Linen wool or jute, which is better: the expert answers
Today we will talk about wooden structures made of timber and logs, namely about inter-crown insulation for these structures. The leaders in this area are jute and flax wool. The materials are very similar: both in structure and properties. In order to sort out the issue of flax wool or jute and which is better, we turned to an expert in the field of insulation and construction of wooden structures, heating engineer - Leonid Zverev.
Hello, Leonid! Help me and our readers understand which insulation material is better to use: flax wool or jute belt to ensure high-quality insulation of a wooden structure. Tell us about your experience working with these thermal insulation materials, their distinctive properties and advantages.
Hello, indeed, the ideal insulation materials for the construction of a wooden frame are flax wool and jute. I will try to briefly describe each of these types.
This is a fibrous fabric made using special technology from the East Asian region. The peculiarity of this strip is a non-woven fibrous base of a textile nature, obtained as a result of processing the plant of the same name. The insulation, after appropriate processing and drying, is pressed on special needle installations, where the already thin fibers are fluffed mechanically. In this case, the threads do not break, but delaminate. The result is a “braid”: thick and flexible, with increased tensile strength characteristics.
In the workshops that process this raw material, a strip of the required length and width is produced, and the trimmings are used for subsequent processing to produce thinner layers. It is worth noting that jute fiber contains a large amount of lignin, it is this substance that gives jute its elastic properties. A related, and quite important, characteristic is that such a strip is not susceptible to destruction by small insects, parasites and birds.
The basis for the thermal insulation material is flax, or rather its fibers, also produced from plants. It is easily grown and processed throughout the post-Soviet space. Light and soft insulation is made on special machines, where flax fiber is used to produce a strip of specific dimensions.
The main advantage of flax wool is its high thermal conductivity. The cost of flax is lower than jute - this is due to the methods of production and delivery. Linen has shorter fibers, so its strength is slightly less, and the microfilaments themselves are thinner. The main distinguishing characteristic is density: flax wool has less than jute. As a result, to achieve the same insulating effect, the strip consumption increases.
Summarizing the description of these insulation materials, we can highlight their following positive qualities, different for each insulation.
This is where the differences end; the remaining thermal and physical properties are absolutely the same. Linen wool loses a little in terms of heat capacity, but this is compensated by its good shrinkage and the possibility of laying in several layers. Cost is also not an indicator; the consumption of jute tape is much higher than linen tape.
Both fibers do not require any special knowledge or skills during installation and are absolutely harmless to humans. They do not lose heating properties after a long time. Jute or flax wool are practically no different.
For the average builder, the emphasis in this case will be on finances. More experienced builders will choose jute, because... it is easier to cut and achieve gaskets of the required shape without delamination of the tape. But the high cost is easily compensated by the high thickness. Under the same conditions, flax wool will be needed 1.5 times more.
The ideal solution would be to use two insulation materials: one is suitable for straight sections of cylindrical logs, the other will fit well on turns and fill all the cracks and cracks. Outside (on the street side), in this case I lay jute, because... flax wool is often taken away by birds. This way you will get 100% insulating effect of any wooden structure at a reasonable price.
Source
New generation insulation materials
New generation insulation materials are called thermojute and thermolen. These are all the same natural materials with special impregnation. Low-melting biocomponents are used as impregnation. Despite the improved performance characteristics, both materials are based on jute and flax. This means that most of the shortcomings of flax are preserved in the thermal mill. Thermojute does have improved characteristics, but the price of the material is significantly increased.
Another new generation material is polyester insulation - holofiber. Holofiber is a springy material that is not susceptible to rotting, mold or pests. Calmly withstands moisture, mechanical stress and sub-zero temperatures. At the same time, due to its elasticity, the material fills the gaps between the logs well. The use of this material is especially important when building a house from logs without grooves.
How to distinguish flax and jute?
