Increasingly, the bathhouse is considered not only a place for pleasant leisure, but also an indispensable attribute of every private property. The owners build baths from a variety of materials, equipping them with modern stoves and comfortable dressing rooms. And pools with cool water have long become a permanent addition to almost every bathhouse. But few people know that a correctly calculated bathhouse foundation is the key to the longevity of the structure and the receipt of good steam and ventilation throughout the entire building.
Foundation for a bathhouse: its main types, rules for calculating the load
The bathhouse is a favorite relaxation place for many people.
Almost every person dreams of having a bathhouse on their plot. The construction of such a facility is a complex and expensive process, so the vast majority of land owners outside the city strive to complete the maximum possible amount of work themselves, thereby saving a tidy sum.
The first step is to build a foundation for a bathhouse - this is the most important work of all the activities associated with arranging a steam room on a personal plot.
Building a foundation is a job that every person can do independently. All you need is to remember that it must withstand the load of the entire structure and protect the walls from moisture.
It is necessary to carefully calculate its dimensions based on the expected mass of the structure and the type of soil and select the most suitable type of foundation. You can do this by following the instructions below.
Foundation reinforcement and reinforcement tying
The reinforcement cage is designed to compensate for the tensile forces that the tape experiences under bending load. Concrete can easily withstand high pressure, but it cannot work in tension, so installing reinforcement is a necessary procedure.
The frame design is a spatial lattice, the main elements of which are longitudinal rods. They are held in position by vertical rods of smaller diameter with a smooth surface . They are needed only to support the main rods until pouring.
The frame is connected by welding or by knitting with annealed steel wire. Welding is not always available, but knitting provides some elasticity to the structure, which allows it to maintain its integrity with small movements.
The knitting process is not complicated and does not require much time, but it does require some skill..
Soil features
Before making a foundation for a bathhouse, you need to carefully examine the soil. It must meet a number of specific requirements.
If you exclude this item from the action plan, then perhaps the foundation and the entire structure will sag significantly and will be unsuitable for use.
It is possible to correctly fill the foundation in areas with many types of soil, excluding peat bogs and fine sand. The ideal solution is a homogeneous soil with a high density, but this is rare.
Most often, the foundation for a bathhouse has to be built in an area with high humidity. Here you should adhere to the following rule: the depth of the trench must be at least 0.5 meters.
The ideal solution is to fill at a depth of at least 20 centimeters below the soil freezing level.
Columnar depth
This type of foundation is considered not only the most common, but also reliable.
It is usually used when walls are made of lightweight materials - timber, as well as panel and frame baths. The first step is to draw up a special project for a bathhouse, and then begin work. In most cases, during construction of this type, pipes with a diameter of 20 centimeters are used.
Thus, the diameter of the holes for them should be about 27 centimeters.
The depth of the holes for the columnar and pile type is calculated by the formula - 40 centimeters are added to the freezing depth of the soil, which usually results in 1.5 meters (in mid-latitudes). This is a very important point that requires attention.
Calculation of the foundation for a bathhouse
The first step is to calculate the mass of the building. To do this, it is enough to multiply its volume by the specific gravity of the material (in a bathhouse this is usually wood). The mass is calculated using the following formula:
- P – element weight;
- V – element volume;
- Y – specific gravity of the material.
Volume calculation is performed by breaking down a structural element into its simplest components (V₁, V₂, V₃...), calculating their volumes and adding up the results.
The main task of such calculations is to determine the total area of the foundation resting on the ground. Based on the total weight of the bath, the specific pressure R on the ground is found.
A correctly calculated foundation must have a specific pressure that is at least 80% less than the standard value of soil resistivity W. Standard values of soil resistance are established by SNiP. They mean the maximum permissible specific load of a building on the ground, at which settlement does not occur.
Depth for a foam block building
To build a foundation for such a bathhouse, it is worth preparing all the materials. It should be noted that foam blocks are a very light material, so there is no point in making a strong foundation. In this case, usually a tape version with a sand base is prepared, onto which a waterproofing material is then applied, with the help of which the base will be reliably protected from moisture.
