Not all stones are suitable for the formation of “correct” steam in a bathhouse. Preference is given to rocks enriched with minerals and beneficial properties. One of these stones is Dunite. This is an igneous rock.
The stone originates at great depths, and comes to the surface of the earth during volcanic eruptions along with magma. The stone is mined in mountainous regions. In Russia, Dunite deposits are located in the Urals.
The appearance of the stone is unremarkable. The color is predominantly dark: from black and gray to dark green with splashes of different colors.
Dunit is considered the best breed for a bath. It tolerates temperature changes well, is completely harmless and is able to retain heat.
Application
Where can dunite stone be used:
- Most often used as a breed for laying in a steam room.
- Acts as a facing material in ovens.
- Can act as a fertilizer when planting potatoes.
- In combination with clay, it acts as a refractory material for laying out stoves in bathhouses.
- It is an ornamental stone.
- As a floor covering with an anti-slip surface.
- In the manufacture of heat-resistant ceramics.
This mineral is not used in construction.
Pebbles of river or sea origin
This is a very cheap option for arranging a furnace.
These stones can be laid as the first layer, and a little soapstone on top of them. You just need to select the right pebbles, then the heater will turn out beautiful and durable. It is recommended to take flattened sea stones, not oval or ovoid ones - in this case, more of them will fit in the oven.
Thanks to this, accidental contact of water with metal will be practically excluded. You should look carefully at the stones - those with even slight red veins are not suitable for the stove, since these inclusions indicate the presence of iron, the evaporation of which in the steam room will not benefit health.
It is also not recommended to take soft stones for saunas and baths - limestone is harmful to health, especially in a steam room.
In addition, it also quickly breaks down and turns into unpleasant dust, which is very difficult to get rid of.
If there is no sea or rivers nearby, then quite good pebbles can be found under high-voltage electrical lines - they were covered with it back in Soviet times.
Some people even use porcelain cups, although their environmental friendliness is questionable. In addition, they crack, although the steam is good. The only problem is that the cups are difficult to place in the oven.
Properties
Dunite is considered one of the ideal minerals for baths. It belongs to the olivinite-dunite family, a class of ultrabasic, plutonic rocks.
Origin
A mineral such as dunite is formed much below the earth's crust at the level of the upper mantle. In the process of gradual cooling of magma at the beginning of crystallization and differentiation of lava, this rock is formed. It is usually found in deep caves, where it accumulates due to the displacement of plates during tectonic processes.
Chemical composition
The mineral contains practically no volatile substances. It is based on various oxides. Their percentages are:
- SiO₂ 35-40%;
- MgO 38-50%;
- FeO 3-6%;
- Fe₂O₃ 0.5-7%;
- Al₂O₃ up to 2.5%;
- CaO up to 1.5%;
- Na₂O up to 0.3%;
- K₂O up to 0.25%;
- TiO₂ up to 0.02%.
Mineral composition
Most of the composition of dunite - about 90% (sometimes more) belongs to the mineral olivine. It also includes chromite, pyroxenes and, in rare cases, hornblende. The mineral has a medium or fine-grained structure. Under the influence of hot underground waters and weathering, serpentinization begins, as a result of which it becomes another mineral - serpentine.
Dunite color
Dunite stone can be of different colors, up to very light or deep dark tones, even black. The most common option is various shades of green. In structure it is a completely opaque stone.
Spreading
There are dunite deposits in different places around the globe. In Russia, it can be found in the Caucasus, the Baikal region and the Northern Urals. Also on the continent you can find this breed in Ukraine and in the countries of Central Asia.
Physical and mechanical properties
List of physical and mechanical properties of the mineral:
- Retains its shape when heated or wet.
- Refractory stone with a low coefficient of linear expansion when heated.
- Thermal conductivity coefficient is 1.1-1.9 W/m*K.
- Specific heat capacity 0.6-0.8 kJ/kg*K.
- Thermal diffusivity coefficient is 7.1-8.5 m2/s.
- Density 3280 kg/m2.