For a long time in Rus', flax fiber was used for caulking log houses - wooden houses, bathhouses, barns. It had antiseptic properties, did not rot and did not turn into dust over time. Relatively recently, flax has had an overseas competitor - jute. Both plants belong to the class of dicotyledons and grow in similar humid climate conditions, but in different climatic zones. Flax grows in central Russia, as well as in Belarus. Jute is brought to us from Bangladesh and India (it is also grown in China and some other Asian countries). This is due to the fact that jute is accustomed to other soils, or rather, it grows in water.
There are also external differences. Flax blooms with blue flowers, flax fiber has a grayish, ashen tint. Jute is more yellow and golden. But these differences are not fundamental; what's inside is much more important. Both flax and jute are made of cellulose. Cell membranes contain molecules of a complex polymer, lignin. Also present is pectin, wax, and water. Jute has more lignin, which is responsible for the hygroscopicity and tensile strength of the fiber (it kind of glues the microfibers together). This is its advantage. The drawback is the small percentage of pectin and wax, which give the plant proper elasticity when laying. Therefore, flax is softer and more elastic, and jute is more durable and rigid.
However, due to the fact that both plants have the same qualitative composition, we can say that their properties are largely similar. Both materials :
- harmless; - hygroscopic; — provide good sound and thermal insulation; - durable; - easy to use
Now you know how to distinguish flax and jute. Both plants have truly outstanding characteristics, due to which they are widely used in the production of insulation, ropes, and plumbing cables. Both flax and jute are equally good in use; but each has its own “niche” of use in which it manifests itself best.
Source
Synthetic materials
Working with these is much easier and faster than with natural ones. The sealant is leveled with a special spatula and applied with it.
Synthetic sealant
But synthetics also have significant disadvantages:
- Some sealants cannot withstand exposure to sunlight. They fade, become thinner, or are simply blown out of the cracks by the wind. In this case, it is necessary to think about how and with what to cover the joints of the log house;
- Most synthetic sealants do not have the required elasticity. They do not shrink in cold or increase in heat, preventing the natural expansion and contraction of wood.
When choosing synthetic products for caulking a folded log bathhouse, it is extremely important to carefully read the information on the packaging. Make sure that the sealant is suitable for the log wood type, weather conditions and humidity level. Only after this can the product be purchased.
Inter-crown insulation: Linen and Jute. What is the difference?
Currently, most construction organizations opt for jute inter-crown insulation, but there are also those who continue to use flax wool.
Let's figure out what Jute is good at and what Flax is good at.
Both inter-crown insulation made of jute and flax batting are made using needle-punched technology and consist of 100% natural fibers, which are bonded using needle-punched technology (without the use of glue or synthetics). These are environmentally friendly and safe materials.
Flax grows in Russia and Belarus. Annual herb.
Jute, compared to flax, contains a much higher percentage of lignin, which is responsible for “gluing” the fibers together and hygroscopicity, hence its resistance to moisture and strength. When jute gets wet (slanting rain, sleet) it dries and restores its properties, it will not rot.
But, unlike Jute, Linen must be tucked immediately, because When exposed to moisture, it quickly disintegrates and rots.
Another distinctive feature of Flax from Jute is that jute is not at all interesting to insects and birds, while flax is mercilessly taken away by birds, moths, bark beetles, bedbugs, etc. appear in it. Therefore, when using flax wool, it is necessary to treat the wood generously with an antiseptic.
How to distinguish Linen from Jute?
Linen, unlike jute, has a mouse-gray color; the remains of fire are visible to the naked eye, because it is impossible to comb it out completely. Soft to the touch.
Jute inter-crown insulation has a golden color, closest to the color of wood. Feels stiffer than linen. If you rub a piece of inter-crown jute insulation between your fingers, you will be left with an oily feeling; this is lignin.
When building a wooden house, first of all you need to pay attention not to the price, but to the quality of the roof insulation. Linen, although it has similar properties and is cheaper than jute, is also in many ways inferior in quality.
Source
What to put between the crowns?
To create a gasket between the crowns of a log house, there are many insulating materials.
