To organize a trouble-free in-house power supply, it is necessary to allocate separate branches. Each line must be equipped with its own protection device that protects the cable insulation from melting. However, not everyone knows which device to buy. Do you agree?
You will learn everything about choosing automatic machines based on load power from the article we presented. We will tell you how to determine the rating to find a switch of the required class. Taking into account our recommendations guarantees the purchase of the required devices that can eliminate dangerous situations during the operation of the wiring.
Circuit breaker functions
From the name it is clear that this is a switch that turns off automatically . That is, himself , in certain cases. From the second name - circuit breaker - it is intuitively clear that this is some kind of automatic device that protects something.
Here are examples of the installation and use of such machines - when installing an apartment meter and when replacing electrical wiring in an apartment.
Now more details. The circuit breaker trips and turns off in two cases - in case of overcurrent , and in case of short circuit (short circuit) .
Overcurrent occurs due to faulty consumers, or when there are too many consumers. Short circuit is a mode when all the power of the electrical circuit is spent on heating the wires, while the current in this circuit is the maximum possible. More details will follow.
In addition to protection (automatic shutdown), machines can be used to manually turn off the load. That is, like a switch or a regular “advanced” switch with additional options.
Another important function (this goes without saying) is the connection terminals. Sometimes, even if the protection function is not particularly needed (and it never hurts), the terminals of the circuit breaker can be very useful. For example, as shown in the article Laying the input cable from the gander to the meter.
Performance
Its service life largely depends on how quickly the switch turns on and closes its contacts. However, is it possible to determine at home how well your device corresponds to this parameter without disassembling the case itself and without resorting to specialized laboratory tests?
Of course you can. Everything is done very simply. Take a regular battery-powered indicator screwdriver. Exactly with the battery.
It is usually used for testing and determining the integrity of the circuit. Although knowledgeable people use this useful device in many other ways. Read about which ones in a separate article.
Use the tip of a screwdriver to touch the upper contact, pressing the metal patch on the handle from above, and with the finger of your other hand, touch the lower contact of the switch.
After which, you slowly begin to turn on the machine, cocking the tongue.
The contact should appear (the LED in the screwdriver will light up) only at the very last moment, when the device has already clicked.
If the same manipulation is done with another switch, the light comes on when the power lever reaches the middle of the stroke.
It turns out that the device is not yet cocked, but the contacts are already closed. This is what this sometimes leads to under heavy load (view of the contacts from inside the machine):
This ultimately affects the rapid wear and burnout of contacts. While the quick-start mechanism increases the service life of the product by almost 30%.
Number of poles
Depending on the number of poles, the machines are:
- Single-pole (1p, 1p). This is the most common type. It stands in a circuit and protects one wire, one phase. This is shown at the beginning of the article.
- Bipolar (2p, 2p). In this case, these are two single-pole circuit breakers, with a combined switch (handle). As soon as the current through one of the machines exceeds the permissible value, both will turn off. These are mainly used to completely disconnect a single-phase load when both the zero and the phase break. It is the two-pole circuit breakers that are used at the entrance to our apartments.
- Three-pole (3p, 3p). Used to break and protect three-phase circuits. Just as in the case of two-pole ones, these are actually three single-pole circuit breakers, with a common on/off handle.
- Four-pole (4p, 4p). They are rare, they are installed mainly at the input of three-phase switchgears (switchgears) to break not only the phases (L1, L2, L3), but also the working zero (N). Attention! Under no circumstances should the protective grounding (PE) wire be broken!
Correct terminals
If you look at individual brands of machines, you can see that if the terminal is not completely open, the wire can accidentally get into the terminal space.
When you connect wires in a panel at a height, you usually do not see the top terminal and the core is inserted there, as they say, by touch.
An electrician who tightens a terminal with an incorrectly inserted wire will not feel anything. There seems to be an effort, which means the tightening was successful.
Some even check this tightening torque using a torque screwdriver scale.
In fact, the wire will not be secured.
In good circuit breakers, such an oversight or error is simply impossible. In them, as soon as you begin to tighten the terminal, the terminal space is immediately closed with a special plate.
It can be either metal or plastic.
Another recommendation, but not a mandatory feature regarding the terminals, is an additional connector for a comb busbar.
When a number of machines are assembled in an electrical panel, they are connected to each other through just such a bus. It is very convenient and reliable.
