Refractory materials are products made using mineral raw materials. They are characterized by a stable structure when exposed to flame, chemical reactions and long-term operation. They are used at industrial facilities, where technological processes involve the use of significant temperatures, and in residential buildings, where thermal apparatuses are used. Due to their high technical and operational characteristics, refractory materials are used in facilities where the requirements for reliability and durability are high.
Technical and operational characteristics
The main property of such materials is fire resistance, which expresses the temperature at which the deformation process begins. With respect to this value, the effectiveness of their use for certain purposes is considered. In addition to this parameter, others are also considered. Namely, how refractory behaves under the influence of strong heat:
- change in shape and violation of the integrity of the product under load at elevated temperatures;
- compression force parameters when heated, they reflect the stability of the structure;
- Neutral to chemical influences.
On a note! Fire-resistant materials can withstand significant temperatures, the minimum value is +1580 degrees C, the maximum is 3 thousand degrees C. Products that can maintain properties at the highest temperature parameters are called super-fire-resistant.
Fireproof cardboard MKRKL
The right choice of materials
In order to increase the fire resistance of materials, special means are used - fire retardants. These are components that are added to organic materials to increase fire protection. Their use is based on the melting of low-melting components when the treated material is exposed to fire (salts of phosphoric acids, borax, ammophos, diammonium and others), as well as on the decomposition of substances when heated. In this case, a certain percentage of thermal energy is spent on their melting, and part of the salts that are released during decomposition extinguish the flame.
Fire retardants:
- prevent fire and smoldering of the processed material;
- protect against corrosion;
- have a long-term effect;
- do not moisten the tree;
- do not emit toxic substances;
- do not spoil the paintwork of wood;
- provide the maximum level (independently or together with antiseptics introduced as part of one solution) of biostability of impregnated materials;
- do not create difficulties during mechanical impregnation of materials;
- do not affect the properties of treated surfaces.
One of the most effective fire retardants is diammonium phosphate, which, when heated, is capable of releasing phosphorus oxide, which covers the wood with a protective film. For improved protection of wooden products from fire and mold, antiseptics (for example, sodium fluoride) can be added to fire retardants, which do not reduce their fire retardant properties.
During severe fires, wooden buildings are significantly reduced in volume, and this occurs as a result of charring. There is a sharp loss of safety margin, which, in turn, can lead to collapse in 90% of cases. Reinforced concrete structures are among the strongest and most durable, however, despite this, their behavior in fires is also ambiguous. The fire resistance limit of reinforced concrete products is determined by many factors: the type of fire and the concrete compositions, aggregates and reinforcement used, the thickness of protective words in concrete, humidity and load of concrete.
If the fire has already developed, the temperature in the combustion zone, as a rule, exceeds +1000 °C. In such conditions, parts of load-bearing units may experience significant thermal stress, and the local temperature of individual elements of these structures may exceed critical fire resistance limits and lead to their deformation. The need to carry out a set of fire protection work against the hazardous effects of high temperatures is obvious and meets the requirements of building codes and regulations.
They regulate that various building structures made of metal or wood, including load-bearing elements of structures, interfloor ceilings and other parts, must have a fire resistance limit that corresponds to their functional purpose. Today, most fire retardant materials differ:
- simplicity and manufacturability of application;
- maintainability of coatings;
- duration of operation;
- relatively low cost;
- high efficiency at work.
Fire retardant materials are used in cases where achieving the required fire resistance limit of building structures or the fire hazard characteristics of building materials is technically impossible or economically unprofitable. Today, there is a large selection of different materials (paints, varnishes, plasters, mats made of non-combustible materials) and methods for qualitatively increasing the fire protection of building structures.
Classification
Fire-resistant products are available in various forms: in plates, sheets, rolls and there is a group of unformatted materials. In addition, it is divided into types according to other characteristics:
By size and shape:
- wedges and straights of small, normal and large sizes;
- shaped simple, large-block, complex, weighing more than 60 kilograms;
- laboratory or industrial use.
By production method:
- production of refractory materials by sawing rocks from blanks;
- cast, made using liquid casting technology;
- production from plastic masses with subsequent additional pressing;
- formatting by pressing from powders;
- made by hot pressing;
- manufactured by thermoplastic pressing;
- formatted from hot melt.
According to deformation temperatures:
- from 1580 degrees C to 1770 degrees C - ordinary fireproof;
- up to 2 thousand degrees C – highly fire-resistant;
- up to 3 thousand degrees C – materials with the highest fire resistance;
- more than 3 thousand degrees C – super-fire-resistant.
By degree of porosity:
- the pores are open, their volume does not exceed 3% - especially dense;
- pores open up to 10% - highly dense;
- pores are open, volume up to 16% is dense;
- pores are open, up to 20% are compacted;
- pores are open, up to 30% - medium dense;
- total porosity up to 45% - low density;
- total porosity up to 75% - highly porous;
- total porosity more than 75% - ultra-porous.