But not all of them are ideal for these purposes. First, you need to safely cross out synthetic and artificial materials from the list of candidates for inter-crown insulation. They will cope with the thermal insulation task well, but the price of their work will be damaged crowns of the log house. There is another drawback to these insulation materials - they are made from non-ecological components. And it seems to me that many people choose wood for construction in order to be closer to everything that is clean, safe and natural. The use of artificial, synthetic insulation will disrupt the entire beneficial microclimate of the room. It is for these reasons that I do not recommend focusing your attention on these insulating materials.
And it is advisable to lay insulation between the crowns from natural materials, which consist of fibers of natural plants. They also have good thermal insulation characteristics, but they are in perfect harmony with the wood and do not cause any harm to it. Among such materials are:
- Moss.
- Jute.
- Tow.
Many builders cannot make the final choice of insulation, deciding which of these three materials is better.
Insulation for a wooden house: what to choose - moss, flax or jute?
To seal the cracks between the crowns in log and log houses, today they use both traditional moss and tow, and modern tape seals. It is up to the consumer to decide which material to choose. The main thing is to familiarize yourself with the properties and features of each in advance.
What qualities should a sealant have?
The main function of the inter-crown seal is heat insulation ,
which means that the material used for this purpose must have a low thermal conductivity coefficient.
Secondly, since wood is a “living” material that reacts to changes in environmental conditions, the gasket between the crowns is designed to prevent the appearance of blown gaps, and for this purpose it must be sufficiently dense and elastic
. Thirdly, it is required
to be resistant to rotting,
the process of which threatens to destroy not only the material filling the cracks, but also the wooden walls themselves, as well as
the ability to give and absorb moisture, adapting to changes in the humidity regime both outside and inside the room.
The next condition for the effectiveness of interventional insulation is non-susceptibility to biological damage
from insects, rodents and birds and, finally,
environmental friendliness,
that is, safety for human health.
Good old moss and tow
Long-fibered bog moss
(red moss, sphagnum, “cuckoo flax”) with fibers from 15 to 30 cm is an environmentally friendly natural material with a low thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.04 W/(m °C).
Such insulation “can” absorb and release moisture, reacting to the level of air humidity; It is very resistant to decomposition, is never affected by rot, and in addition, contains tannins that have a bactericidal effect and prevent fungal diseases of wood.
Moss is used slightly damp, creating a mossy bedding from it for each subsequent crown of the house. However, the elasticity of this material is low: it gradually dries out and shrinks after a year and a half, resulting in the formation of cracks in the walls. Repeated caulking is done with flax or hemp tow.
Moss is sold at a price of 280 rubles. per bag.
Considering the natural origin of the material, many consider the use of moss to be the best solution when building baths. However, it should be borne in mind that dry moss will instantly flare up from any spark, so for fire safety reasons it is not advisable to use it in baths
Flax and hemp tow
- short-fiber material made from waste of natural hemp and flax. The density of hemp is 160 kg/m3, and the thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.047 W/(m °C). It is more labor-intensive to use (in particular, due to the heterogeneity of the fiber structure, it is difficult to spread it in an even layer), but, unlike moss, it is suitable not only for caulking walls, but also for sealing joints, window and door frames, etc. Lay pieces of tow across the log, and it continues to hang from under the crowns until the house is assembled. Then its ends are twisted into a roller and sealed into the cracks using wooden or steel caulk and a mallet. The second time the building is caulked after the initial shrinkage. The tow costs 900 rubles. for a 30 kg bale.
The main disadvantages of tow are its instability to rotting, flammability, and also the fact that it is an excellent building material for bird nests, and feathered neighbors will definitely use it.
Please note: it is permissible to caulk only log houses with moss and tow. Having a proven geometry, the beams fit so tightly to each other that they require a strictly uniform layer of inter-crown insulation
Tools
In order to properly insulate the seams of a log house, you need to have certain skills and experience in handling the material and tools. When carrying out the work, a mallet (wooden hammer) and a whole set of metal or wooden caulks are used: typesetting - in the form of a flat spatula; curve - for sealing corners; split - with a wedge-shaped blade for opening grooves, as well as the so-called road worker with a groove along the blade to give the tow strands the shape of a roller.