For the construction, it is recommended to dig a trench, the depth of which should not be less than 60 centimeters.
The width may vary, but the optimal width is 35-40 centimeters. In this case, it is better to use reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm.
How to build a foundation for a bathhouse - step-by-step instructions
Previously, our ancestors, when building baths, did not particularly “bother” with the foundation of such a structure. A small frame was set with its corners on four large stones. The resulting space between the lower crown and the ground was filled with earth. Sometimes cement mortar of the lowest grades was poured under the lower logs, sometimes they were sealed with clay, etc. The advantages of such a foundation are extreme simplicity and extraordinary low cost.
But that's where the advantages end. And there are much more shortcomings, the first and main of which is that the foundation, designed to serve as a support for the walls of the building, itself destroys them. Due to contact with the ground, the life of the lower logs is extremely short. Therefore, it makes no sense to dwell on this option in more detail.
The choice of foundation type depends both on the structure of the soil and on the design of the bathhouse itself. Some summer residents build tiny frame bathhouses on their plots, insulating the walls well. Other baths are buildings made of thick logs, or even brick, with a rest room on the second floor. Naturally, such different buildings require completely different approaches to the design and construction of the foundation.
Which foundation to choose: advice from experienced builders
The choice of one design or another will depend on factors:
- the presence of relief differences of more than 50 cm by 10 m;
- soil bearing capacity;
- GWL level.
Most often there are 4 types of combinations:
- Flat area with low groundwater level, dense or medium-density soil. Slab foundations of various configurations are recommended. Even though they are labor- and material-intensive, they have an undoubted advantage. Already at the stage of laying the foundation, the rough floors will be ready.
- There is no change in relief, but weak soil and high groundwater level. For wooden buildings that are not afraid of uneven deformations, it is advisable to use slab foundations. Whereas brick and concrete baths will be more stable on deep strip foundations or pile foundations with a recessed grillage.
- Difficult terrain, the soil is quite strong, groundwater is low. For light wooden structures in these conditions, pile foundations or strip foundations are optimal, but with a larger cross-section and with a large sample of soil (an accurate calculation of costs is required). It is better to install stone and brick buildings with a difference of up to 1.5-2 m on strong strip foundations, but with a wider base. In the resulting basement floor, you can organize a technical room, a billiard room, a garage, etc., that is, expand the usable area of the bathhouse.
- The site is flat, but located on a peat bog more than a meter thick, the groundwater level is high. It’s hard to recommend anything here other than a wooden bathhouse on stilts. Weak subsidence soil will be greatly deformed both under the tape and the slab. Therefore, it is impractical and too expensive to build heavy stone structures in such conditions.
These are just recommendations. The choice of technology remains with the future owner of the bathhouse. After analyzing the soil conditions on your own site, you can choose an option that suits you in terms of bearing capacity and budget.
Strip foundation
It is a “tape” filled around the entire perimeter. Depending on both the soil at the construction site and the design features of the bathhouse building, the tape comes in different depths. The height to which the foundation rises above the ground must be at least 30 cm. A lower height will lead to constant contact of the walls with the snow mass, which will negatively affect both their durability and the internal microclimate.
But the depth of immersion of the foundation into the soil depends on several factors.
Shallow (40 cm) applicable:
- for baths of all types of any weight from any building materials on rocky rocky foundations, on such soils the depth of the foundation may be even less;
- on sandstones, a shallow foundation will support light panel structures, small one-story log houses (up to 5...6 meters in plan);
- on loams, the use of this type of base is applicable only for small, lightweight frame structures;
- This type of foundation is not applicable on alluvial soils and peatlands.
Medium foundation (100 cm):
- on rocky soils its use is not justified;
- sandy and gravel soils make it possible to build chopped wooden bathhouses of all types on such a foundation, incl. with an attic level, as well as one-story buildings made of gas silicate;
- on clay soils, this foundation will support light, small buildings made of logs and panel structures;
- on peat bogs, this type, like the previous one, should not be used.