But the problem arises if you later need to make some kind of desoldering and bring out a separate wire from this terminal.
The contact density changes, it is not fully pressed and gradually burns out. As a result, the machine has to be replaced.
So, in some models (mainly from ABB), there is an additional connector for this purpose, designed specifically for the comb bus.
The main contact remains free and you can safely connect the cable core to it without compromising the reliability of the connection.
Also look for notches on the terminals. It is advisable that they are not smooth.
With these notches, the terminal material bites into the copper core, thereby promoting better transient resistance.
Also make sure that the plastic near the screw does not come apart when tightening. You can check this right in the store using screwdrivers.
Insert the tip of one screwdriver into the terminal, and with the other forcefully tighten the contact. Next, watch how the two halves of the housing behave near the clamp.
If they crawl to the sides and a fairly visible gap appears, this is a reason to think about such a purchase.
Circuit breaker current
Automatic currents come from the following series:
0,5, 1, 1,6, 2, 3,15, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 13, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63.
The denominations most often used in everyday life are highlighted in bold. There are other denominations, but we won’t talk about them now.
This current for the circuit breaker is rated. If it is exceeded, the switch will turn off. True, not immediately, as stated below:
Weak link protection
So, we are convinced that the calculation of the circuit breaker should be made based not only on the total power of the devices included in the circuit (regardless of their number), but also on the cross-section of the wires. If this indicator is not the same along the electrical line, then we select the section with the smallest cross-section and calculate the machine based on this value.
The PUE requirements state that the selected circuit breaker must provide protection for the weakest section of the electrical circuit, or have a current rating that will correspond to a similar parameter for the installations connected to the network. This also means that the connection must be made using wires with a cross-section that can withstand the total power of the connected devices.
How to select the wire cross-section and rating of the circuit breaker - in the following video:
If a careless owner ignores this rule, then in the event of an emergency that arises due to insufficient protection of the weakest section of the wiring, he should not blame the selected device and scold the manufacturer - only he himself will be to blame for the current situation.
Time-current characteristics
Obviously, the machine does not always turn off instantly, and sometimes it needs to “think and make a decision”, or give the load a chance to return to normal.
The time-current characteristic shows after what time and at what current the machine will turn off. These characteristics are also called tripping curves or current-time characteristics. Which is more precise, since it depends on the current after what time the machine turns off.
Tripping curves or current-time characteristics
Let me explain these graphs. As I said above, the circuit breaker has two types of protection - thermal (against overcurrent) and electromagnetic (against short circuit). In the graph, the operation of thermal protection is a section that smoothly descends. Electromagnetic – the curve abruptly breaks down.
The thermal one works slowly (for example, if the current is twice the nominal value, the machine will go out in about a minute), and the electromagnetic one works instantly. For graph B, this instant “begins” when the current exceeds the nominal value by 3-5 times, for category C - 6-10 times, for D (not shown, since it is not used in everyday life) - 10-20 times.
How it works - you can imagine what will happen if the current exceeds the nominal value by 5 times, and the protection is with the “C” characteristic, as in all houses. The machine will only go off after 1.5-9 seconds, depending on your luck. In 9 seconds the insulation will melt and the wiring will need to be changed. In this case, therefore, short circuit is better than overload.
The best models of automatic fuses
Russian models
The Russian industry for the production of automatic fuses has recently made a big leap. New technologies for manufacturing cases are used. The contact group is meeting in a new way. Improved design. For individuals and businesses, the choice of introductory machines has become much wider and the quality is no worse than the best European brands.
Contactor
Rating: 4.7
The domestic enterprise “Kontactor” is in first place in our ranking. The plant initially made classic automatic machines. Now it is reoriented to industrial designs of 380 V. The company’s line also includes a household series “KPRO” with support for current up to 100 A. But basically the “Contactor” specification is industrial samples for electric motors designed for current up to 1600 A, which should protect industrial equipment. The Proton line also includes models of the three-phase Electron circuit breaker with a rating of 6300 A.
Advantages
- models are equipped with regulation of operation during short circuit or overload;
- a wide range of automatic machines from 16 to 6000 A;
- All products are certified for sale in the Customs Union.
Minuses
- the design is not very well developed;
- There are very few switches for household use;
- high cost of models;
- the mounting contacts are not recessed into the automatic fuse.
