Hello, dear readers!
How are you? Are you ready for the cold? Have you warmed up? Today I came across an article that, to put it mildly, puzzled me. It said that this winter would be very vigorous. That is, frosty and snowy. Well, what can we say? There are both advantages and disadvantages to this. The positive aspect is the fun entertainment - sleds, skates, skis, snowballs. And negative - heating the house will cost a pretty penny. In order not to be speechless when looking at the amount on the receipt, it is recommended to insulate the “nest”. Fortunately, there are plenty of materials for insulating a room.
I decided to look at what manufacturing organizations are offering today. My attention was drawn to the “old new” raw material – foam glass. Why "old new"? Well, how can I explain it to you? The old one is 86 years old, and the new one is improved. However, let's study the material in more detail. So, here’s a topic for you - foam glass: disadvantages, advantages, production, cost and much more. Shall we begin? Go!
Cellular glass: product features
A little history
Foam glass was invented by the honored worker of technology and science Isaac Ilyich Kitaygorodsky. The professor specialized in glass production technology, because he considered it the material of the future. The professor's invention was improved by US specialists in the 40s. Initially, foam glass was used as a floating material. But it soon became clear that it demonstrates excellent heat and sound insulation properties, is easily glued together, and is easy to process. Therefore, it was decided to use it in construction.
Thus, in Canada a building appeared, created from concrete slabs with a layer made of cellular glass. This event happened back in 1946. The experiment was very successful. The material has received well-deserved recognition. But, to the great regret of the inventor, it did not gain popularity in Soviet countries, since the cost was high and the production technology had not been developed. It was manufactured in the USSR, but the quality of the product left much to be desired, which led to the closure of factories.
But currently the production of this product is in full swing!
Concept
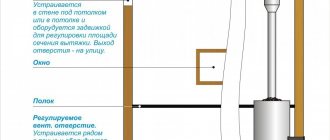
Balcony insulation
Foam glass is a heat-insulating material made from silicate glass and raw materials that promote gas formation. The insulation is often called foamed or cellular glass because it has a honeycomb-like structure. Due to this, it can boast of unique properties.
Production
Thermal insulation raw material - foam glass - is manufactured using powder technology. The process is quite simple, but labor intensive. It consists of the following steps:
- broken silicate glass is crushed;
- the crumbs are thoroughly mixed with gas-forming substances;
- the charge (homogeneous mass) is placed on a conveyor belt or in molds and sent to the oven;
- the glass softens, turning into a liquid but viscous mixture;
- under the influence of gases the gruel foams;
- the mixture cools slowly;
- the product is formed into blocks, slabs (sheets) or granules;
- the product is processed according to requirements;
- slabs, granules or blocks of foam glass are packaged.
We can say that ordinary glass, which is used in everyday life, and the cellular product are twins, since they are identical in composition, the only difference being the gas-filled pores of the foamed product.
Only high-quality materials and innovative equipment are used to produce blocks, granules or slabs. In addition, the products undergo control, which is carried out by experts in accordance with European quality standards.
What is foam glass?
The combination of two different substances in one material always gives an interesting result. This happened with foam glass. The classic silicate glass that is used in our windows is a transparent, very hard and fragile material. Foam is a weightless, “ephemeral substance”. Its basis is a gas, the bubbles of which are held together by the thinnest layers of liquid by the force of surface tension.
You may ask, is it possible to combine incompatible things? It turns out that it is possible. The production of foam glass consists of heating a silicate mass into which a gas-forming substance is added. Under the influence of high temperature, the raw material melts, and the gas-forming agent decomposes, releasing tiny bubbles. Caught in the hot melt, they, like “flies in amber,” remain in it forever.
As a result, the material receives unique properties:
- Ease;
- Strength;
- Chemical inertness;
- Waterproof;
- Heat resistance and non-flammability.
The material inherits some of the listed properties from silicate glass, and receives some from gas microcapsules. Foam glass loses its transparency, but acquires excellent thermal insulation and acoustic characteristics.
Kinds
Today there are two types of foam glass - granular and block.
In addition, there are three types of granular insulation:
- foam glass gravel;
- foam glass crushed stone;
- foam glass sand.
There are also three types of block insulation:
- slabs (foam glass sheets);
- blocks;
- shells (shaped foam glass).
If we compare the thermal properties of granulated and block glass, of course, gravel, crushed stone and sand are inferior to slabs, shells and blocks. But, nevertheless, granular insulation is more popular due to its relatively low price.
Scope of application
Foam glass, due to its properties, is used for insulation:
- private houses;
- outbuildings;
- sports complexes;
- underground structures;
- industrial buildings;
- medical institutions;
- educational institutions;
- office facilities;
- recreational facilities - (for example, for baths, water parks, etc.).