Modern tape seals
We are talking about linen and jute materials. Both can be combed or needle-punched (stitched).
Linen tape tow and linen felt
easy to use, have low thermal conductivity - 0.034 W/(m °C), are able to absorb moisture and quickly get rid of it, and are not susceptible to fungus and moths. In addition, felt also serves as a good sound insulator.
The materials are made from primary raw materials cleared of brome (coarse parts of the stem) and other impurities, without subjecting it to any chemical treatment. During the machine carding process, tow fibers are oriented in one direction, and in the case of felt, the fabric is additionally pierced with serrated needles for maximum compaction.
Linen felt is produced in strips of different widths, and tow is only 15 cm wide, but due to its loose structure, if necessary, it can be slightly compressed or stretched at the place of installation. Unlike ordinary tow, it lays down in an even, uniform layer, and the required amount of insulation is easier to calculate.
Flax tape tow is the best option for caulking houses made of chopped logs and ordinary timber, and felt is recommended for buildings made of rounded logs and profiled timber.
The cost of a 60-meter skein of flax tow is 350 rubles, and a 20-meter roll of felt with a thickness of 5–6 mm is from 80 to 700 rubles. (depending on the width of the tape).
, inter-crown insulation based on
jute fiber
, a plant material with a beautiful golden color that goes well with the tone of natural wood, has become increasingly in demand Materials made from primary processed jute do not contain foreign inclusions, do not emit any harmful substances and are absolutely environmentally friendly. They are strong and durable, have good vapor permeability and low thermal conductivity (0.035–0.036 W/(m °C) for jute felt), do not attract birds, insects and rodents, and are easy to use.
Due to the high content of lignin - a natural resin, jute is characterized by water absorption within just 1% and resistance to the formation of mold and rot. For this reason, it is widely used in the construction of baths. However, it must be taken into account that the material, although in small quantities, still absorbs moisture, and, as a result, its heat-insulating properties deteriorate, and jute takes quite a long time to dry. (Jute tow is less hygroscopic than felt, so it is preferable for wet rooms.)
When using jute insulation, you should not, as is often practiced, bend the edges of the tape in order to further seal the seam and form an even, beautiful edge along it. Over time, such a fold will lose elasticity, become brittle and collapse. It is better to make the seam decorative using twisted linen or jute cord
Jute fibers are coarse and therefore brittle, and in order to give the insulation greater elasticity, density and tensile strength, usually 10 or 50% flax is added to them, respectively, producing jute (90:10) or flax-jute (50:50) felt, made by needle-punched felt. method. In these materials, jute acts as a rigid base, and flax acts as a filler that improves their characteristics.
Combed jute tow consists exclusively of jute alone, without any additives. High-quality material should not include any impurities in the form of foreign fibers that differ in color, thickness, etc., which may indicate that the manufacturer uses recycled materials that do not guarantee a long service life for the products.
Since tow has a low density, as a rule, it is laid in two layers, which eliminates the possibility of blowing through the walls. To make the crown joints look more presentable, they are decorated with jute cord or completely hidden, for example, behind the plaster finishing of the facade.
The width of the tape for jute insulation can be different, which makes it easier to select them for the specific parameters of the wall material. The price of a roll of tow is 400 rubles/60 m, jute felt - from 100 to 820 rubles/20 m, flax-jute felt - from 230 to 500 rubles/50 m.
Types of moss for interventional insulation
Usually two types of moss are used, white, also known as sphagnum, and red, the so-called “cuckoo flax”.
Red moss has some advantages over white: it is less moisture-absorbing than sphagnum, durable and lightweight, and thanks to its long fiber structure, it makes installation much easier. By laying such moss crosswise, you can be sure that the moss will not fall out of the inter-crown space and be blown away by the wind.
Kukushkin flax is elastic and hard, it is much stronger than sphagnum and contains more substances that prevent rotting and fungal growth. The only disadvantage of this type of moss is that it grows in rather limited areas and harvesting it can be very difficult.