Varieties by composition:
- oxygen-free;
- siliceous;
- silicon carbide;
- aluminosilicate;
- carbon oxides;
- glass-magnesite;
- aluminous;
- carbon;
- magnesium;
- oxide;
- magnesian-calcareous;
- zirconium;
- limestone;
- chromium;
- magnesia-silicate.
Basalt fireproof insulator
Types of substances
It is customary to distinguish three main types of non-flammable substances of different origins.
The first type includes solid materials presented in various structural and aggregate states. These can be bulk substances, structures, and individual piece products. This number includes:
- various rock samples, both hard and softer, including limestone, dolomite, marble;
- concrete and reinforced concrete products;
- loose rocks, including gravel, sand, crushed stone;
- binders - chalk, clay, cement, gypsum, lime, plasters, mortars;
- cast iron and steel products of various types and designs - angles, channels, beams;
- non-ferrous metals, including bronze, copper, brass, aluminum alloys;
- mineral fibers, such as basalt;
- various types of textile materials, including asbestos fabric, basalt fiber;
- regular and fire-resistant glass.
Liquid substances:
- foaming agents and detergents;
- all types and conditions of water, from a drinking source to use as a coolant;
- synthetic liquids that cannot burn;
- acids, alkalis, salts in the form of an aqueous solution.
Gaseous substances:
- carbon dioxide;
- nitrogen;
- freon;
- argon.
Scope of application
Fire-resistant sheet materials are most in demand. Their purpose is determined by the size and set of properties of a specific product. The products are mainly intended for lining stove structures, boiler rooms, fireplaces, chimney ducts, thermal insulation of columns and heating boilers, in baths and saunas. Such protective screens can significantly increase the service life of structures and equipment as a whole, and their individual elements. Powder and molding products are widely used in instrument making to protect devices from temperatures and regulate operating conditions in accordance with technical specifications. Unmolded raw materials are used to produce special clothing, such as equipment for foundry workers.
Non-flammable refractory based on magnesium oxide
Protective screens for heating devices
If safety rules are observed, protective screen panels are used. These are structures that insulate the side walls of furnaces. Most often, brick and steel are used as a protective screen. Depending on the shape, screens can be front or side. You can also see stoves on sale where a screen is not needed, and their safety is ensured by a special casing that reduces thermal radiation.
Screens for fireplaces will not only protect you from open fire, but will also be a wonderful addition to the interior
Nowadays, fireplace screens are very common, which not only protect against open fire, but also become an excellent accessory and decoration for a country house or city apartment. There are different materials available for screens: glass, copper, iron, brass, bronze.
Heat-resistant ceramic glass is especially often used, which reliably protects against sparks and coals and gives the home a special comfort and attractiveness. The disadvantage of this material is that the penetration of heat into the room is reduced.
You can make a fireplace screen with your own hands. A metal strip, cut to the size of the firebox, is decorated with a large number of chains, which are sold freely in any store. Hooks are hung on both sides of the firebox to secure chains when the fireplace is not lit.
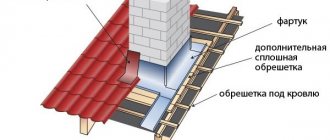
In this video you will learn about thermal protection of walls:
OLM production
The production of refractory materials begins with the preparation of raw materials. Often workers manually pick out contaminants and impurities from it. Next, the raw materials are crushed and sifted. Then the powder and additives are mixed in strictly defined dosages. The mixture is formatted, dried under natural or special conditions, and fired.
You should understand! OLM are made from natural and artificial raw materials. The most compatible chemical and mineral substances are selected. The structure, density, porosity and strength of the required parameters are formed using a specific technology.
Fireclay heat-resistant bricks
Fire-resistant products differ according to the types of raw materials:
- Organic components. Such products are made from mineral raw materials and are able to withstand significant temperatures. But not all types. For example, expanded polystyrene is characterized by a low resistance to heat and fire, but it can be used to make a stove or fireplace with low heat.
- Inorganic components. This is the largest group of products, the range of fire resistance of which is large. The category includes mineral and basalt slabs, fiberglass, cellular concrete, vermiculite, honeycomb plastic, perlite. The cost of such products is not high - from 300 rubles per 1 m2.
- Composite compositions. This group includes asbestos-based products: asbestos-lime and asbestos-cement materials. This also includes foamed silica products and some others.
Varieties
Here is a classification of what types of non-combustible materials are:
- insulators;
- insulation;
- finishing for interior partitions, floors, ceilings.
Additionally, they differ somewhat in their ability to transfer heat:
- do not allow thermal energy to pass through due to special physical and chemical properties;
- reflect the infrared spectrum of radiation.
Manufacturers offer sheet, panel, and roll products according to the form of release.
According to the place of application for finishing interior spaces, for cladding facades - installation on the external walls of buildings.
Note! In addition to basic fire-fighting characteristics, fire-resistant products may have additional parameters. For example, moisture resistance allows its presence in a commercial catering unit, in a kitchen, or in a swimming pool. Almost absolute sound absorption makes it possible to create acoustic structures, such as conservatories and recording studios.