The scope of application of the material is very wide, since the thermal insulation material is impeccable:
- to insulate the ceiling: the attic floor is filled with cement-sand mortar, and then the slabs are laid, after which a reinforcing screed is made;
- for walls: the surface is prepared, special glue is applied, the product is applied, pressed tightly and covered with plaster;
- for the floor: a layer of sand (3–5 cm) is poured, thermal insulation is laid or backfilled, joints are sealed, screed is applied, the covering is installed;
Yes, the material is popular due to its good technical characteristics.
Liquid glass production technology
Foam glass was created in the pre-war thirties in the USSR.
Its creator was Academician I. Kitaigorodsky.
This scientist came up with an interesting know-how - to combine opposites - hard, finely ground silicate glass and loose, light foam .
Kitaigorodsky knew that silicate glass softens quite well. It was these properties that the scientist took advantage of to create a new, more advanced material.
He proposed adding a gas-forming agent (carbon or carbonate) to ordinary broken glass, crushed to a powder state, and then heating the resulting mixture to an ultra-high temperature of 800-900 degrees.
At this temperature, the glass mass becomes viscous-liquid, and the gas-forming agent begins to oxidize, resulting in the formation of gas bubbles . It is they who make the glass melt foam.
When the foam glass cools, the gas bubbles freeze tightly in the silicate melt. Cool it slowly - thanks to this, the material does not crack and is evenly distributed in the molding container.
Properties
Cellular glass is famous for the following properties:
- noise absorption – 56 dB;
- water absorption – 0–5%;
- vapor permeability – 0–0.005 mg/m*h*PA;
- thermal conductivity – 0.04–0.08 W/(m*K);
- humidity (sorption) – 0.2–0.5%;
- bending strength – 0.4–0.6 MPa;
- compressive strength – 0.7–4 MPa;
- effective operating temperature – -260 – +400°С;
- actual operating temperature – -260 – +230°С;
- deformation temperature – +450°С.
Based on this data, recognized advantages and annoying disadvantages can be determined.
Advantages
The material has many advantages. Let's look at the main ones.
- Safety. Does not contain substances harmful to the human body.
- Environmentally friendly. Made from environmentally friendly raw materials.
- Hygiene. Has antiseptic properties.
- Durability. Service life - more than 100 years.
- Versatility. It is used for insulation of any buildings.
- High adhesion. Combines with a lot of building materials.
- Biological passivity. He is not afraid of rodents, insects and microorganisms.
- Resistance to the negative effects of climatic factors. He is not afraid of temperature changes, precipitation, UV, etc.
- Resistance to mechanical factors. It does not deform and does not lose its properties, since it can withstand impacts and high loads.
- Unaffected by chemical factors. Does not react to acid.
- Resistance to thermal factors. Foam glass is an absolutely non-flammable insulation material.
- Ease of processing. It cuts perfectly with a regular hacksaw.
The material is worthwhile, but there are drawbacks and there are many of them, unfortunately.
roof insulation with foam glass
Execution options
Foam glass can be presented in several versions, the main of which are:
- blocks and slabs;
- chit;
- crushed stone
Blocks (slabs)
Block foam glass is a very reliable material. They have a lot in common with polystyrene foam and mineral wool boards. Blocks come in very different shapes and sizes.
Their parameters are set during the creation of foam glass - immediately after foaming it is given the desired shape.
Standard sizes of foam glass blocks are 600x450 mm. Their usual thickness is 3-8 cm. The main purpose of the blocks is to insulate.
They are used in:
- external perimeters and plinths of buildings;
- floors made of various materials;
- roofs made of wood, ceilings and roofs made of concrete;
- internal walls of various rooms.
The average price of foam glass slabs from leading manufacturers is:
- material from Isostek company RUB 18,000. per m3
- blocks from Neoporm company RUB 29,000. per m3
Granular (crumb)
Granules are the smallest particles of foam glass that remain as waste (crumbs) after the production of foam glass slabs and crushed stone. This material is also obtained from ordinary broken glass, which is not suitable for recycling.
Crumbs are produced in several fractions: the smallest is 0.15 mm, and the largest reaches 5-10 mm.
Material used :
- as a thermal insulation backfill in construction;
- as an insulating additive in various mixtures; crumbs are added to masonry mortars, mixtures for screeds and grouting, plaster and tile adhesives;
- crumbs often serve as finishing materials for houses of various types; to get a good thermal filler, it is simply mixed with glue.
The price of granular material depends on the particle size. The smaller it is, the higher the cost:
| Fraction size, mm | Price for 1m3, rub. |
| 0.25-0.63 mm | 8000 — 10500 |
| 0.63-2 mm | 7800 — 9500 |
| 2-4 mm | 7500 — 8000 |
| 4-10 mm | 5700 — 7500 |
| 10+ | 4500 — 5500 |
Crushed stone
Crushed foam glass is specially crushed elements of this material without a specific shape.
