Gabbro-diabase
We have made an attempt to thoroughly answer the question: what is gabbro-diabase, to consider all its properties and characteristics. The result of the work done was this section. If you don’t want to get acquainted with its subject so completely, look only at the subtitle that interests you.
Physical properties of gabbro
The color is dark, dark green, black. The structure is coarse-grained, medium-grained. The texture is mottled, banded or massive. Specific gravity 2.76-3.27 g/cm3. Hardness 6-7 on the Mohs scale. The melting point reaches 1250ºС. The compressive strength is on average 280 MPa.
Features . Gabbro is characterized by a granular structure, containing mainly feldspar and pyroxene, the absence of quartz, dark color, and high density. The stone can be confused with diorite. The difference is that it is heavier than diorite, contains more dark-colored minerals and has a darker color.
Granite deposits
Gabbro (gabbro, gabbro) is a uniform, granular natural rock. It consists of plagioclase and monoclinic pyroxene, most often dialago.
The structure of all gabbros is granitic, holocrystalline, medium- and coarse-grained.
The color of the stone is most often black, but dark green is also found, sometimes you can find spotted (gray patches) or banded rock. The texture is massive. Gabbro practically does not absorb moisture and dust, is frost-resistant, and can withstand any atmospheric conditions.
The stone is easy to process: it is excellently ground and polished. The optimal surface treatment texture is polished.
The rock has the first class of radioactivity, which means that gabbro products are absolutely safe for human life and health.
Since the stone is very durable, it is used as a building and facing material for walls and floors, landings and steps. Both simple and complex products are made from it: window sills, table tops, vases, etc.
Gabbro is used to produce high-quality crushed stone, stone for road work, polished slabs, finishing materials, etc. Rock monuments are very popular in the ritual sphere. Stone can be used as a raw material for stone casting and the production of mineral wool.
Gabbro from Ukrainian deposits is highly valued as a finishing material.
There are many deposits of this stone, the most popular are:
- Aleksandrovskoye - (located in the Zhytomyr region, Volodarsko-Volynsky district, Shadura village) various monuments are mainly made from it, both ordinary and exclusive memorial complexes;
- Bystrievskoe - (located in the Zhitomir region, Korostyshevsky district, Kamenny Brod village) facing stone with an expressive natural pattern: white inclusions on a black background;
- Bukinskoe - (located in the Zhitomir region, Malinsky district, village of Buk) is distinguished by its rich black color with virtually no white inclusions (they are present, but very small and almost invisible);
- Irshitskoye - (located in the Zhytomyr region, Volodarsko-Volynsky district, 1 km from the city of Volodarsk-Volynsky) the texture of the stone is similar to the gabbro of the Bystrievsky deposit, the difference is that the inclusions have a blue tint;
- Lugovoe - (located in the Zhitomir region, Korostyshevsky district, near the village of Kamenny Brod) has a little more inclusions than the gabbro of the Bukinskoye deposit, but the pattern is different;
- Slipchitskoe - (located in the Zhitomir region, Chernyakhovsk district, Slipchitsy village) is used for external cladding.
Physical properties
- Relative density of the material – (2890 -3100 kg/m3).
- Compression resistance – (346MPa)
- Modulus of elasticity in compression – (91550MPa)
- Abrasion – (0.12g/cm2)
- Porosity – (0.68%)
- Frost resistance grade – (100F)
- Water absorption – (0.19%)
Mineral composition
- plagioclase – (53.2%);
- quartz – (0.58%);
- pyroxene – (33.3%);
- hornblende – (4.5%);
- titanomagnetite – (6.8%);
- biotite – (0.8%).
Gabbro-diabase bush hammer processing
In addition to heat treatment, to impart roughness and achieve an anti-slip effect, a processing method is also used - bush hammering. Using a special tool called a bush hammer, granite is processed using shock-rotational movements. In this case, the “roughness” is achieved deeper than with fire treatment, which provides the surface with even higher adhesion qualities.
Where can it be used?
According to sanitary and hygienic standards, gabbro-diabase stone is one of the rocks permitted for use in construction with background radiation not exceeding permissible standards. This material is used quite widely in industry.
One of the features of gabbro-diabase is its interesting fine-grained structure. This stone is polished better than, for example, granite and basalt. Therefore, it is sometimes used as a facing material in the construction of buildings and structures. This breed can also be used:
- for the manufacture of paving stones (for example, exactly this material was used on Red Square in Moscow);
- in precision engineering.
Very often, tombstones are made from such stone. Polished black gabbro-diabase looks very solid and presentable. Therefore, tombstones made from it, like no other, create an appropriate mournful and solemn atmosphere at the burial site. For the manufacture of monuments, Karelian diabase is usually used, which can maintain polish for a long time.
Very often this breed is used to create optimal temperature conditions in baths. That is, they simply put these inexpensive stones in the heaters. Dense gabbro-diabase can retain heat very well and for a long time. In addition, the material is absolutely environmentally friendly.
Like granite, gabbro-diabase is often used in the interiors of apartments and houses. This material is used, for example, to make countertops, railings and window sills. Such products actually look very impressive. In addition, they also have very good performance characteristics.
Polished gabbro diabase:
Before polishing, gabbro-diabase is gray in color; after polishing, it acquires a color from dark gray to coal black.
However, light accumulations of plagioclase are always present and will be visible on the surface of gabbro-diabase.
Depending on what color of minerals there will be more in the composition: light or black, the color of the polished surface of the product will also differ.