Igneous rocks
Dunite belongs to the igneous rocks. Igneous rocks are the result of crystallization of molten magma. The class of rocks depends on the depth at which magma solidifies and the process of its crystallization occurs.
There are three classes of rock division: plutonic, volcanic and hypabyssal.
Plutonic and volcanic rocks are used in the stone backfill of the sauna stove.
But the division and classification of breeds does not end there. Plutonic and volcanic rocks are divided into four groups based on their silica content.
These are: ultrabasic, basic, medium and acidic. Ultrabasic rocks contain from 30 to 45%, basic rocks from 45 to 53% silica.
Olivinites-dunites belong to ultrabasic plutonic rocks.
Consequently, dunites contain a minimal amount of silica, which is good for a sauna stove. Less unnecessary waste.
Advantages and disadvantages
The mineral rock dunite has both pros and cons. Among its positive qualities:
- the ability to heat up quickly, conduct heat well and not expand in the process. Heat is also released evenly;
- fire resistance – the ability to withstand temperatures up to 1200 degrees and not crack during operation;
- does not emit odors when heated;
- improves the condition of hair and skin, restores the functioning of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems;
- reacts with carbon dioxide, thereby preventing poisoning in the steam room.
But the stone also has the following disadvantages:
- short service life of about 5-6 years;
- unattractive appearance due to the scarcity and dullness of the color scheme;
- there are a large number of fakes;
- most often you can find small stones;
- There are rocks interspersed with sulfur, which, due to elevated temperatures and humidity, turns into hydrogen sulfide acid.
Requirements for bath stones
Choosing stones for your steam room is both simple and complex. The material must meet certain requirements:
- Ability to accumulate heat. The mineral chosen for the bath should heat up fairly quickly, and at the same time give off heat for a long time. Dense stones with a uniform structure and high specific gravity have such abilities.
- High temperature resistance. This is the most important quality, since with large temperature changes the stones may begin to split or crack. You can check them by knocking a stone against a stone or hitting it with a hammer. A more serious test can be carried out in a steam room by first heating the mineral red-hot and then throwing it into cold water. High-quality stones will withstand all this.
- Correct format. The choice of stones directly depends on the type of stove. For wood-burning stoves, the best choice would be large minerals with a diameter of 70–120 mm. Electric ovens are compact in size, so small stones measuring 50–60 mm in size are suitable for them. Minerals that are correctly chosen in format will serve for a long time and delight owners with their aesthetic appearance.
When choosing material for your heater, you need to make sure that the stones are:
- approximately the same in shape and size, so that the circulation and heating of steam and air is uniform;
- without cracks - this will be indicated by a clear sound when hitting the stone with a hammer;
- homogeneous in structure - minerals with inclusions will heat up unevenly and will collapse over time;
- environmentally friendly.
Some experienced bath attendants prefer crushed minerals, explaining that they are more effective because they have a larger area of reflective heat. This is true. But at the same time, smooth stones last much longer without damage.
How to choose the right dunit for a bath?
Although dunite is considered an inexpensive rock, sometimes you can stumble upon crafts or alternative minerals. Clinopyroxenite and serpentinite are often sold under the guise of dunite. They are not suitable for use in a heater, as they are not able to retain heat for a long time.
In order not to make a mistake in choosing to buy real dunite, you can use the following tips:
- Scratch the surface of the stone with a sharp object. The scratch will remain on the serpentinite.
- The stones should be free of small spots and veins of golden, gray or yellow hue. These are sulfur harmful inclusions.
- Stones can be tested for strength by simply hitting them with a hammer. They should not crack or crumble.
- You need to buy stones that are dense, durable, without defects or cracks. Otherwise, they will not last long and will quickly deteriorate.
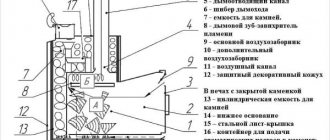
Soapstone stoves
All the characteristics of a soapstone stove are no worse than its common counterpart - the “Russian stove”. In addition, soapstone prevents the harmful effects of infrared radiation on humans, unlike metal fireboxes. One such stove can evenly heat a bathhouse with an area of 40 to 120 square meters.
