In heat and mass transfer, air condensation is one of the fundamentals of the theory. Considering humidity is important in many areas of construction and design.
Before calculating the dew point when insulating walls, you need to figure out what this indicator is and what initial data is needed to find it.
To keep your house dry and warm, you need to correctly calculate the dew point when insulating the walls.
Areas of application
There are many areas that take this temperature into account. One of the areas is aviation. During aircraft operation, condensation may form on some of its parts and freeze. This leads to freezing of the engine, metal structures of the flying vehicle and its breakdown.
In forestry, fire conservationists use dew point to calculate fire hazard class.
Experts calculate the likelihood of forest fires and develop protective measures.
Most often, determining the point is necessary in construction and agriculture.
Video: Dew point - insulating the house wisely
Construction
In construction, this value is determined when insulating the facades of buildings and private buildings. If you do not take into account the indicator or calculate it incorrectly, due to settling moisture, the wall finishing material will deteriorate or pathogenic flora and mold will appear.
Agriculture
In agriculture, experts determine the likelihood of damage to crops due to weather conditions, knowing the point and atmospheric humidity.
When cultivating new plants, breeders try to create varieties that condense moisture on the vegetative parts. Such plantings can exist with little precipitation.
Some facts
The issue of the position of the critical point in the wall is removed if you cover it from the inside with a vapor barrier material. Some types of finishes, such as vinyl wallpaper, have these properties. No steam enters the structure, and it will be dry regardless of the temperature distribution. The exception is the case when the wall freezes through and the critical point is on the inner surface.
Covering enclosing elements with vapor barriers is practiced in Western European countries. But this solution has a drawback: to remove excess moisture, you have to increase the air exchange rate, i.e. ventilation performance. This entails an increase in heat loss and, as a consequence, heating costs. A house with “breathing”, i.e. vapor-permeable walls are cheaper.
Comfortable values for a person
For most people, conditions with a point value in the range of +10…+15℃ are optimal. If the indicator increases, then the person feels discomfort. When the point value is less than +10℃, the environment becomes dry, and from +15℃ humidity begins to be felt. If the indicator is above +20℃, it becomes stuffy. People with heart and respiratory problems are more susceptible to environmental parameters than others.
The dew point temperature determines the comfort level of living in the house
How to calculate the dew point when insulating walls
Only a specialist can make an accurate calculation. But when choosing insulation yourself, you can find out the approximate point values in several ways.
Formula for calculating dew point temperature
The calculation using the formula is considered quite accurate, but gives a deviation of 0.5℃.
Formula for calculation: Tp=(b*f(T,Rh))/(af(T,Rh)) , where:
- f(T,Rh)=(a*T)/(b+T)+ln(Rh/100);
- a = 17.27 and b = 237.7 are constants;
- T —air temperature;
- Rh —relative humidity.
Using an online calculator
Not every person is able to calculate the value using the formula. For such cases, we came up with an online calculation calculator. All you need to do is enter the temperature and relative humidity. The result will appear on the monitor.
Application of devices
To calculate the value, you first need to determine the parameters by which the calculation will be carried out. This is done using meteorological instruments. To avoid using a separate thermometer and hygrometer (a device for measuring humidity), a thermohygrometer was invented. It simultaneously measures the necessary parameters and displays the values on the screen.
Using a thermohygrometer you can calculate the dew point temperature
In addition, there is a device that itself is capable of calculating the point. The tool is brought to the desired surface, records the values and stores them in memory. The results can be transferred to other media for later use.
Using table data
Using the table, you can quickly determine the point, knowing the necessary parameters. The value you are looking for is at the intersection of the column and row of the two indicators. However, the tabular data provides only approximate results.
Dew point determination table
According to the table, at a humidity of 60% and a temperature of +20℃, the value is +12℃.