OLM for walls
OLM is used in the construction of buildings and structures. Such products are presented in a wide range. Concrete is in high demand; it is accessible, easy to use and safe for human health. Fire-resistant sheet material is often used for cladding walls and ceilings. This finish significantly increases fire safety and is used in facilities with high fire safety requirements. There are many varieties, the most popular types are:
- Cardboards and boards based on fiberglass and asbestos. This is the most cost-effective solution; the materials can withstand exposure to an open flame for half an hour, and heating up to +700 degrees C.
- Vermiculite. The heat resistance of the boards reaches +900 degrees C, they are chemically neutral, resistant to moisture, and do not react with organic solvents.
- Mineral slabs. They are in high demand due to the optimal combination of operational and fire-fighting qualities. They are based on white cement.
- Magnesite. The sheets are resistant to aggressive environments and strong heating.
- Rolls made of basalt fiber. An aluminum heat-reflecting coating is applied to the surface. They can withstand temperatures up to +900 degrees C. The fabric is light and flexible, optimal for installation on structures with complex geometries.
- Terracotta tiles and porcelain tiles. Air- and moisture-permeable tiles with good thermal insulation properties. They are easy to use and maintain; stains can be removed with ordinary detergents. They retain their structure and characteristics for decades and multiple heating cycles. They are both refractories and finishing materials.
There are OLMs that should not be used in rooms where people are, for example, basalt slabs with the addition of formaldehyde resins. When they reach +300 degrees C, they begin to release toxic substances and toxins.
Fireproof high strength brick
Non-flammable foam decor
The same conditionally non-flammable polystyrene foam can be used to decorate the facade with various architectural elements. Figured decor made of foam plastic is very popular due to its aesthetic appearance and affordable cost. You can buy foam plastic products relatively inexpensively, and the visible result is comparable to what real stone decor looks like.
A significant advantage of expanded polystyrene is its low weight. It does not create a load on building structures, and in addition, it can be easily installed by one person. As for fire safety, high-quality material fully meets the requirements for fire resistance of building and finishing materials.
For the manufacture of facade decor, the above-mentioned high-density PPS F is used, which belongs to the group of low-flammable materials (group G1).
OLM for a bath
In saunas and bathhouses, protective fireproof screens for stoves are installed. Thermal insulation structures are made from various refractories. They offer more than two dozen composites and ceramics on sale. They are resistant not only to high temperatures, but also to aggressive gas environments. The materials were initially developed for use in critical industrial environments, and then adapted to everyday use. According to TU and GOST they are classified according to the following positions:
- Silica. They are made from high purity minerals and quartz. Their content in materials reaches 95%. Quartz-based products can withstand temperatures up to 2 thousand degrees C and aggressive influences.
- Alumina-based refractories sintered into blocks. The base can make up up to 90% of the total composition. This category includes fireclay and mullite bricks. This is the optimal solution for fireplaces and stoves running on natural fuel.
- Magnesian. The products are made from oxides of various metals through sintering at high temperatures. It is resistant to aggressive environments and temperatures up to 2 thousand degrees C.
- Minirite slabs. They are made from environmentally friendly raw materials and have high heat-resistant characteristics. Up to 90% of the composition is cement reinforced with fibrous materials. When heated, they increase slightly in size, so during installation you should leave small gaps between the sheets.
Important! Officially, metal is not a fire insulator, but it is often used as such to protect building structures from the heat and flames of stoves and fireplaces. Steel has the highest heat reflection coefficient parameters; it is not afraid of sudden and significant temperature changes.
Mullite heat-resistant brick
Brief historical background
The need for fireproof materials arose early in the development of human culture, when fire appeared. Gradually they became the basis of blast furnaces, steel-smelting and other furnaces. In the middle of the 17th century, refractory bricks began to be produced in Russia. During the reign of Peter I, a larger number of them were made on the basis of Moscow clays.
The cladding of the walls around the stove should not only be heat-resistant, but also match the interior of your room
In the 19th century, fireproof production developed only at metallurgical plants, while in Germany it was organized back in 1810, and in Europe they were already producing fireproof products in full swing. With the entry of the bourgeois class into the economic arena and with the development of industry, Russian scientists also began to work in this direction, and in 1893 the Belokamensk, Bryantsevsky and Latninsky refractory clay factories appeared.
In 1929, research on the fire protection of building materials began to be carried out in research laboratories. Fire-resistant paints were invented for wood coatings and intumescent paints for metal. Methods and rules for treating wood with fire retardant compounds are described in SNiP Sh-V.7−69, and GOST 16363–76 established the use of heat-resistant materials for the stove.
Today, out of 212 countries in the world, only 35 can claim to have a refractory industry, and half of the world's production belongs to the CIS and the USA. The importance of refractories in the economy of our country is very great. Without them, the production of many materials, the construction of various thermal units and space exploration are impossible.