A foundation dug to a depth of soil freezing (150 cm): can withstand bathhouse buildings made of any material of any number of floors, but performs somewhat worse on alluvial soils.
Auxiliary stages of construction of a columnar base
The most economical option for creating a base is columnar. It takes less time to create it and less money.
Marking is carried out in the same way as described above. And then, along the resulting corners, you should dig holes for the pillars. Since this type of base is used only for light buildings, the depth remains at 80 cm. And often even less - only half a meter.
In addition to the main corner holes, it is worth making several auxiliary ones. This will help distribute the load more evenly on the soil of the entire structure. The distance between the pillars should be at least 3 meters for a small building. But for a building with a large area, it is worth making pillars at a distance of 2.5 m from each other. The calculation is carried out from one of the corners of the future building.
Bathhouse projects
- 12² Total area
- 2 x 6m Building area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 70² Total area
- 8 x 6m Construction area
- 2 x 5m Building area
- 2 x 5m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 188² Total area
- 11 x 16m Construction area
- 1 room
- 2 bathrooms
- 18.55² Total area
- 5 x 5m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 146² Total area
- 9 x 12m Construction area
- 24.5² Total area
- 5 x 5m Building area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 67.5² Total area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 7 x 4m Building area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 36² Total area
- 6 x 4m Construction area
- 18² Total area
- 5 x 5m Building area
- 88² Total area
- 27² Total area
- 6 x 6m Construction area
- 2 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 64² Total area
- 10 x 8m Construction area
- 3 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 104.5² Total area
- 8 x 7m Construction area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 152² Total area
- 11 x 9m Construction area
- 18² Total area
- 5 x 5m Building area
- 2 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 70² Total area
- 5 x 7m Construction area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 30.5² Total area
- 7 x 5m Building area
The first thing to do before starting construction of any structure, including bathhouses, is to choose a location and start pouring the foundation. There are several types of foundation structures, so the question arises by itself - how to choose a foundation for a bathhouse: which is better, and from what materials it is more profitable to build it.
Excavation
Regardless of the choice of material for installing columnar supports, all foundations of this type are mounted according to a similar principle (except for the option with a grillage). This also applies to excavation work, before starting which you need to determine the type of soil, proximity to the surface of groundwater and the depth of its freezing.
These factors directly affect the installation depth of the support pillars. To determine the type of soil and groundwater level, you need to dig a hole at least 1-1.2 meters deep (optimally). If there is no groundwater at this depth, and the soil is not heaving - freezing, then this depth is quite sufficient for a columnar foundation of a bathhouse.
Otherwise, you need to dig to a dense, incompressible layer of soil, focusing on the following indicator: freezing depth + 40 centimeters. It must be remembered that heaving soils include those that contain clay. And the more it is contained, the more prone the earth is to freezing. If these conditions are not met, then under the influence of water or sub-zero temperatures the foundation may not only crack or deform, but also completely collapse.
Deformed foundation
Columnar foundation supports must be located at the corners of the building, at the intersection of walls, along the entire perimeter and under the partitions every 1.5-2.0 meters, depending on the total weight of the structure. Holes for supports can be dug with a shovel, or you can use a special hand-held cone-shaped drill of the required diameter, thanks to which it is possible to obtain the most even holes.
Two ways to dig holes
Based on what material will be used for the construction of the columnar foundation, the required diameter of the holes is determined, which should be 7-10 centimeters larger than the following parameters:
- for pillars made of brick and stone, the optimal size is 50x50 centimeters;
- for pillars made of rubble stone - 60x60 centimeters;
- for asbestos-cement pipes Ø200 mm;
- for reinforced concrete supports 30-35 centimeters is enough;
- for intermediate ones it is 25-30 centimeters.
We pour about 20 centimeters of sand into the bottom of each prepared hole, add a little water and tamp it thoroughly, thus obtaining the desired sand cushion. At this point, the preparatory and excavation work is completed. You can begin directly constructing a columnar foundation from the selected material.
What influences the choice of foundation
This is not an idle question, because the foundation determines the load-bearing capacity of the entire structure. Therefore, it must be resolved before construction begins, because after the completion of construction work, adjusting something will be a big problem.