| Relative humidity, % | Thermometer temperature, ℃ | ||||||||||
| 0 | 2,5 | 5 | 7,5 | 10 | 12,5 | 15 | 17,5 | 20 | 22,5 | 25 | |
| 20 | −20 | −18 | −16 | −14 | −12 | −9,8 | −7,7 | −5,6 | −3,6 | −1,5 | −0,5 |
| 25 | −18 | −15 | −13 | −11 | −9,1 | −6,9 | −4,8 | −2,7 | −0,6 | 1,5 | 3,6 |
| 30 | −15 | −13 | −11 | −8,9 | −6,7 | −4,5 | −2,4 | −0,2 | 1,9 | 4,1 | 6,2 |
| 35 | −14 | −11 | −9,1 | −6,9 | −4,7 | −2,5 | −0,3 | 1,9 | 4,1 | 6,3 | 8,5 |
| 40 | −12 | −9,7 | −7,4 | −5,2 | −2,9 | −0,7 | 1,5 | 3,8 | 6,0 | 8,2 | 10,5 |
| 45 | −10 | −8,2 | −5,9 | −3,6 | −1,3 | 0,9 | 3,2 | 5,5 | 7,7 | 10,0 | 12,3 |
| 50 | −9,1 | −6,8 | −4,5 | −2,2 | 0,1 | 2,4 | 4,7 | 7,0 | 9,3 | 11,6 | 13,9 |
| 55 | −7,8 | −5,6 | −3,3 | −0,9 | 1,4 | 3,7 | 6,1 | 8,4 | 10,7 | 13,0 | 15,3 |
| 60 | −6,8 | −4,4 | −2,1 | 0,3 | 2,6 | 5,0 | 7,3 | 9,7 | 12,0 | 14,4 | 16,7 |
Calculation using the formula with the same initial data:
Tr=(237.7*((17.27*20)/(237.7+20))+ln(60/100))/((17.27-((17.27*20)/(237 ,7+20))+ln(60/100))=12℃
The result shows that the tabular data and the mathematical calculation coincide.
Regulations
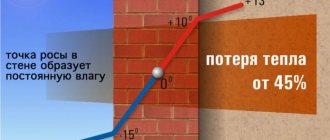
The need to calculate the dew point is regulated by building codes and regulations. SP 23-101-2004 “Design of thermal protection of buildings”, as well as SNiP 23-02 “Thermal protection of buildings”. Insufficient insulation moves the dew point closer to the room.
Since the temperature in the area of window units or doors is lower than the overall calculated dew point, condensation in these segments is inevitable during the cold season. Determining the dew point is important for deciding which side to carry out insulation work on and what thickness it is more appropriate to purchase insulation.
Table . Dependence of wall material thickness on thermal conductivity
| Wall material | Coeff. heat-conducting I , W/(m* o C ) | Required thickness in meters |
| Expanded polystyrene | 0,039 | 0,12 |
| Mineral wool | 0,041 | 0,13 |
| Reinforced concrete | 1,7 | 5,33 |
| Solid silicate brick masonry | 0,76 | 2,38 |
| Perforated brickwork | 0,5 | 1,57 |
| Glued laminated timber | 0,16 | 0,5 |
| Expanded clay concrete | 0,47 | 1,48 |
| Gas silicate | 0,15 | 0,47 |
| Foam concrete | 0,3 | 0,94 |
| Cinder concrete | 0,6 | 1,88 |
Minimizing heat loss and maintaining a comfortable microclimate are the top priorities when designing and insulating buildings. Compliance with building rules and regulations, as well as sanitary and hygienic standards, will allow you to competently prepare engineering documentation and calculate the volume of required building materials.
Determination of dew point position
Before determining the position of a point in the wall, several indicators are recognized:
- ambient and indoor temperature;
- humidity outside and inside the building;
- wall thickness.
Video: Thermal engineering calculation. Dew point
In uninsulated walls
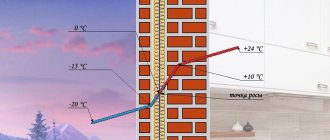
Uninsulated walls lose a lot of heat, the point is located directly in it. The material becomes damp and becomes moldy. Due to temperature changes outside and inside, the wall is subject to destruction.
In externally insulated walls
In this case, the point is insulated, and the wall is protected from weather conditions. The ceiling is always dry, and the heat in the room is retained.
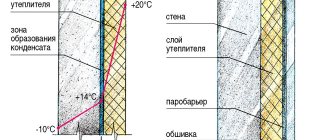
In internally insulated walls
The wall outside begins to freeze and collapse. Condensation accumulates between the outside and the insulation because the point is in the middle of the layers. This leads to the proliferation of pathogenic flora.
Options for location of problem areas
The dew point tends to shift, but most often there are three zones of its location:
- Closer to the outer surface of the wall. This option occurs if the wall is not insulated . The appearance of a problem area is also possible if the external insulation is of insufficient thickness.
- Closer to the inner surface of the wall. In the absence of insulation, condensation easily forms in this place during cold weather. Internal insulation shifts the area of condensation formation to the area between the wall surface and the insulation . With external insulation, this phenomenon rarely occurs if all calculations were performed correctly.
- In the thickness of the insulation. For external thermal insulation this is the best option. With internal insulation, there is a high risk of mold appearing in the room and, as a result, microclimate disturbance .
Note! The formation of condensation in the wall is affected not only by the temperature and humidity conditions from the street and the room. Determining factors are also the thickness of the structure and the thermal conductivity of the materials used.