The main advantage of foam glass crushed stone is that it does not deform under sufficiently strong compression (0.95 - 5.0 MPa).
That is, a road roller or truck can easily roll over it and not cause any harm.
Crushed foam glass is used in:
- agriculture and horticulture - in the drainage system for protection from groundwater;
- industrial equipment;
- pipelines and heating mains, as well as buried tanks as insulation and sound insulator;
- in road construction;
- creation and interior design; it is used in roofs, attic and balcony floors, floors and foundations of various premises and not very tall buildings.
The average price of crushed stone per m3 ranges from 3,500 to 4,500 rubles .
Flaws
Of course, every raw material has its negative aspects. Foam glass is no exception. Before purchasing material, you need to carefully study the negative aspects.
- High price. The production of raw materials requires innovative high-tech equipment, which leads to its rise in price. And also the production of foam glass requires high energy costs.
- Fragility. The raw material, despite its strength, is very fragile, which leads to cracking if installation recommendations are ignored.
- Lack of steam conductivity. Foam glass, as was said, is not subject to the destructive effects of biological factors, but the surface under it is easily damaged.
- Fear of alkalis and hydrofluoric acid. Cellular glass, like an aspen leaf, trembles at the “sight” of alkalis and hydrofluoric acid, since they are capable of destroying it.
- Heaviness. The raw materials are relatively heavy, which negatively affects the building structure.
- Durability. Of course, a long service life is a plus. But the materials used to construct the facility are unlikely to last more than 100 years. This means that the structure must be repaired periodically, and cellular glass is not intended to be reused. Which exit? Replacing insulation.
- Low impact strength. Cellular glass does not withstand even light impacts. Mechanical influence is the “death” of the material. Of course, if the insulation is in the structure, it is not afraid of impacts. He is afraid of them during transportation, unloading and installation.
- Impossibility of “reanimation”. If the glass is damaged, it can be taken to a landfill. It is impossible to glue or cover up the cracks.
Properties played a cruel joke on cellular glass, turning a huge number of advantages into disadvantages.
Application
What is especially valuable is that cellular glass combines high strength and heat-insulating ability.
We are all accustomed to the fact that the harder the material, the stronger it conducts heat. Here everything is the other way around. This is a tough, effective insulation material that can be driven on by a truck. Therefore, the use of foam glass is primarily associated with thermal insulation of load-bearing walls, basements and pipelines.
Cellular glass has a thermal deformation coefficient close to that of concrete and brick, so it can be used to cover any type of structure made from these materials.
Due to its low water absorption, foam glass is ideal for waterproofing basements and the basement of buildings. This positive point is most often noted in consumer reviews.
In addition to block glass, granular foam glass is produced. It is cheaper than a monolith and is used as an insulating additive in concrete, as well as backfill in wall cavities.
Despite its high mechanical strength, foam glass is easy to process. It drills and cuts without forming cracks, is easy to glue and holds finishing compounds (putty and plaster) well.
Foam glass is used not only for insulating building structures. It can be found in the housings of industrial refrigerators and technological equipment operating at elevated temperatures.
External foam glass finishing also deserves attention. In addition to its original appearance, it reliably solves the problem of protection from aggressive atmospheric factors (cold, heat and precipitation).
Price
The cost of foam glass is steep. Prices, of course, vary, as they depend on many factors, but on average you can buy blocks by paying $120–400 per cubic meter. You can purchase slabs and shells by paying $110–350, and you can get a granular version by spending $35–100 per cubic meter.
What can we say? Insulation with foam glass is a very dubious and costly undertaking, since the material has a lot of serious drawbacks, and, in addition, is incredibly expensive. But, as they say, the master is the master. Maybe it’s not for nothing that they call it the raw material of the future. To buy or not to buy? That is the question! The choice is yours, dear readers.
Warmth and comfort to your home, dear friends! See you on other blog pages!
Wisdom quote: Reading is the best teaching (A.S. Pushkin).
Attention! Low-quality “analogs” of foam glass
Speaking about this material, one cannot fail to mention its cheap “analogue”, also called foam glass by the manufacturers. In fact, it is made not from standard solid raw materials by firing, but from liquid soda-potassium glass.
Substances that actively absorb water are added to this substance. As a result, liquid glass foams and then hardens. The process takes place at a temperature of +100 - +200C. Even an inexperienced person understands that such a material, in principle, cannot be durable and waterproof. Essentially, this is ordinary office glue with gas bubbles.
At the slightest soaking, it flows, and in terms of mechanical strength it is tens of times weaker than classic porous material. Therefore, insulation with foam glass of this type (it is sometimes called “vapor-permeable”) cannot be called profitable.
The only advantage that manufacturers are trying to attract consumers is low cost (2-3 times lower than conventional foam glass).