KEAZ
Rating: 4.7
A factory with history. The company opened back in 1945. It produces both classic machines and devices of the KEAZ Optima brand, in which one can notice new machine capacities and know-how.
They produce machines for both alternating current and direct current. All electrical equipment adjusters note the good design of the devices and the ease of their installation. If you are choosing which machines to install in a private home, this is the place for you.
Advantages
- there are different types - you can choose protection for different lines that use both direct and alternating current;
- acceptable price;
- compact design.
Flaws
- short service life (1–2 years).
DEKraft
Rating: 4.6
Electric machines under the general brand DEKraft are produced at the Russian enterprise Delixi Electric. These products are widely known not only in Russia and the CIS but also abroad.
True, in Europe they are better known by a different name - Himel. Mainly concentrated in China for reasons of reducing the cost of final products.
This policy made it possible to reduce the price of the machine and extend its service life. It was announced that the circuit breaker will withstand at least 6000 contact opening cycles during a short circuit. And with a slow increase in load, when the wiring is already starting to heat up, the circuit breaker can disconnect the electrical circuit at least 25,000 times!
Advantages
- all company enterprises have passed international certification;
- wholesale supply is well established in all regions of Russia;
- it is easy for the buyer to understand which machine is in front of him - all the signatures are in Russian.
Flaws
- maximum current 63 A;
- The maximum permissible cross-section of supply cables is 25 mm².
The best foreign companies
Foreign brands are still popular in our country. It is believed that these are higher quality and durable products. Therefore, our review presents products from foreign manufacturers.
ABB
Rating: 4.9
This bright red acronym is well known to professional electricians due to its wide range of circuit breakers from 0.5 to 100 A.
Both ordinary users and professionals note the reliable plastic case and control lever, which will not break off even after repeated off/on cycles. It’s not for nothing that professional electricians choose these circuit breakers for apartment switchboards.
Advantages
- The dimensions of the breaker body allow it to be easily installed in the panel;
- high level of security;
- ease of installation;
- You can also purchase four-pole models of circuit breakers.
Flaws
- high cost;
- DIN rail mounts are quite fragile;
- no or few type D devices.
Legrand
Rating: 4.8
In the catalog of the French company, you can choose machines of the DRX series - corresponding to the load for industrial use and the DX, RX, TX series for domestic use. The housings of the devices in the apartment are dustproof.
Current ratings range from 6 A to 630 A, including 125, 260, 320 and 400 A. Such a wide range allows you to select a fuse for both domestic needs and large-scale industries.
Advantages
- there are machines with poles from 1 to 4;
- There is a laser barcode on the case.
Flaws
- rarely, but there are models with defects;
- the toggle switch is carelessly executed;
- high cost.
Selecting a circuit breaker. Basic Rule
It is necessary to select a circuit breaker based on the cross-sectional area of the wire that this circuit breaker protects (which is connected after this circuit breaker). And the cross-section of the wire is based on the maximum current (power) of the load.
The algorithm for selecting a circuit breaker is as follows:
- We determine the power and current of the line consumers that will be fed through the machine. The current is calculated by the formula I=P/220 , where 220 is the rated voltage, I is the current in amperes, P is the power in watts. For example, for a 2.2 kW heater the current will be 10 A.
- We select the wire according to the cross-section selection table depending on the current. A cable with a conductor cross section of 1.5 mm² is suitable for our heater. In the worst conditions in a single-phase network, it holds a current of up to 19A.
- We choose a machine so that it is guaranteed to protect our wire from overload. For our case - 13A. If you install a machine with such a rated thermal current, then at a current of 19A (one and a half times higher), the machine will work in about 5-10 minutes, judging by the time-current characteristics.
Is it a lot or a little? Considering that the cable also has thermal inertia and cannot instantly melt, this is normal. But considering that the load cannot just increase its current by one and a half times, and in these minutes a fire can occur - this is a lot.
Therefore, for a current of 10 A, it is better to use a wire with a cross-section of 2.5 mm² (the current with an open installation is 27 A), and a 13 A machine (if it is exceeded by 2 times, it will work in about a minute). This is for those who want to play it safe.
The main rule will be this:
The wire current must be greater than the current of the machine, and the current of the machine must be greater than the load current
Iload < Iaut < Iprov
This refers to maximum currents.
And if there is such a possibility, the rating of the machine should be shifted towards the load current. For example, the maximum load current is 8 Amperes, the maximum wire current is 27A (2.5mm2). The machine should be chosen not for 13 or 16, but for 10 Amperes.