At the same time, it is worth taking into account that the presence of light minerals in gabbro determines not only the color of the stone, but also its fracturing. According to the observation of many stone processing specialists, the higher the content of light mineral in granite, the less cracked it is, the more resistant it is to aggressive environments and temperature changes.
Visually, gabbro-diabase will be perceived as darker with high-quality polishing. Even “gray” gabbro-diabase will look black and uniform if the required polishing depth has been achieved during processing.
Crushed and tumbling gabbro-diabase
Obviously, a useful quality of gabbro-diabase is that it pricks very well. Therefore, crushed paving stones from Drugoretsky gabbro turn out to be more or less even, which is an important indicator for laying and further operation.
Another type of processing is tumbling. By placing diabase in a special gabbro drum, the output is tumbled paving stones, which are popular today and have found wide application.
Production
On our website there are articles that are devoted to the extraction of gabbro-diabase - this is material about the deposits (with addresses) and an article about the extraction and processing of this stone.
You may also be interested in materials about a variety of products that are made from it (including monuments) and what can replace gabbro-diabase in a bathhouse, in construction or in the manufacture of a monument.
Gabbro-diabase heat treatment:
Thermal treatment, thermal treatment or fire treatment of gabbro-diabase is done to give the granite additional roughness.
The surface is exposed to fire with temperatures up to 2500 degrees, resulting in the removal of unstable and brittle minerals from the surface. Due to this, the surface acquires a rough texture and the anti-slip effect increases.
Advantages and disadvantages
- The main advantages of gabbro-diabase for baths are high thermal conductivity combined with a very affordable price. The flattened shape is convenient for placing in the oven.
- One of the disadvantages is that it takes a long time to heat up. In addition, if this breed is exposed to too high temperatures, it begins to emit an unpleasant odor. Decoctions and herbal elixirs cannot be poured onto gabbro-diabase. A persistent soot immediately forms on the surface.
Reference! Advanced bath attendants complain about the simple and “flat” steam obtained from gabbro-diabase: it is not as voluminous and refined as from the same jadeite. There is no dispute about taste, but the attractive price of the mineral makes it a very good choice for inexperienced users and beginners.
Selection rules
When choosing gabbro-diabase for use in a heater, pay attention to the following key points:
- At the fracture, the structure should be as fine-crystalline as possible. Large grains indicate low strength, and such a specimen will quickly collapse when heated.
- Examine the structure using a magnifying glass for microcracks. When heated, they will begin to rapidly increase in size until the stone turns into dust.
- The body of the mineral should not contain a large number of inclusions of quartz. If this is observed, you are offered not gabbro-diabase, but some other rock.
- When struck, the stone should respond with a clear, transparent and elastic sound. A dull, annoying echo indicates the presence of hidden defects in the thickness.
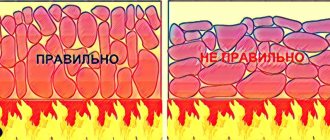
- Form. In a closed heater, rounded stones will behave better, because there is always a little space between them, enough for water to flow inside. In the open, split gabbro-diabase is preferred for more dense installation.
- Many varieties of gabbro-diabase contain increased amounts of sulfides. Visually, they look like a scattering of small crystals with a mirror-like silvery or less often golden sheen. When heated, sulfides will break down and release a pungent odor, which will cause a sore throat and stinging in the eyes. The decomposition of sulfides can take quite a long time, so such a stone should be discarded.
- To test for strength, knock 2 stones together or hit them with a hammer. There is another indicative way to check the suitability of a stone. Heat it until red hot and immediately plunge it into cold water. If cracks or splits do not appear, you can safely use the stone in steam rooms and baths.
- Availability of a certificate. You should not collect any stones yourself in unverified places, near railways or in close proximity to industrial facilities. The stone tends to absorb various microparticles and odors, which can subsequently affect the quality of the supplied steam, and in some cases even pose a health hazard.
For your information! Domestic varieties of gabbro-diabase fully meet the basic requirements of a bath attendant and at the same time have an affordable price. The purchase of a more expensive Finnish stone is justified only by a better selection of stone and the absence of harmful sulfites in its array, which is often the case with Karelian analogues.
Characteristics
The distinctive characteristics of the stone include its high hardness and strength. In addition, it is frost and moisture resistant. It has these properties due to the crystal lattice, which serves as the basis of its structure.
Gabbro-diabase is a holocrystalline fine-grained volcanic rock, chemically and in mineral composition close to basalt. Diabase is characterized by a relatively low silica content (45-52%). The structure is diabase (ophite); formed by randomly arranged elongated plagioclase crystals, the spaces between which are filled with augite. The name of this stone is derived from the Latin word “glaber”, which translates as “even, smooth”
Gabbro-diabase is a type of natural stone. Its inherent black color with minor colored spots distinguishes it from other types of stones. Its unusual density makes the stone very difficult to split. To process this material you need to use labor-intensive technological processes with special equipment.
Compared to other types of granite, gabbrodiabase has a low silica content (about 50%) and a high plagioclase content. Plagioclase is represented by a fine-grained (almost monolithic) structure of elongated crystals of the same size and shape.
The main indicators that are important for the use of stone are their density and heat capacity.
For convenience, see these characteristics of jade in the table. Table. Physico-chemical characteristics of gabbro-diabase
| Name of the stone | Density (kg/m³) | Heat capacity, kJ/(kg K) | average price |
| Gabbro-diabase | 2780-3230 | 0,6-0,8 | 300 rubles/20 kg |