Thermal insulation material
To protect buildings from heat loss, high humidity and point shifts, it is insulated with thermal insulation materials. In winter, insulation helps reduce heating costs, and in summer it keeps the room cool. Each product has its own areas of application and properties. Eco-friendly and easy-to-install materials are used in construction. The required type of insulation is selected for certain conditions.
With proper insulation from the outside, the dew point will be located inside the insulation
According to their form, materials are divided into:
- roll;
- leafy;
- bulk;
- single.
By structure:
- fiber;
- cells;
- grainy.
Raw materials can be organic, inorganic and mixed.
Main characteristics of insulating materials:
- thermal conductivity;
- moisture absorption;
- porosity;
- humidity;
- density;
- vapor permeability;
- specific heat;
- strength, etc.
Penoplex
Penoplex is also called expanded polystyrene. Unlike foam polystyrene, the material has a higher density and is less subject to mechanical damage. It almost does not conduct steam due to its low vapor permeability coefficient. However, it belongs to group IV of flammability (it ignites quickly).
Penoplex is recommended for external wall insulation
Penoplex of the “comfort” category is produced for insulating walls, terraces, loggias, and balconies. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 9 times less than that of mineral wool. The material requires little time to heat the room after cooling due to its low heat capacity. The operating temperature range is -70…+70℃. Penoplex of this type does not have the best sound insulation, has the lowest density and lower tensile strength compared to other materials.
Penoplex for walls is suitable only if an effective ventilation system is installed in the room to maintain comfortable humidity.
A 2 cm wide layer of polystyrene foam retains heat almost as well as 40 cm of mineral wool or 37 cm of brickwork.
Styrofoam
Polystyrene foam is a material characterized by lightness and buoyancy. It is resistant to fire, but when exposed to fire it begins to melt. The material is easy to process and is not subject to infection by fungi and mold.
Polystyrene foam is obtained from foamed polymer raw materials: polystyrene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polyurethane. It consists of small identical balls that are fastened together. High-density rigid foam is used for insulation. The panels are easy to connect using rubber or epoxy adhesive.
The temperature range is not important for polystyrene foam, but the material is subject to mechanical damage.
Slabs 5 and 10 cm thick are used as thermal insulation. But, despite the structure, the material is sound-permeable.
Polystyrene foam is one of the most common materials for home insulation.
Mineral wool
Thermal insulation material consists of compressed fibers. Glass, basalt and slag are used as raw materials. The starting material is melted and spun into fibers. Their length is 2-60 mm. The air pores of the mats fill approximately 95% of the total volume. The product is easy to produce and has a low cost.
Mineral wool has many qualities suitable for home insulation.
Due to its porosity, cotton wool allows air and steam to pass through, maintaining air exchange. At the same time, it does not burn and is resistant to moisture, has good sound insulation. But the material has 2 drawbacks:
- contains phenol;
- Flying pieces of cotton wool, falling on human skin, cause itching.
Possible consequences
Improper installation of thermal insulation can lead to unpleasant consequences. The material is applied only to the facade, since additional insulation from the inside is considered impractical for the following reasons:
- Living space is decreasing.
- The wall freezes because the heat from the room does not reach the ceiling. As a result, condensation penetrates inside the thermal insulation. The wall is wet and subject to corrosion.
Poor installation results in wall destruction. If the surface under the insulation is uneven and old, it will have to be reapplied, after making repairs. If the insulation on the outside is not additionally covered, then in one season it will become wet, become unusable and begin to move away from the walls. The thermal layer must be protected from the external environment.
Video: Removing the dew point from the wall
Experts' opinion
Experts believe that the best thermal insulation option is mineral wool. If installed correctly, the material will not cause harm and will last a long time. The main thing is to avoid high humidity. To do this, the cotton wool is additionally covered with a film that limits the access of moisture.
Another option is to install breathable materials on both sides of the insulation that will release liquid to the outside. It is recommended to lay polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene in combination with materials that do not allow water vapor to pass through and prevent moisture condensation.
A short excursion into the physics of the phenomenon
The dew point is the temperature of the air at which excess moisture contained in it falls out in the form of condensation. Why is there too much of it? The fact is that warm air holds a large amount of water vapor, cold air holds much less. It is this temperature difference that forms condensation . An example of the phenomenon are drops of water on cold water pipes or windows, or fog.
What else you need to know about dew point:
- The higher the humidity, the closer it is to the air temperature, and vice versa.
- Its value cannot be higher than the air temperature.
- Condensation always appears on cold surfaces . This is explained by the fact that the warm air next to them cools and its humidity decreases.
The unit of measurement for the condensation point is degrees Celsius.