Oven lined with soapstone
But, like any material, soapstone has its drawbacks:
- modest, dim color;
- takes a long time to warm up the room;
- high price;
- large weight of the workpiece (only about a kilogram of soapstone is required to create a stable foundation for the heater).
But compared to its advantages, you simply don’t pay attention to these disadvantages. It can be used both for cladding walls and floors, and for making a high-quality stove. Soapstone is also an excellent material for creating a unique interior, as it is combined with wooden elements of a sauna or steam room.
Below are some tips on how to choose the right soapstone tiles.
The tile should be:
- hard;
- do not leave dirt on your hands;
- do not crumble from strong finger pressure;
- pores over the entire area should be small and round.
In conclusion, I would like to say that to increase the service life of the tile, it is necessary to take care of it; if you find cracks and chips, then it must be replaced. With frequent use of essential oils in the bath, the resulting carbon deposits must be removed periodically. If you use soapstone that you assembled and installed yourself, it can release chemical elements that are hazardous to human health when heated. Be careful when choosing this stone, buy only in specialized stores and then it will serve you without unnecessary hassle for many years.
How to replace dunite
Finding dunite on sale is often quite difficult. Therefore, it is possible to replace this rock with other minerals. They may have a longer or shorter service life, as well as their own advantages and disadvantages. Alternatives worth considering:
- Gabbro-diabase has the same low cost, is able to retain heat for a long time, and does not emit any impurities during the heating process.
- Soapstone has good heat capacity and does not emit odors.
- Jadeite is another green rock with an attractive appearance and healing properties.
- Porphyrite has a pleasant aroma when heated; it contains various impurities.
- White quartz is an opaque rock.
- Chromite is resistant to mechanical stress.
- Wax jasper has a healing effect and is not afraid of steam.
- Jade is an expensive green rock.
- Rodingite comes in green, gray, and blue colors and has a long service life.
Chemical composition
Chemical theoretical composition: MgO - 69.12; H2O - 30.88; Mn and Fe partially replace Mg; When Mg is replaced by Mn, no distortion occurs in the structure. In small quantities, Mg is also replaced by Zn (3.67% ZnO in manganbrucite from Franklin). Sometimes CO2 content is noted, which is apparently due to the presence of carbonate impurities. In brucite from the chromite-bearing massif of Southern Iraq (Bashkiria), Ga (0.0003%) was spectroscopically identified.
Varieties
Nemalite - nemalite - fine-fibrous. The name comes from the Greek “nema” - thread (Natel, 1821). Synonym of Nematolite - nematolite (Hinze, 1915). The fibers are elongated in parallel (0001). There are two types of nemalite: 1 - the direction of fiber elongation completely coincides with the a-axis (nemalite from Asbestos and Luoyang); 2 - the direction of elongation forms an arbitrary angle with a (nemalit from Lancaster and Hoboken counties). Colors are white, cream, emerald green, teal and black. The luster is glassy or silky. Elongation (—). Usually biaxial. The composition corresponds to the formula of brucite. Fersman distinguished between nemalite and ferronemalite - ferronemalite - with a FeO content of 5-7%.
Nemalit
Ferrobrusite - ferrobrucite (Lacroix, 1909) contains a significant amount of Fea+, replacing Mg (up to 36% FeO, according to Betekhtin). In appearance, in a fresh state, it is completely similar to brucite. In the light it turns brown and splits along cleavage planes. In the weathering zone it acquires a golden-brown color and turns into pyroaurite. It was observed in association with brucite (in zonal intergrowths) and with magnesium hydrocarbonates in cracks among highly serpentinized dunite, sometimes in chromite bodies. Iron-rich varieties were found in Russia in the Urals in platinum-bearing chromite deposits in the Nizhne Tagil dunite massif (according to Betekhtin, 1950). It is possible that collingite or its mixtures are sometimes mistaken for ferrobrusite.
Manganbrucite - manganbrucite (Igelström, 1882) contains a significant amount of Mn2+, replacing Mg. Synonym for manganobrucite. The mineral from Franklin has a ne of 1.60; no = 1.59. In air it quickly turns brown and black. Found in association with hausmannite and other minerals in manganese ores of Jacobsberg (Värmland, Sweden) and zinc ores of Franklin (New Jersey, USA).