Here is the machine selection table:
Calculation of the required denomination
The main protective function of the circuit breaker extends to the wiring, so the rating is selected based on the cable cross-section. In this case, the entire circuit must ensure the normal operation of the devices connected to it. Calculating system parameters is simple, but many nuances must be taken into account in order to avoid errors and problems.
Determination of the total power of consumers
One of the main parameters of the electrical circuit is the maximum possible power of the electricity consumers connected to it. When calculating this indicator, you cannot simply summarize the passport data of devices.
Active and nominal component
For any device powered by electricity, the manufacturer is required to indicate the active power (P). This value determines the amount of energy that will be irrevocably converted as a result of the operation of the device and for which the user will pay on the meter.
But for devices with capacitors or an inductor, there is another power with a non-zero value, which is called reactive (Q). It reaches the device and returns back almost instantly.
The reactive component does not participate in the calculation of used electricity, but together with the active component it forms the so-called “total” or “nominal” power (S), which puts a load on the circuit.
cos(f) – parameter with which you can determine the total (nominal) power from the active (consumed) power. If it is not equal to one, then it is indicated in the technical documentation for the electrical device
It is necessary to calculate the contribution of an individual device to the total load on the current-carrying conductors and the circuit breaker based on its total power: S = P / cos(f).
Increased starting currents
The next feature of some types of household appliances is the presence of transformers, electric motors or compressors. Such devices consume inrush (starting) current when starting up.
Its value can be several times higher than standard values, but the operating time at increased power is short and usually ranges from 0.1 to 3 seconds. Such a short-term surge will not trigger the thermal release, but the electromagnetic component of the switch, which is responsible for the short-circuit overcurrent, may react.
This situation is especially relevant for dedicated lines to which equipment such as woodworking machines are connected. In this case, you need to calculate the amperage and, perhaps, it makes sense to use a class “D” machine.
Taking into account the demand coefficient
For circuits that have a large amount of equipment connected and no device that consumes the largest portion of the current, use the demand factor (ks). The point of using it is that all devices will not work at the same time, so summing up the rated powers will lead to an overestimated figure.
The demand coefficient for groups of electricity consumers is established in clause 7 of SP 256.1325800.2016. You can also rely on these indicators when independently calculating maximum power.
This coefficient can take a value equal to or less than one. The calculated power (Pr) of each device is calculated using the formula:
Pr = ks * S
The total rated power of all devices is used to calculate the circuit parameters. The use of the demand coefficient is advisable for office and small retail premises with a large number of computers, office equipment and other equipment powered from one circuit.
For lines with a small number of consumers, this coefficient is not used in its pure form. Those devices that are unlikely to be turned on simultaneously with more energy-consuming devices are removed from the power calculation.
So, for example, there is little chance of working in a living room with an iron and a vacuum cleaner at the same time. And for workshops with a small number of personnel, only 2-4 of the most powerful power tools are taken into account.
Current calculation
The machine is selected based on the maximum current value allowed in the circuit section. It is necessary to obtain this indicator, knowing the total power of electrical consumers and the voltage in the network.
According to GOST 29322-2014, from October 2015, the voltage value should be equal to 230 V for a regular network and 400 V for a three-phase network. However, in most cases, the old parameters are still in effect: 220 and 380 V, respectively. Therefore, for accurate calculations, it is necessary to take measurements using a voltmeter.
You can measure the voltage in your home network using a voltmeter or multimeter. To do this, just plug its contacts into a power outlet.
Another problem, especially relevant for electrical wiring in the private sector, is the provision of electricity with insufficient voltage. Measurements at such problematic objects may show values outside the range defined by GOST.
Moreover, depending on the level of electricity consumption of your neighbors, the voltage value can vary greatly within a short time.
This creates a problem not only for the functioning of the devices, but also for calculating the current strength. When the voltage drops, some devices simply lose power, and some that have an input stabilizer increase their electricity consumption.
It is difficult to carry out qualitative calculations of the required circuit parameters under such conditions. Therefore, you will either have to lay cables with a deliberately large cross-section (which is expensive), or solve the problem by installing an input stabilizer or connecting the house to another line.