It is necessary to add the fact that the foundation structure allows the entire building to shift under the influence of various loads without violating the integrity of the structure. Therefore, before placing a foundation for a bathhouse, you need to choose its type and the materials from which the structure will be built. But this is just a consequence, and the reasons for the choice are:
- type of soil at the construction site;
- soil freezing level;
- ground water level.
To be more precise, these are three pillars that are taken into account when choosing a foundation. But there are a number of other minor factors that need to be taken into account. We'll talk about this below.
Common mistakes and tips
Typical beginner mistakes:
- savings on the foundation and materials for its laying;
- ignoring the need for calculation;
- choosing a design type without taking into account all operating parameters.
Inexperienced developers mistakenly classify a bathhouse as a light secondary building and lay underneath it the most budget-friendly, but far from universal, shallow strips or columnar bases with a large distance between supports. On stable soils, such structures can withstand bathhouse boxes made of any materials other than stone; on quicksand or heaving soils, the consequences can be fatal.
In addition, laying or arrangement errors include:
- Weak or insufficient ventilation of the underground floors of the bathhouse. Lack of ventilation in monolithic structures or errors when installing the intake lead to the proliferation of fungal colonies, which is unacceptable. The same violation causes poor draft of the furnace.
- Concreting the foundation at low or near zero temperatures.
- Mistakes when choosing the type of drainage system, in particular - accumulation of moisture near concrete structures when the drain is open.
- Lack of waterproofing cut-off between the foundation and wooden or porous structures of the bathhouse.
- Loading the foundation until the processes of strengthening the mortars are completed.
- Lack of its own foundation under massive sauna stoves.
A plan that reflects all the design features and the location of communications helps to avoid mistakes. If possible, work is carried out in dry and warm weather, during the period of minimum groundwater level.
Types of foundations for a bathhouse
There are three types of foundation structures that are installed under baths:
Let's look at them separately and determine which foundation for a bathhouse is better.
This variety is built only on soils classified as “weakly water-saturated.” That is, these are soils with low bearing capacity, plus the moisture concentration in them is quite high.
The pile foundations themselves are of three types, which differ from each other in the materials used for construction and the method of installation:
- Piling and driving. This technology is driving reinforced concrete piles into the ground using special equipment. Sometimes even steel pipes are used as piles, which are then filled with concrete. Previously, they even used logs for this. Concrete piles are an excellent option, guaranteeing high strength of the base, plus long-term operation. But for small-sized baths this option is very expensive, so private developers rarely use it.
- Screw piles. This variety appeared on the Russian construction market relatively recently. This is a new technology based on steel piles, which are a pipe with a screw at the end. They are simply screwed into the ground to the required depth. By calculating the number of elements, you can build a foundation even for a house of several floors. But screw piles are rarely used for baths due to the high price of the material.
- The third option is popularly called a columnar foundation due to its similarity to pillars. There is no such term in construction science. They are constructed in the form of a monolith, pouring concrete solution into formwork or pipes: steel, plastic or asbestos. Or they raise a prefabricated structure from piece material: brick, concrete blocks or stone. Both the first and second options are considered low-cost, so they are used more often than others as the basis for a bathhouse.
Online foundation calculator
To find out the approximate cost of a columnar foundation, use the following calculator:
Let's look at how to make a foundation for a bathhouse in the form of free-standing pillars.
Columnar foundation construction technology
Before making a foundation for a bathhouse from concrete pillars, it is necessary to determine their number. If the bathhouse is a small building, for example, 6x6 m, then the piles are erected at the corners of the building and at the intersection of the internal and external walls. Of course, a lot will depend on the material from which the bathhouse is constructed. The greater the weight of the building, the more support pillars will have to be constructed.
Here is the sequence of operations:
- in places where supports are constructed, round or square holes are dug;
- a cushion of medium-fraction crushed stone is filled in;
- formwork is installed in them;
- a reinforcing frame made of steel reinforcement with a diameter of at least 10 mm is inserted inside;
- Concrete of the classic recipe is poured.
