20-30 cm from the floor.
- Periodically the door is closed and opened briefly.
- A 1 cm gap is made at the bottom of the door, or an opening is left between the floor and the door.
- If the log house of the bathhouse is not sheathed, a gap is left between the first crowns below the floor level if the boards do not fit tightly.
Penetrating into the room, the cold flow moves towards the heat source, the heated air is forced upward. Circulating up and down, the warm flow gradually cools, descends and is drawn in by the ash. Together with combustion products, it goes outside through the chimney.
Note! Ventilation through the chimney duct occurs only when the stove . In the absence of fire, air exchange does not take place.
Ventilation through vents
In case the stove is not heated, but ventilation is needed, air flow is made through special holes. To do this, before constructing and installing the stove, you need to provide a diagram of how to properly make a hood in a bathhouse :
- The exhaust hole is planned where the heated air accumulates - under the ceiling of the bathhouse.
- The inflow is provided low above the floor on the wall opposite the hood, choosing the place closest to the stove. It is best if the inlet is located immediately behind the stove.
The vertical distance between the vents is 1.5 - 2 m. The exhaust hole is larger in cross-section than the exhaust hole.
Cold air entering the room immediately begins to heat up. It displaces warmer air upward, which rises upward towards the exhaust hood. In a steam room with this type of ventilation, there are no noticeable cold flows and levels with different temperatures.
Important! There must be a difference in height between levels. Being at the same level, the vents create a straight-line air flow, without circulation, which is known as a “draft”, which is dangerous to health, especially for a heated and wet body.
Vent size
When choosing the size of the exhaust opening, you must follow several rules:
- The largest one should be at the maximum distance from the stove so that the heat does not escape from the steam room in a direct flow.
- The remaining holes can be placed around the perimeter of the ceiling.
- The hole size is calculated based on 24 square meters. cm per cubic meter of room. Most often, the diameter does not exceed 30 cm, but the number is 2 or more.
- The traction force is determined by the height difference between the supply and exhaust openings.
IMPORTANT! Holes cannot be placed opposite each other. This will inevitably cause drafts in the steam room.
Methods for installing forced ventilation
Modern baths can be located in a house, be attached and have common walls with the main structure. In such rooms it is difficult to ensure natural ventilation, especially if the bathhouse has many functional rooms.
Ventilation in the steam room of a Russian bath is forced; for this purpose, exhaust or supply type fans are used. The devices create artificial air currents and make them move quickly. Forced ventilation is:
- Supply and exhaust, when equipment of both exhaust and supply types is used.
- Exhaust: A fan pulls air outside, creating a rarefied effect in the room. The deficiency is compensated by the natural supply of air from the street, which occupies the freed-up volume.
- Supply air, when a fan blows air from the street, creating excess gases in the room. Under the created pressure, the exhaust air is pushed out.
When choosing what type of ventilation to install in a Russian steam room , the needs are taken into account. Supply and exhaust equipment creates intensive air exchange; this is not required in small baths. When using one supply ventilation, the air does not have time to warm up to the required temperature. Most often, baths and steam rooms are equipped with exhaust .
Forced ventilation schemes
In a steam room that has only one outer wall, it is possible to install vents only on it. In this case, as well as when you need to refresh several rooms at once, you will have to force air displacement. To prevent incoming fresh air from immediately escaping into the exhaust vent, one of the following schemes is used:
- The stove is placed opposite the “inlet”. The hood is mounted as high as possible from the floor, or in the ceiling. If the attic is residential, make an air vent and bring it to the roof. How it works: cold air entering the room immediately moves to the heating device. As it heats up, it rises, giving way to the next portion of cold mass from the street. Warm air rises to the top, is sucked in by a fan, and comes out.
- The second option is suitable for a steam room that has a common wall with a room without a firebox. The exhaust vent is not mounted under the ceiling, but below, on the opposite wall from the supply vent. The channel through which the hot air escapes is hidden in the wall; it simultaneously heats the adjacent room. This room is provided with its own individual, possibly natural, ventilation.