Moss as insulation for log crowns
Sphagnum is much more common - in almost any swampy area you can find it in abundance. It is white moss that is used by many builders precisely because it is much easier to harvest this material and in any quantity, despite the fact that in many respects it is inferior to cuckoo flax. Over time, sphagnum undergoes destruction faster, but by and large, this is its only significant drawback over red moss: it retains heat just as well and contains, albeit in slightly smaller quantities, the same antiseptics. You should not think that only bad builders use sphagnum - sometimes they simply may not have a choice due to the low prevalence of cuckoo flax. White moss is an excellent material and is quite sufficient for the average life of a log house.
Is it possible, using modern tape insulation, to do without secondary caulking?
No you can not. Despite the high surface density and uniform thickness of the insulation layer along its entire length, when settling a house, linen and jute fabric still shrinks up to 5–6% in its height, which is 10–15 cm per floor. This means that the resulting cracks will have to be sealed. This can only be avoided in the case of a building made of laminated veneer lumber, and not at all because of the special properties of the insulation, but only because such buildings themselves are practically not susceptible to sedimentary processes and lose only 1–1.5 cm of height per two floors .
Main characteristics
Density is considered the most important parameter of textile products. It determines how many warp and weft threads are located per 10 cm of material.
- Rough samples have low scores.
- For loose specimens - 26x25, for dense ones - 69x63.
- You can see with the naked eye how dense the technical canvas fabric is. A rare specimen has large cells resembling a spider's web.
- Samples with tight weave are more expensive. Fine-grained bulk substances are stored in such bags.
- The surface density of the fabric is calculated by weighing the sample. The indicator for natural options is 190-450 g/m2, for polypropylene - 48-200 g/m2.
- The width of the product varies between 95-110 cm for natural materials. The diameter of the polypropylene sleeve is 35–110 cm.
Upholstered furniture upholstered in Aegis fabric will take on an exclusive look. Along with the traditional jacquard fabric of this brand, you can purchase soft chenille upholstery fabric with an original pattern.
How to choose and care for fabric roller blinds? Answers to frequently asked questions are in this article.
Insulation: what to choose - flax or jute?
A house made of wood creates an extraordinary aura of warmth and comfort. In such a house it is easier to breathe, and the humidity level is also optimally maintained. If you are going to build a house made of wood, then, of course, you will approach the matter with all responsibility, having initially developed design documentation and estimates. Have you provided everything to make your wooden house warm and cozy? Has worthy attention been drawn to a very important detail, which used to be called “tow”, and in our time is called “inter-crown insulation”?
This can determine the future of your building, whether the log house will remain for your children and grandchildren in its original form, or you yourself, in ten years, scolding yourself for the wrong choice, will begin to repair it. Did you know that until now chemist-technologists have not been able to create fibers that would fully correspond to natural fibers. That is why today we prefer to wear clothes made from fabrics of natural origin. Therefore, a wooden house also needs natural insulation.
Recently, wooden house construction in Belarus has been developing at a very fast pace. Special inter-crown insulation materials began to be created. To facilitate the work of builders and assemblers and without compromising the age-old properties of flax as a traditional thermal insulation material for a wooden house, inter-crown insulation materials were immediately created from the flax fiber historically used in the Republic of Belarus: tape linen tow (rolled tow in a tape) and linen cloth (flax batting, Euro flax, flax ribbon). However, using only flax fiber as a raw material for production it is impossible to meet the growing demand for inter-crown insulation. And the appearance of such insulation left much to be desired (fire, waste).
In this situation, there was a need to use imported raw materials for the production of inter-crown insulation, namely jute fiber supplied from Bangladesh.
In the Republic of Belarus, jute was supplied mainly to twine and carpet factories, where twines, ropes, and carpets were produced from jute fiber. The jute tow obtained after processing was used to produce canvas as a base for linoleum. It was this fabric that builders began to use as insulation for laying between the crowns of a log house.