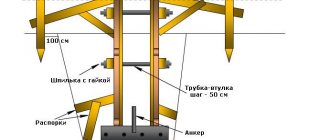
The main task of the work contractor is to bring all the pillars to the same height so that their ends are in the same horizontal plane. This is not always possible even for masters, so leveling is done with a grillage. The latter is either a concrete structure in the form of a tape connecting the pillars, or wooden beams laid on supports and interconnected
A few words about formwork. If the support posts have a round cross-section, then you can install pipes and fill them with concrete mortar. If the soil on the site is clayey and strong, then holes with a diameter of 20-30 cm are drilled in the ground, for which a drill is used. Roofing felt rolled into a cylinder is placed in them, and a reinforced frame is inserted into it and concrete is poured. In this case, the roofing material will act as a waterproofing device. For the above-ground part of the foundation, formwork is installed in the form of the same pipes.
If you plan to pour rectangular pillars, then boards that are knocked into a box are used as formwork. Everything else is done as in previous cases.
Attention! It is not recommended to construct a columnar structure on moving soils. The reason is that over time the pillars will lose their position relative to the vertical, which will affect the strength of the bathhouse as a whole.
This is the most effective base option for any structure, because it is a tape laid around the perimeter, on which all the external walls of the building rest. But this is also the most expensive and labor-intensive option for the foundation structure. Of course, everything will depend on the size of the foundation structure and whether it will be reinforced or not.
Today in construction, strip foundations of various types are erected:
The first is concrete poured into the formwork. The second is a structure made from ready-made block materials: concrete blocks of standard sizes, special products for foundations, bricks and stone. The third is the use of both monolith and blocks.
The monolithic variety is the most reliable design. It can be erected on any soil, on any terrain, on sloped areas. At the same time, concrete can be poured to any depth, which is an important characteristic for many regions. At the same time, builders also use shallow structures, which are often poured under bathhouses. This is when the depth of installation in the ground does not exceed 30 cm.
Let's look at how to properly make a strip foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands step by step. In principle, the technology is not much different from pouring pillars. Nevertheless:
- a trench is dug to the required depth, taking into account the width of the foundation strip, which is included in the house design;
- sand is poured onto the bottom and compacted; the thickness of the compacted layer is at least 30 cm;
- crushed stone is poured in, which is also compacted, its thickness is 30 cm;
- formwork is installed, if the soil is fragile, if it is clayey, then the formwork is installed only for the base - the surface part;
- a reinforcing frame is laid inside, placed on bricks so that it is inside the concrete structure and not lying on a cushion;
- Concrete is poured with vibration;
- after a week the formwork is dismantled, but the foundation can be loaded only after 28 days;
- Usually during this time it is waterproofed by covering the open surfaces with bitumen mastic, and the open areas between it and the walls of the trenches are filled.
Online foundation calculator
To find out the approximate cost of a strip foundation, use the following calculator:
As for the installation of a prefabricated foundation, first of all, a cushion is created from lean concrete, which is poured in a layer of 10-20 cm. And after drying, piece elements in the form of blocks, stone or brick are laid on it. The connection between the blocks is cement mortar.
The advantage of this variety over others is the gap between the parts of the structure, which reduces the shrinkage rate, which varies in the range of 20-30%. And this makes it possible to increase the weight of the bath by the same amount.
And one moment! Before correctly marking the foundation for the bathhouse, you need to decide on the size of the building. You shouldn't do this by eye. There is always a possibility that inaccuracies will be made, which will primarily affect the overconsumption of building material.
Let's move on to the topic: foundations for a bathhouse - which one is better to choose, and move on to another variety, which is rarely chosen for small buildings. In fact, this is a slab that fills the entire perimeter of the building and is the solid foundation of the structure. The slab can be prefabricated or monolithic.
The first option is ready-made reinforced concrete slabs, which are laid on leveled and compacted soil with horizontal alignment. The second is a do-it-yourself slab, into which a reinforcing mesh is pre-installed.