View this post on Instagram
Publication from Ideas for home and garden. Lifehacks (@asbocem)
Both methods of forced ventilation have a drawback - cold air, which rushes from the supply opening to the stove, crosses the room and cools the floor. Therefore, air exchange is carried out when there are no people in the steam room, and the rest of the time the hole is closed with a valve.
Fan selection
Equipment for premises with special conditions must meet safety requirements. Therefore, they choose devices that can withstand heat, high humidity, and temperature fluctuations. Where to begin:
- Select a fan from among the devices for baths and saunas. Made of glass-filled polyamide, the sauna can withstand temperatures up to 180°, while maintaining functionality. The motor has special moisture protection, as well as bearings that provide 30,000 hours of operation.
- You need to know the area of the room to calculate power . The area is calculated using the formula S = l * b * h (length*width*height). The resulting number is multiplied by 5 (air exchange coefficient recommended for baths). For example, the area of a room is 12 m2. 12*5=60 m3/h. Choosing a fan with excess power is wrong; it is dangerous in bathhouses. In addition, the fan must be used according to the instructions .
- A device with a timer will help make ventilation easier. The option periodically turns the fan and regulates power.
- Built-in humidity and temperature sensors in auto mode turn on the fan only when the settings reach certain values.
Depending on the system, the fan is installed directly into the hood opening or on the wall behind it.
Video description
It is easy to find units on sale that are specifically designed for baths and saunas - these are the ones shown in this video:
It is also necessary to determine the power of the device, since excess power is completely unnecessary and even contraindicated. This is easy to do if you know the volume of the ventilated room and the air exchange rate recommended for baths, which is 5.
For example, for a 2x3 m steam room with a height of 2.2 m, the fan power is calculated as follows:
2 x 3 x 2.2 x 5 = 66 m3/h
Advice! Buy a device with variable adjustable power and a timer that will periodically turn the device on and off. You can fully automate the system by including humidity and temperature sensors configured to certain values, upon reaching which they will start the fan.
If desired, you can assemble an automated system with remote control Source nevoton.ru
Such devices, depending on the design, can be installed directly in the exhaust vent (duct fans) or on the wall behind it.
Ventilation of walls in a steam frame bath
The constant humidity that is present in the bathhouse leads to the risk of moisture accumulation. In order not to shorten the service life of the premises, they make the correct design for moisture and wind insulation of the panels, and also equip the building with sufficient ventilation. The “pie” is formed as follows: a wind-hydroprotective membrane is laid on the frame posts, a sheathing block is sewn onto it, on which decorative siding or other facing material is mounted. If a large amount of moisture potentially enters the plane of the wall from the inside, the membrane freely releases this moisture using a ventilation gap.
To better protect the insulation from the inside of the bath, it is covered with foil material, and all joints are sealed with an airtight film. Additionally, slats are mounted after the foil, creating an air space between them. Elements of interior decoration are screwed onto the slats.
The absence of an exhaust hood “kills” the building in 2-3 years. Walls and floors damaged by fungus cannot be repaired. Installing ventilation in a bathhouse does not require significant funds, and openings for natural air circulation are completely costless. You just need to know how to make ventilation in the steam room , where to place it, and what cannot be used specifically in this room.
Principles and main components of ventilation organization
The main condition that the ventilation system in the steam room must meet is ensuring effective air exchange. Fresh air must come from outside, displacing exhaust air. In this case, the hot steam should remain in the steam room.
When designing ventilation in a steam room, the requirements for it are simple:
- coolness should be concentrated near the floor, and heat should be concentrated near the ceiling;
- even temperature level, without fluctuations;
- “exhaust” air must be replaced with fresh, oxygen-enriched air.
For this purpose, they organize:
vents - supply openings that serve as channels for fresh air;
hoods are outlets through which heated, exhaust air leaves the bathhouse.