Jute for a bath - the key to its benefits
It would be unreasonable to fill a structure made of natural material with elements of artificial origin. And any building made of wood requires insulation and insulation. In the old days, moss and hemp, flax and hemp were used for this. Today, jute inter-crown insulation is taking first place in the construction market.
It is made from a fibrous plant grown in the southern countries of the Middle East, where the tropical climate reigns. Our consumers have known it for a long time. Products that are sensitive to high humidity are transported and stored in jute bags. Sugar, rice and coffee are most often brought to us in such containers. Due to the special strength of the fibers and their unique properties, this material is the best packaging for goods that deteriorate from water.
Builders also appreciated jute, and now its scope has become much wider. It is used as insulation in the construction of wooden buildings. And for a bath it can be considered the best option. The environmental friendliness of this material is beyond doubt, which allows it to be used without any restrictions. In addition, when heated and wet, it is absolutely harmless; when burned, it does not emit harmful or toxic substances, and when dry, there is no dust from it. In a wooden building, for which jute is used for insulation, a special microclimate is established that has a beneficial effect on the condition of the person in it.
We can also add that jute fiber, twisted into rope, has a very decorative appearance, which allows it to be used as a finishing material.
Jute as an interventional sealant
The uniqueness of using jute for the manufacture of inter-crown insulation is due to a number of its unique properties. The golden color of jute fibers is closest to the color of wood; they are also pure and do not contain impurities, debris, etc. Excellent appearance, this is not one of its advantages. Also, the physical characteristics (low thermal conductivity, ability to conduct excess moisture) turned out to be very similar to linen. And the higher content of lignin (a natural resin that protects against rotting) has made jute a leader as a raw material for the production of inter-crown insulation.
Jute tow and jute felt
jute tow (100% combed jute) is an inexpensive option for houses made of planed and hand-cut timber. Jute tow can be used like regular linen tow - for caulking work. The main application is deep recesses of the groove, for the highest quality seal between the crown. There is no connection to the width or thickness of the material (it is adjusted independently during installation). Jute tow, in turn, is divided into the classic bale type and combed rolled type.
Jute tape (jute felt, jute fabric) is the most attractive in appearance, but also more rigid (100% jute fiber). Jute fabric with a small addition of flax for softening (up to 10-15% is acceptable as a binding material).
There is also a third option, mixed raw materials flax fiber and jute fiber. FLEN-JUTE (different manufacturers may have different blending percentages).
Hard fiber burlap
The coarse and durable material is made from thick yarn in the same way as ordinary fabrics - by plain weave of threads. Fibers for yarn are of plant and artificial origin.
The raw materials for threads are:
- flax, hemp, jute;
- synthetic fibers - polyester, polypropylene, polyamide;
- mixed specimens combine plant bast and chemical components.
Note. Synthetic fabric is woven from flat threads. Natural material looks more textured, with a pronounced cellular structure.
Installation recommendations
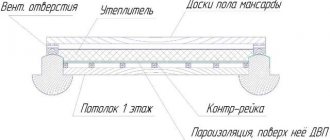
If you are building a house from high-quality timber or rounded logs, it is quite enough to lay the insulation in one layer. In the case of using ordinary timber, I recommend laying insulation in 2 layers or of increased density. This is especially important for houses made of timber without a groove, because they lack special selections for insulation and are more susceptible to blowing.
To ensure that the insulation does not slip off during installation, you can secure it with a stapler. After completing the installation of the log house, caulk the protruding sections of the insulation inside. The main thing is that the insulation must be laid in an even layer and protected from direct contact with atmospheric moisture.
A newly built house must “stand” for at least a year, after which it is necessary to carry out the final caulking. For caulking, you can buy ribbon tow or jute. Recently, decorative finishing of crown joints with linen or jute rope has been very popular, which gives a particularly attractive appearance to a wooden house and provides additional protection for jute insulation.
What is the time frame for caulking baths?
When can the final stage of insulation begin after the construction of the log house?
If the frame was laid with moss, then it is necessary to cut off its excess. Then the remaining material is tucked into the cracks and carefully pushed inside. All. You should not be particularly zealous - the first caulking will take place six months after the completion of construction. During this time, the tree will finally shrink and excess moisture will evaporate. After completing the first caulking, you can install windows and doors.