Trigonal syngony.
Class. Ditrigonal-scalenohedral D3d - 3m (L33L23PC).
Crystal structure
The structure is layered, similar to the structure of CdJ2; the role of an anion is played by the (OH)1- group with an ion radius of 1.33 A. Such groups are arranged according to the principle of the closest hexagonal packing. Each layer consists of two parallel (0001), flat sheets folded by groups (OH), and a layer of Mg atoms located between them, occupying all the octahedral voids between the sheets (OH); each Mg atom is located between six (OH), linking three (OH)1- of one sheet with three (OH)1- (rotated by 180°) of the other sheet. Perfect cleavage passes between triple layers, linked to each other by weak residual bonding forces.
Nemalit
Main forms:
Place of Birth
Ultramafic igneous rocks are widespread in the Urals and the Caucasus. The Kytlym dunite deposit, which is located in the north of the Middle Urals and is associated with a large deposit of alluvial platinum, is famous. Greenish and yellowish dunites form a 1.5 km wide intrusion in the Sverdlovsk region, called the Job Body.
When building a bathhouse on your own plot, the owner is faced with several questions. How to line the stove and fill it? How to choose non-toxic materials? The answer is to use dunite. We will talk about this stone in more detail.
Peculiarities
Dunite has a grainy texture. Most often it is fine, but there are stones with medium and coarse-grained texture. The color scheme is not very diverse. The mineral is found in gray, brown, green and black shades. Note the inclusions of gray or metallic color, which indicates the presence of sulfur in the rock. When they come into contact with high temperatures and high humidity, sulfuric and sulfurous acids begin to be released, the vapors of which irritate the mucous membrane of the eyes and respiratory tract, and even cause burns.
If such inclusions are insignificant, then after several heating-cooling cycles all the sulfur will completely disappear and the sauna will become safe. But if there is a large accumulation of sulfur, it is better to throw away the entire stone.
Reviews
Reviews from real customers are very contradictory. Some say they are very pleased with the purchase. The stone perfectly withstands a large number of heating-cooling cycles, does not crack, and does not emit unpleasant odors. They note an improvement in health after going to the bathhouse where dunite is used.
Others note that the stone quickly collapsed, when heated, it forms a porous structure, and when moisture gets on it, it absorbs it. Most likely, this is due to the fact that a low-quality stone was used, which quickly turned into serpentinite.
About the disadvantages
It's time to talk about the unpleasant. We also talked in other articles about the fact that sulfides are the reason why many users speak unflatteringly about Karelian stones (here we are talking not only about dunite , but also about gabbro , and porphyrite , and other stones mined there). However, it cannot be said that sulfide admixture is a problem only in Karelian deposits. They are found quite often in deep igneous rocks everywhere.
IMPORTANT! How does sulfide behave in a bath? Under the influence of high temperature in the presence of air, it releases sulfur, which turns into oxides, and under the action of water vapor, sulfur oxides immediately become acids . Tiny drops of acids (sulfuric and sulfurous) enter the nasopharynx when breathing, burn it, causing soreness and coughing. The eyes also suffer - a sharp pain is felt in them. The more sulfides in the stones, the more dangerous they are for vapers.
Compared to acid, another drawback will seem trivial: dunite is not found very often on the surface, so it is considered relatively rare, and this is reflected in its price .
serpentinization, which has been mentioned more than once, is also one of the disadvantages of the stone.
Price
Dunite is a relatively inexpensive stone. Its cost on the market ranges from 20 to 55 rubles. for 1 kg. Dunite for baths is usually sold processed and packaged in boxes of 20 kg, which ensures ease of transportation.
Important! You should not chase the price, as there is a risk of running into a fake, which releases sulfur when heated, resulting in the formation of sulfuric acid, which can be harmful to health.
Also, under the guise of dunite, pyroxenite is often sold, which is easier to mine and therefore its cost is lower, but it can crack under the influence of high temperatures and release toxic substances.