Such a foundation structure can be built on any soil. It perfectly withstands horizontal loads when layers of earth move. But this is the most expensive option of all those offered, plus it is the most labor-intensive.
Let's take a step-by-step look at how to make a slab foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands:
- a pit is dug so that its perimeter is 10 cm larger than the perimeter of the foundation on each side;
- the bottom is leveled and bedding is made in the form of a pillow, for which you can use sand or crushed stone;
- the pillow is leveled horizontally and compacted;
- a reinforcing frame is installed from reinforcement in the form of a mesh with cells 20x20 cm;
- if the bathhouse is built of brick on two or three floors, then the reinforced frame should be in two or three layers;
- formwork with a height of 20 cm is installed along the perimeter of the pit on the ground surface;
- The concrete solution is being poured.
Online foundation calculator
To find out the approximate cost of a slab foundation, use the following calculator:
As you can see, if we talk about how to properly make a foundation for a bathhouse, then the construction processes are the same, and they consist of almost the same operations.
Stages of construction operations for the construction of the foundation
After the calculation and type of base for the bathhouse has been made, you can begin to create the foundation itself. All work can be divided into several stages:
- Preliminary activities - calculating dimensions, marking the site, clearing the area and preparing materials.
- Auxiliary actions - digging holes for pillars, trenches for tape or a pit for a monolithic slab.
- The main operations are cushion, waterproofing, reinforcement, formwork.
- Final work - filling the prepared earthen areas with mortar, leveling the top layer of the foundation, wetting the finished base as it hardens for the strength and integrity of the future structure.
Since the first stage has already been discussed above, we skip it, stopping only at marking the area for the bathhouse.
Having decided what type of soil is at the construction site, you can begin work on clearing it. Silty soils should be removed from the construction site, replacing them with black soil or denser soil. But sandy types of soil are often left untouched, removing only the small top layer consisting of roots. Heavy and dense soils can be left untouched at all, removing only those places that are necessary for digging a trench, pit or hole.
Marking must begin from one of the corners of the future building. In the chosen place, you should drive a peg into the ground, and then move away from it to calculate the length of the larger wall. Having calculated the location of one wall in this way, it is worth marking out all the others. It is necessary to stretch a thread or twine between the pegs, so that later it will be more convenient to begin excavation work.
To check the correctness of the resulting markings on the soil, you can compare the lengths of the diagonals of the resulting rectangle. Coinciding results – correctly applied markings and calculation of the base.
It is worth remembering that if the values of the diagonals diverge by more than 5 cm, then one of the pegs should be adjusted, otherwise the bathhouse will be skewed or have uneven walls.
Foundation materials
Practice shows that when the question of how to make a foundation for a bathhouse with your own hands is raised, private developers give preference to monolithic structures, regardless of shape. Rarely does anyone undertake the construction of prefabricated structures. This still requires special skill, especially if a stone is used as a basis. Although there is a fairly simple technology.
For example, how to properly make a strip foundation for a stone bath:
- a trench is dug around the perimeter of the building;
- large stones are thrown into it in one layer;
- concrete mortar is poured to fill the space between the stone elements;
- a layer of medium-sized stones is created;
- another portion of concrete;
- and so on to the surface of the soil;
- the formwork of the above-ground part of the foundation is installed;
- and everything is repeated with the middle stones;
- craftsmen even lay out the ground part by hand without formwork, precisely maintaining the dimensions of the structure;
- the most important thing is that there is no reinforcing frame, which increases the cost of the foundation structure.
In fact, the foundation is built from so-called rubble concrete. Stone is a durable material that is not susceptible to strong influences of water and moisture, so such a foundation will last a long time. The only thing you need to know is that it is better to use a stone with sharp edges, uneven planes, depressions, tubercles and other irregularities. Therefore, large river pebbles will not work here. And one more thing - masonry concrete mortar of a grade not lower than M200 will help increase strength.
Which base is better for a timber bath?
The choice of foundation for a timber bathhouse depends on the quality of the soil on the site.