A year after the first caulking, the second one is carried out as the last stage of insulation. After about five years, another caulking procedure may be used, which is optional and depends on what specific materials were used.
About quality
With all the huge range of inter-crown insulation materials currently available on the market, their quality should remain the main criterion. Only insulation products in the production of which high-purity natural fiber was used (whether flax or jute) meet all quality parameters (density and uniformity of density , thickness), only these will provide reliable protection of the inter-crown cavity.
I suggest buying jute in Minsk. The price is low. Also available:
Intercrown insulation, flax batting, tape tow, jute, jute rope, dowel, construction staples, tow, jute tape, heel, jute sealant, linen tape, rolled tow, jute rope.
Criterias of choice
Each insulation itself is unique. If there were two materials on the market that were absolutely identical in their properties, then one of them would very quickly supplant the other. Therefore, you need to select insulation according to your needs. The criteria for choosing insulation include:
- Price. The insulation must be cheap. If we talk about building houses, then insulation should occupy a smaller part in the cost column. Other factors are secondary. When installed correctly, any insulation can perform its function. Therefore, further criteria should be taken into account only if there are several options that meet the price parameters.
- Ease of installation. Inter-crown insulation is laid between the joints of the logs. As a rule, insulation is available in the form of tow, tape or rope. It is most difficult to work with tow, easier - with tape. It is not difficult to guess that the tape version costs more.
- Local conditions. Depending on local conditions, it is necessary to take into account the level of humidity, the activity of pests and the presence of various types of vegetation.
It is especially worth focusing on the vegetation. The fact is that since the times of Ancient Rus', moss has been used to insulate log houses. In modern times, this fact has not changed much. Moss is an excellent substitute for purchased natural insulation materials. The problem is that you will have to collect the moss yourself. Finding a sufficient amount of moss, drying it, and clearing it of branches is not such an easy task. The labor intensity of such insulation is off the charts, but the financial investment is close to zero.
Comparison of jute with other materials
Jute, flax and sisal are actively used in construction. They are natural fibers and have a sufficient number of both similarities and differences. We will talk about what jute is and how it differs from other materials in this article.
How much material will be needed?
It is impossible to accurately derive a formula by which you can calculate the amount of material for sealing cracks.
Natural material, be it jute or moss, is highly compacted and compressed when processing cracks. So its consumption can be quite large. First of all, material consumption depends on the methods of processing logs and cutting grooves.
In any case, you need to buy material for caulking with a large supply - it will not go to waste and will be useful for a repeat procedure. As for industrial sealants, as a rule, the manufacturer indicates a method for calculating the approximate number of packages.
Differences from flax
Jute is an inter-crown insulation material that is often used as a thermal insulator for bathhouses and other structures made of timber and logs. This material is a fabric made of fibers, which is made using a special technology from the East Asian region. Jute is distinguished by its elasticity, which is given to it by the lignin contained in the jute fiber, hardness, high strength, breathability and good density. It is often used to insulate certain wooden buildings, and is also actively used in industrial production.
If we talk about linen insulation, that is, flax wool, then first of all it is worth mentioning the increased thermal conductivity of this material. It is flexible and soft, making it quite easy to divide it into strands of the size you need. However, unlike jute, flax batting has lower density and strength, since flax fibers are usually short and thin. Because of this, in order to achieve the same insulating effect as jute, the consumption of linen materials during construction will have to be increased by about one and a half times. At the same time, the price of this material is much lower, which is its big advantage.
In addition, it is worth saying that flax, unlike jute, is prone to absorbing water vapor from the air, that is, it is highly hygroscopic, which is why it is very susceptible to rotting.
In addition, this material is often exposed to pests, which can also be included in the list of its disadvantages.