To achieve maximum efficiency of the ventilation process, experts recommend adhering to the following principles:
- locate the inlet openings as close to the stove as possible, and always near the floor;
- choose walls for placement of exhaust openings that are diametrically opposite to those on which the vents are located;
- do not place hoods under the ceiling;
- equip exhaust openings with special dampers or doors that allow you to control the air supply/exhaust.
To properly make ventilation, you need at least three holes:
- inlet – air flow;
- exhaust - gravity or forced - outflow of exhaust air;
- chimney.
What do we now know about ventilation?
The following conclusions can be drawn from the information provided:
- Ventilation in the sauna should be linked to general ventilation.
- The natural inflow should be close to the heater.
- The natural exhaust should be higher than the inflow, and the size of the hole should also be larger.
- The hood can be carried out through the adjacent room.
- To ventilate the sauna, you can use the ventilation valve near the ceiling or open the door.
- Mechanical ventilation should only be used if you have the necessary knowledge. Do not forget about the correct operation of the sensor.
- The air exchange rate should be 3-6/hour.
Tell us what you know about ventilation, ask your questions and clarify unclear points in the comments.
Canadian cedar lining - buy in Moscow at a low price
ventilation
Ventilation of the waiting room
When considering whether a hood is needed in a bathhouse, you should remember that the dressing room also needs to be ventilated, especially if it is combined with a relaxation area. The temperature difference between the dressing room and the steam room can cause condensation to collect and fine moisture to settle in the form of a slight fog.
Here, the exhaust opening is installed at the top under the ceiling, opposite the door of the steam compartment, in order to promptly remove the hot air flow. Placed at a distance of 15-20 cm from the ceiling, but not inside it. A ventilation duct can also be used to remove air masses. This method is more effective.
If natural exhaust ventilation is not functioning sufficiently, it is possible to install a fan for artificial stimulation.
How to make cellar ventilation in a garage with your own hands >>>>
Types of baths
Homemade steam generator for a bath
Steam is formed by the evaporation of water. They get it in different ways. The effectiveness of steaming and the bathing procedure itself depends on what kind of steam is produced, what temperature is maintained and how it is maintained. There are 3 options for steam baths.
- Sweat - sweat room. Here a person “washes himself” with his own sweat. In a Finnish sauna, sweating is achieved by high temperature, in a Russian sauna by relatively high temperature and whipping with a broom, in a hammam by high humidity. In the sweat room, a steam installation is not needed.
- Steam room - condensation from high-humidity air forms on human skin. Steam is obtained here by pouring water or kvass onto hot stones.
- Shaeck - the steamer is washed with warm water from numerous basins, checkers, barrels by splashing and dousing. It differs from a shower or bath in its short interaction with water. The main condition of the gang is that the temperature is high enough so that after dousing the person does not feel cold.
The need for steam generation appears in traditional Russian steam rooms and their analogues.
Ventilation of a foam block building
The question of whether a hood is needed in a foam block bathhouse is always accompanied by a positive answer. Unlike wood, cellular concrete does not have such hygroscopicity and extraction is simply necessary here.
The foam block structure is characterized by tightness, so it is dried thoroughly. Concrete is susceptible to the destructive effects of moisture and high temperatures. There are types of mold that get along well on concrete surfaces. If mold or fungal colonies have appeared, removing them will create a problem.
To ventilate the foam block bath structure, vents are organized inside the foundation even at the stage of its laying. Plastic pipes filled with sand are laid inside the frame at a certain distance. This ensures the flow of fresh air under the premises and along their lower tier.
Exhaust openings are located at the top of the walls, under the ceiling. It is important to remember that ceiling ventilation openings will create a quick release of hot air flow, which will look like a constant draft, reduced temperature of the steam room. The holes should be made 30-50 cm below the ceiling.
In addition, it is necessary to take care of ventilation of the roof and attic space, where condensation will accumulate due to the temperature difference between the external and internal flows.