All of the listed types - strip, pile and columnar - are suitable for light wooden buildings. The first option is the most expensive, but also the most durable. Pile and column structures are suitable for wetlands where groundwater comes too close to the surface. The advantage of a columnar base is its low cost, simplicity and speed of construction.
The foundation for a bathhouse made of timber, built with your own hands, is not subject to too high demands on strength and reliability. This is due to several factors:
- timber is a lightweight material;
- bathhouse - a low building on one floor;
- There will be no heavy furniture or decor inside the room.
In this regard, you can only focus on the soil and the construction budget.
Work order
If you have the desire and at least some construction skills, then it is quite possible to build a bathhouse on the site yourself. But everyone asks the question: “How to make a foundation for a bathhouse?”
The first thing you need to start with is the foundation:
Make markings of the proposed structure. Set the diagonal. The width of the future base should be 10-15 cm larger than it.
Dig a trench. The depth depends on the building material used. Approximately from 20 to 50 cm. In places where the soil is not dense, you need to fill the bottom of the trench with sand or large crushed stone and compact it using a rammer.
If you don’t have it at hand, you can use a block (the diameter of which should not exceed the width of the trench), into the middle of which a tube with a diameter of 20-40 mm is driven.
Install the formwork level by determining the height of the future foundation. It depends on the place where the bathhouse is built. If it is a hill, then the height can be no more than 20 cm, but if it is a lowland and spring and rainwater flow, it is advisable to take a higher height.
The boards that are intended for it can be wrapped in cellophane; you may need them in further construction. To ensure the strength of the foundation, you can reinforce it using small diameter pipes, thick wire and fittings.
The foundation must be poured entirely during the day so that it sets and dries at the same time. You can mix the solution yourself or order ready-made concrete.
Carrying out approximate calculations
The depth of the concrete foundation is selected 24-25 cm above the groundwater level and 27-30 cm below the freezing line. A sufficient depth, based on strength properties, is considered to be 120-130 cm.
The cross-sectional dimensions of the support are calculated taking into account the loads from the mass of the bathhouse and soil resistance. In the case of a strip foundation, the width of the concrete strip is determined by the formula: B = F/(RxL), where L is the total length of the strip or the perimeter of the building; F – total mass of all elements: baths; bath equipment and communications, water, all people washing at the same time; R – soil resistance for a given category of soil. The mass of the sauna stove is usually not taken into account, since it is built on its own foundation.
Calculations are carried out according to the formula: N = F/(RxSо), where N is the number of supports, Sо is the cross-sectional area of each support, F is the total load, similar to the case considered above.
When drawing up a bathhouse project, estimating the cost of construction is important. Building a foundation is an expensive undertaking
So the cost of a more economical columnar base can reach up to 20-25% of the cost of the entire bathhouse. When constructing a strip version, the cost of pouring concrete for 1 m3 of foundation is on average estimated at 12.5-13 thousand rubles.
Two important differences: shallow or deep
Before considering the types of foundations in detail, two main types should be distinguished - shallow and deep. The difference is in the depth of immersion in the ground. Why is this moment important?
In winter, the top layer of soil freezes, and all the moisture in it turns into ice. When it freezes, it expands, causing the top layer of soil to change its volume. This phenomenon is called “frost heaving”, it is typical for soils with a high moisture content, clay and loam.
The depth of soil freezing depends on average annual temperatures and soil composition. For deep ones, the basic rule is to immerse below the freezing point to eliminate the effects of heaving loads. For some areas, this type is difficult to implement - the soil can freeze to 2.4 meters. There is a way out.
A shallow type is used, the feature of which is a shallow immersion depth. Such a base is located in the upper layers of the soil, above the freezing point, but the loads from heaving processes are much lower - 2 or even 3 times.
The point is to properly arrange the foundation: the trench is dug a little wider, a sand cushion is installed, a concrete strip is erected, which is subsequently filled with sand on the sides. As a result, there is a sand cut-off on all sides.
Sand does not retain moisture; it goes deeper in warm weather, so there is nothing to freeze in winter.
Only loads emanating from the lower layers of the soil remain, so it is impossible to use a shallow type of foundation on soils with large seasonal heaves.