The stabilizer is installed next to the switchboard. It often happens that this is the only way to obtain standard voltage values in the house
After the total power of electrical appliances (S) has been found and the voltage value (U) has been determined, the current strength (I) is calculated using formulas that are a consequence of Ohm’s law:
If = S / Uf for single-phase network
Il = S / (1.73 * Ul) for three-phase network
Here the index “f” means phase parameters, and “l” means linear.
Most three-phase devices use the “star” connection type, and it is also according to this circuit that the transformer operates, delivering current to the consumer. With a symmetrical load, the linear and phase forces will be identical (Il = If), and the voltage is calculated using the formula:
Ul = 1.73 * Uf
Nuances of selecting cable cross-section
The quality and parameters of wires and cables are regulated by GOST 31996-2012. According to this document, specifications are developed for manufactured products, where a certain range of values of basic characteristics is allowed. The manufacturer is obliged to provide a table of correspondence between the cross-section of the cores and the maximum safe current.
The maximum permissible current depends on the cross-section of the wires and the installation method. They can be laid hidden (in the wall) or open (in a pipe or box) way
It is necessary to select a cable in such a way as to ensure the safe flow of current corresponding to the calculated total power of electrical appliances. According to the PUE (electrical installation rules), the minimum design cross-section of wires used in residential premises must be at least 1.5 mm2.
Standard sizes have the following values: 1.5; 2.5; 4; 6 and 10 mm2.
Sometimes there is a reason to use wires with a cross-section one step larger than the minimum allowable. In this case, it is possible to connect additional devices or replace existing ones with more powerful ones without expensive and time-consuming work on laying new cables.
Calculation of machine parameters
For any circuit the following inequality must be satisfied:
In <= Ip / 1.45
Here In is the rated current of the machine, and Ip is the permissible current for wiring. This rule ensures guaranteed release when the permissible load is exceeded for a long time.
The inequality “In <= Ip / 1.45” is the main condition when completing the “machine-cable” pair. Failure to comply with this rule may result in a fire in the wiring.
The rating of the machine can be calculated both by the total load and by the cross-section of the wires of the already installed wiring. Let's say that there is a diagram for connecting electrical appliances, but the wiring has not yet been laid.
In this case, the sequence of actions is as follows:
- Calculation of the total current strength of electrical appliances connected to the network.
- Select a machine with a denomination not less than the calculated value.
- Selection of cable cross-section according to the machine's rating.
Example:
- S = 4 kW; I = 4000 / 220 = 18 A;
- In = 20 A;
- Ip >= In * 1.45 = 29 A; D = 4 mm2.
If the wiring has already been laid, then the sequence of actions is different:
- Determination of the permissible current for a known cross-section and method of wiring according to the table provided by the manufacturer.
- Selection of circuit breaker.
- Calculation of the power of connected devices. Equipping a group of devices in such a way that the total load on the circuit is less than the nominal value.
Example. Let two single-core cables be laid openly, D = 6 mm2, then:
- IP = 46 A;
- In <= Ip / 1.45 = 32 A;
- S = In * 220 = 7.0 kW.
In point 2 of the last example there is a slight acceptable approximation. The exact value In = Ip / 1.45 = 31.7 A is rounded to 32 A.
Choice between several denominations
Sometimes a situation arises when you can select several machines with different ratings to protect the circuit. For example, with a total power of electrical appliances of 4 kW (18 A), wiring with a copper core cross-section of 4 mm2 was chosen with a reserve. For this combination, you can install 20 and 25 A switches.
If the electrical wiring diagram assumes the presence of multi-tier protection, then you need to select circuit breakers so that the value of the rating of the higher one (in the figure on the right - 25 A) is greater than that of switches of lower levels
The advantage of choosing a switch with the highest rating is the ability to connect additional devices without changing the circuit elements. Most often this is what they do.
The choice of a machine with a lower rating is supported by the fact that its thermal release will respond faster to an increased current. The fact is that some devices may have a malfunction, which will lead to an increase in energy consumption, but not to the point of a short circuit.
For example, a failure of a washing machine motor bearing will lead to a sharp increase in current in the winding. If the machine quickly reacts to exceeding the permitted values and switches off, the motor will not burn out.
Table for selecting a circuit breaker based on cable cross-section
The choice of circuit breaker clearly depends on the cable cross-section. If the current of the machine is selected more than necessary, then the cable may overheat due to the flow of high current. If the machine is selected correctly, then if the current exceeds it will turn off and the cable will not be damaged.