In general, if you compare jute and linen, you will notice that these two materials have similar properties. Both of these types of fibers are equally often used and do not require any additional knowledge and skills during installation, however, flax wool is mainly used in the construction of residential buildings. At the same time, both flax and jute are environmentally friendly materials that, as a rule, do not emit harmful fumes. And therefore they are absolutely safe for human health. Plus, both materials are produced and sold in formats that are convenient for installation - tape tow or batting.
Thus, the difference between jute and flax at first glance may not seem so critical. These materials have many similar properties, but flax is still less wear-resistant than jute. However, if you are little concerned about the hygroscopicity and reduced resistance of flax to moisture, then in this case, when choosing between these two fibers, the main emphasis should be on the financial component of the issue.
How difficult is it to caulk the walls of a bathhouse with tow?
Tow or combed flax fibers twisted into bundles are safer than moss or jute. Due to its soft and thin structure, working with linen material is more difficult than with any other sealants. Tow is convenient for caulking the seams on the walls of a rounded bathhouse. Interventional gaps on log buildings are too large, so the fiber has to be folded into several loops. Technologically, this does not affect the quality, but it can seriously delay the caulking process over time.
Flax tow, thanks to the small amount of non-drying oils remaining in the fabrics, has the best damping properties of all possible sealants, both natural and synthetic. Tow for a bath is very well suited for sealing corner locks, especially hand-cut ones. When shrinking, the bathhouse log does not make frightening creaks and sounds; the process itself occurs without any complications.
The only drawback is the low durability of flax fiber. In a log house, tow caulk will last up to 5 years; in a bathhouse, the fiber burns out in 2-3 years.
Comparison with sisal
Sisal is a naturally occurring fibrous material. It is obtained from the foliage of a perennial plant belonging to the genus Agave, which grows in African countries, as well as in some Asian and South American areas.
Sisal is distinguished by its strength, rigidity and wear resistance. In its structure, it is much reminiscent of the structure of tree bark. Nowadays, sisal is actively used in the production of washcloths, nets, cat scratching posts and ropes; in addition, it is often used in needlework.
Jute has many similarities with sisal. So, this material is also used to produce scratching posts for pets. Jute, like sisal, is distinguished by its rigidity and strength, is of natural origin, is absolutely harmless, and does not attract dust and other debris.
In addition, the windings made from these fibers are quite similar in appearance, and the materials themselves are biodegradable: if you bury them in the ground, this will not harm the soil, but, on the contrary, will benefit it.
However, there are also differences. Thus, sisal has higher wear resistance, and products made from it last somewhat longer, which is why the cost of this material increases. In addition, the texture of jute is smooth and soft, while sisal is more scratchy.
The color of the fibers of these two materials also differs. Thus, jute fibers, as a rule, have a yellowish color with an admixture of gray, while sisal, in its color, is much like flax.
We can say that sisal is still better in its properties than jute. It is stronger, more durable and lasts longer, but its price is higher, which is also important to consider when choosing between these two materials.
Areas of application
Burlap is a universal material that is used:
- for the production of soft containers, indispensable for the transportation and storage of food, construction, and chemical products. High-density fabrics are suitable for these purposes - from 380 g/m2 for products made of flax and jute;
- for packaging and covering. Sparse options are suitable, with a density of up to 300 g/m2. They wrap rolls of textiles, bales of wool and cotton, cover lawns and crops, and protect plant roots;
- for technical purposes. Used in the production of upholstered furniture and geotextiles, cable products and filtration equipment;
- in public utilities and for domestic needs. A linen rag is suitable for washing floors; polypropylene containers are suitable for collecting leaves and debris;
- for decorative purposes. Unpretentious natural fabrics are at the peak of popularity. Interior decoration, theater scenery, fine and applied arts, handbag and shoe making - creative people are attracted to the natural beauty of flax, hemp and jute.
To suit your needs
When choosing a technical material, it is based on the specific purposes of application.
- Dry glue will require a tighter, more airtight package than potatoes or cabbage.
- Natural canvas will protect heat-loving plants from winter cold, while its density does not matter much.
A variety of practical bag fabrics allows you to find the optimal solution for every occasion.
© 2022 textiletrend.ru