Table for selecting a machine according to cable cross-section
Pay attention to the cable routing methods (installation type). Depending on where the cable is laid, the current of the selected circuit breaker may differ by 2 times!
According to the table, we have the initial cable cross-section, and select a circuit breaker for it. For us, as electricians, the first three columns of the table are most important.
Now - how to choose a circuit breaker if the power of the devices is known?
Why is a short circuit dangerous?
This situation can arise during repairs if an electrician accidentally shorts the neutral and phase wires together, or due to the destruction of insulation in an adapter box or some electrical appliance.
In this case, the current flowing in the wires can grow to a very large value, limited only by the resistance of the wires and the capabilities of the line. In this case, the current-carrying conductors heat up to the temperature at which the insulation ignites, which can lead to a fire, so it is necessary to immediately turn off the power to the line.
Table for selecting a circuit breaker based on load power
Table of consumption and current of the circuit breaker according to the power of devices
It can be seen that the manufacturer recommends different time-current characteristics for different electrical appliances. Where the load is purely active (different types of heaters), the characteristics of the machine “B” are recommended. Where there are electric motors - “C”. Well, where powerful engines with difficult starting are used - “D”.
The time-current characteristic D is not included in this table because it is not for domestic use. More details about starting engines are described in the article about connecting an electric motor through a magnetic starter. And also about turning on the solid-state relay.
Why turn off the network when overloaded?
No less dangerous is line overload. When more than rated current flows through the wires, they heat up. This leads to destruction of the cable insulating sheath and subsequent short circuit.
The process of heating the wires takes some time, so to protect the line from overload, protection is used that turns off the power to electrical appliances some time after the problem occurs.
| Information! An increased current when starting an electric motor is normal and lasts less than the response delay of the machine. |
The cause of overload may be the simultaneous switching on of high-power electrical appliances, a malfunction of electrical equipment, or the start of an electric motor, for example, in a vacuum cleaner or air conditioner.
If almost any circuit breaker is tripped by a short circuit, then an incorrectly selected device will turn off the power at the rated current of the line or will not be able to protect the wiring from overheating, so before installation it is necessary to calculate the power of the circuit breaker.
Table of dependence of the current of the circuit breaker (fuse) on the cross-section
And here is how the Germans treat the circuit breaker current depending on the cross-sectional area of the wire:
Table for selecting a circuit breaker for different wire cross-sections
As you can see, the Germans are playing it safe and are providing for a larger reserve compared to us.
Although, perhaps this is because the table was taken from instructions from “strategic” industrial equipment.
What is important to know when connecting electrical appliances
So, having calculated the approximate rating of the required machine, you need to give an explanation regarding the power. Many people wonder whether it is possible to plug in very powerful electrical appliances into a regular outlet, such as an electric boiler, for example.
According to the rules of the PUE, connecting an electric boiler with a power of more than 3 kW to a regular outlet is unacceptable. And each outlet has its own specific characteristics. Most often, home sockets are rated at 16 amperes, and, therefore, electrical appliances with a power of no more than 3.5 kW can be connected to them.
Therefore, any more or less powerful electrical appliance must be connected only through a separate circuit breaker. Moreover, it is the phase wire that is supplied to the circuit breaker, and not the working zero. Thus, knowing the approximate power of the equipment, you can easily calculate the rating of the circuit breaker.
How does a circuit breaker work?
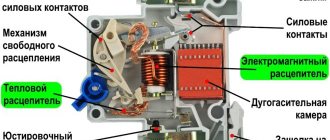
A bonus is the device of the protective circuit breaker, several photos of the circuit breaker, which is given at the beginning of the article.
Circuit breaker device. As you can see, the device is not simple. Upper (fixed) contact – right
Circuit breaker. One second before the trash can)
Is it worth taking a machine with a reserve?
This is a moot point. On the one hand, the circuit breaker must correspond to the power of the electrical appliance; on the other hand, it must have a small margin so as not to turn off during operation.
As an example, we can cite the same electric boiler with a capacity of 6 kW. Divide 6 kW by 220 volts (mains voltage) and get a value of 27. These are amperes. That is, to connect a 6 kW boiler, you need a 27 Ampere circuit breaker. However, such machines do not exist in nature.
Therefore, here you have to choose between a 25 and 32 Ampere machine. Ideally, of course, so that the boiler does not turn off, you need to install a 32 Ampere machine. But this does not mean that a 25 Ampere machine will not work as expected. It’s just that, given the somewhat reduced power, it may turn off from time to time when the boiler operates at full capacity for a long time.
Download
For those who are interested in the topic deeper and more thoroughly, I am posting GOST, which describes in detail all the characteristics and terminology of circuit breakers.
• GOST R 50345-2010 / GOST R 50345-2010 (IEC 60898-1:2003) Small-sized electrical equipment. Automatic switches for overcurrent protection for household and similar purposes. Part 1. Circuit breakers for alternating current. This standard applies to air circuit breakers (hereinafter referred to as circuit breakers) for alternating current for operation at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz with a rated voltage (between phases) of not more than 440 V, a rated current of not more than 125 A and a rated breaking capacity of not more than 25,000 A. , pdf, 1.89 MB, downloaded: 1003 times./
• Kharechko V.N., Kharechko Yu.V. Automatic switches of modular design / Kharechko V.N., Kharechko Yu.V. Automatic circuit breakers of modular design: Reference manual. The reference manual sets out the requirements of GOST R 50345-99 (IEC 60898-95) for household circuit breakers intended for overcurrent protection, examines the design of circuit breakers, gives characteristics and their classification. Errors that are partially corrected in the new version of GOST R 50345-2010, pdf, 7.17 MB, downloaded: 997 times are analyzed./
As always, I will be glad to have questions and comments on the article in the comments!
What types of circuit breakers are there?
Automatic switches for apartments are modular devices. This means that they can be installed in residential distribution panels on a special DIN rail, while their overall dimensions are the same for different manufacturers and the same number of poles.
In electrical cabinets at enterprises or transformer substations there are also non-modular circuit breakers. They are distinguished by their large overall dimensions and rated current. They look like the picture below.
Breaking capacity of circuit breakers
Breaking capacity of automatic protective switches
The circuit breaker must instantly disconnect the electrical network in the event of a short circuit (short circuit). This indicator refers to a characteristic such as breaking capacity. Short circuit currents can instantly reach thousands of amperes. The disconnecting device must not only withstand such currents, but also quickly disconnect the line. Such a characteristic does not belong to the category of complex.
The breaking capacity indicator indicates how much short-circuit current it can turn off and still maintain its functionality. Short circuit currents depend on various factors, but in any case, short circuit currents are determined experimentally. As for the electrical wiring of a house or apartment, short circuit currents are not particularly powerful, since the electrical network is located at a considerable distance from the transformer substation.
Although there are houses that are located next to transformer substations. In such houses, short circuit currents are much higher. In such cases, you should choose circuit breakers with a short-circuit current of about 10,000 A; in other cases, it is sufficient to install circuit breakers with a short-circuit current of no more than 6,500 A. In rural areas, circuit breakers with a short-circuit current of about 4,500 A are sufficient, since here there are usually old power lines and large There are no short circuit currents. The greater the breaking capacity of the machine, the more expensive it is. Therefore, when choosing electrical equipment, such factors should be taken into account. Why pay more?
Often, owners do not pay attention to these indicators and install circuit breakers with low breaking capacity in residential premises. Of course, such a machine is capable of protecting against short-circuit currents, but there is no guarantee that it will remain in working condition after this. There is also a possibility that such a machine simply will not have time to work, since the contacts may melt before it works. Then the consequences can be very dire.
Nuances
In general, readers should not have any questions regarding the selection of packages according to the cable cross-section, but there are some subtleties that we did not mention above.
- A machine with which type of electromagnetic release to choose. In everyday life, machines of categories “B” and “C” are most often used. This is due to the fastest possible operation of package switches when the rated current is exceeded. This is extremely important when using appliances such as electric kettles, toasters and irons. Depending on the type of equipment used, you should choose a specific category; it is advisable to give preference to category “B” switches.
- A machine with a maximum switching capacity to choose. Depends on the location of the electricity input from the substation to the apartment, if in close proximity, then you should choose one with a switching capacity of 10,000 amperes, otherwise for city apartments there are enough devices for 5,000–6,000 amperes. You can play it safe and choose the option of 10,000 amperes; ultimately, this indicator only affects whether the machine will be operational after a short circuit.
- What type of wire to choose: aluminum or copper We strongly do not recommend purchasing aluminum conductors. Copper wiring is more durable and can handle higher currents.